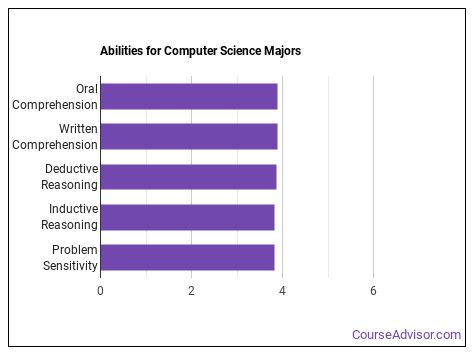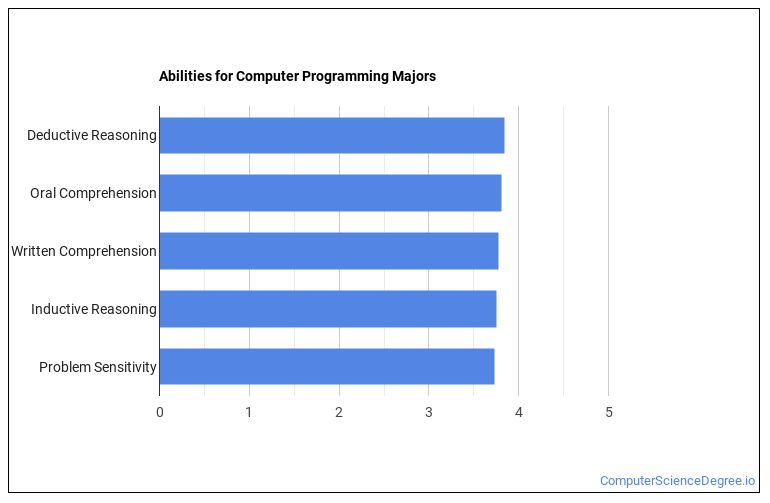
What are some examples of inductive reasoning?
Types of inductive reasoning
- Inductive generalization. In this type of inductive reasoning, a situation is presented, you look at evidence from past similar situations and draw a conclusion based on the information available.
- Statistical induction. This type of inductive reasoning utilizes statistical data to draw conclusions. ...
- Induction by confirmation. ...
When is inductive reasoning typically used?
You might use inductive reasoning when attempting to understand how something works by observing patterns. Deductive reasoning, on the other hand, might be more helpful when defining and establishing relationships between two or more entities.
What is an example of an inductive argument?
What are some examples of inductive arguments?
- Jennifer always leaves for school at 7:00 a.m. Jennifer is always on time.
- The cost of goods was $1.00.
- Every windstorm in this area comes from the north.
- Bob is showing a big diamond ring to his friend Larry.
- The chair in the living room is red.
What does inductive reasoning mean?
Inductive reasoning is a method of logical thinking that combines observations with experiential information to reach a conclusion. When you can look at a specific set of data and form general conclusions based on existing knowledge from past experiences, you are using inductive reasoning.

What reasoning goes from general to specific?
deductive reasoningInductive reasoning follow a flow from specific to general, deductive reasoning flows from general to specific. You might use inductive reasoning when attempting to understand how something works by observing patterns.
What is the rule of inductive reasoning?
The principle of induction, as applied to causation, says that, if A has been found very often accompanied or followed by B, then it is probable that on the next occasion on which A is observed, it will be accompanied or followed by B.
What are the 3 steps to inductive reasoning?
Generalizing and Making ConjecturesFirst, observe the figures, looking for similarities and differences. ... Next, generalize these observations. ... Then, we form a conjecture. ... Finally, in some situations, we can apply your conjecture to make a prediction about the next few figures.
Which of the following is true of inductive reasoning?
Which of the following statements is true of inductive reasoning? It is working from specific evidence to a general conclusion.
How do you identify an inductive argument?
If there is a general statement in the premises, the argument will always be inductive. If the conclusion of an argument is a generalization (all) from evidence in the premises (some), the argument will be inductive.
What is the difference of inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning?
What's the difference between inductive and deductive reasoning? Inductive reasoning is a bottom-up approach, while deductive reasoning is top-down. Inductive reasoning takes you from the specific to the general, while in deductive reasoning, you make inferences by going from general premises to specific conclusions.
What are the types of inductive reasoning?
6 Types of Inductive ReasoningGeneralized. This is the simple example given above, with the white swans. ... Statistical. This form uses statistics based on a large and random sample set, and its quantifiable nature makes the conclusions stronger. ... Bayesian. ... Analogical. ... Predictive. ... Causal inference.
What is inductive reasoning explain with example?
In causal inference inductive reasoning, you use inductive logic to draw a causal link between a premise and hypothesis. As an example: In the summer, there are ducks on our pond. Therefore, summer will bring ducks to our pond.
What is inductive reasoning and examples?
In causal inference inductive reasoning, you use inductive logic to draw a causal link between a premise and hypothesis. As an example: In the summer, there are ducks on our pond. Therefore, summer will bring ducks to our pond.
What is inductive reasoning quizlet?
Terms in this set (4) Inductive reasoning is the process of reasoning that a rule or statement is true because specific cases are true. You may use inductive reasoning to draw a conclusion from a pattern. A statement you believe to be true based on inductive reasoning is called a conjecture.
What is inductive reasoning in math with examples?
Inductive reasoning starts with a specific scenario and makes conclusions about a general population. For our lake example, if you found a trout fish in a lake, you would assume that it is not the only fish in that lake. You may further conclude that all the fish in the lake are trout.
What are the types of inductive reasoning?
6 Types of Inductive ReasoningGeneralized. This is the simple example given above, with the white swans. ... Statistical. This form uses statistics based on a large and random sample set, and its quantifiable nature makes the conclusions stronger. ... Bayesian. ... Analogical. ... Predictive. ... Causal inference.
What is inductive reasoning?
Inductive reasoning is a method of drawing conclusions by going from the specific to the general. It’s usually contrasted with deductive reasoni...
How is inductive reasoning used in research?
In inductive research , you start by making observations or gathering data. Then, you take a broad scan of your data and search for patterns. Fina...
What’s the difference between inductive and deductive reasoning?
Inductive reasoning is a bottom-up approach, while deductive reasoning is top-down. Inductive reasoning takes you from the specific to the general...
What are some types of inductive reasoning?
There are many different types of inductive reasoning that people use formally or informally. Here are a few common types: Inductive generalizati...
What Is Inductive Reasoning?
Inductive reasoning is an approach to logical thinking that involves making generalizations based on specific details. 1 Inductive reasoning is an important critical thinking skill that many employers look for in their employees.
Why is inductive reasoning important?
That makes inductive reasoning a useful skill to highlight in your job applications and job interviews.
What is the difference between inductive and deductive reasoning?
Employers look for employees with inductive reasoning skills. Inductive reasoning uses specific ideas to reach a broad conclusion, while deductive reasoning uses general ideas to reach a specific conclusion.
How is inductive reasoning different from deductive reasoning?
With deductive reasoning, you start with a generalization or theory and then test it by applying it to specific incidents. Deductive reasoning is using general ideas to reach a specific conclusion. Inductive reasoning uses specific ideas to reach a broad conclusion. 3 You may have heard this explained in school as going from big to small when using deductive reasoning and going from small to big when using inductive reasoning.
How does inductive reasoning help you remember?
Committing information to memory: Inductive reasoning is often directly connected to your ability to recall past events and the details leading up to those events. To bolster your memory, take notes so you can reference your observations later on.
Why do scientists use deductive reasoning?
Scientists may use deductive reasoning to test a hypothesis in a lab. Many law enforcement, military, or corporate leaders must be able to use inductive reasoning by taking a quick sweep of a situation and making a vital, time-sensitive decision. Inductive reasoning allows individuals to accurately see the signs of something bigger at play.
What does a teacher notice about hands-on activities?
A teacher notices that his students learn more when hands-on activities were incorporated into lessons. He decides to include a hands-on component in his future lessons regularly.
What Is Inductive Reasoning?
Inductive reasoning is a way of thinking logically to make broad statements based on observations and experiences.
Why do scientists use inductive reasoning?
Scientists use inductive reasoning all of the time to create hypotheses and test them with experiments. Without that generalized assumption based on a few observations, they wouldn’t even have a hypothesis to test.
What is the difference between inductive and deductive reasoning?
While inductive reasoning goes from the specific to the general, deductive reasoning goes from the general to the specific. Think of them as two sides of the same coin. Both are useful reasoning tactics, but they apply to different situations.
What is the meaning of "four oranges" inductive reasoning?
Inductive reasoning follows this basic format — if you have four identical items and you know that three of them are orange, you can assume that the fourth is also orange. You’re going from a fact about a small group (three objects are orange) to a broader generalization that isn’t necessarily true (all four objects are orange), but likely is.
Why do people get stuck in one way of doing things?
People get stuck into one way of doing things because it’s always worked for them, not realizing that there’s a better way. Personal. For more anecdotal inductive reasoning, you’re limited to your experiences, which all of have one thing in common: you.
How to come to a conclusion inductively?
In order to inductively come to a good generalization or conclusion, you need to notice the details and the specifics of a situation. Pay attention to the small things and see how you can build larger inferences from everything around you.
What is the purpose of a general conclusion?
Creating these general conclusions is a great way to understand the world around you and start to make educated decisions, from simple tasks like where to eat, all the way to which company would make a better partner.
What is Inductive Reasoning?
Inductive reasoning (or induction) is the process of using past experiences or knowledge to draw conclusions. It gathers different premises to provide some evidence for a more general conclusion. In this way, it is the opposite of deductive reasoning; it makes broad generalizations from specific examples.
When do children learn inductive reasoning?
Jean Piaget, famed psychologist in the world of child development, theorized that children developed inductive reasoning around the age of 7. It makes sense. A child touches a hot stove and they burn their hand.
How to draw conclusions about a person?
Inductive reasoning can be used to draw conclusions about one specific person, place, or thing. Let’s say you get a new cat. Your friend tells you that their cat loves belly rubs and asks if your cat is the same way. In order to give an answer to your friend, you have to draw from past experiences. One time, you pet the cat on its head and the cat started purring. Petting the cat on its back evoked a similar reaction. But the cat got finicky if you tried to rub its belly. You come to the conclusion that your cat just doesn’t love belly rubs.
What is induction premise?
This premise could be something you’ve personally experienced or witness, or an experience that was told to you by a friend, parent, TV personality, etc.
Why do we use analogy?
You can also use analogy to draw a conclusion about different properties of items. Analogies are comparisons between two things that help to clarify information. Through induction and analogy, you can predict likely characteristics, uses, etc. of different things.
When do kids start using deductive reasoning?
They’ll avoid the hot stove and avoid the burn. Deductive reasoning comes to children at ages 11 or 12. It’s a form of “top-down” logic to inductive’s “bottom-up” logic.
What is the purpose of premises?
The premises provide some evidence to build a conclusion. You might be thinking to yourself, “but the conclusion might not be true if you’re just pulling from a one-time occurrence or a handful of experiences.” To that I say, you are absolutely right.
What is the difference between deductive and inductive reasoning?
The conclusion does not follow logically from the statements. Inductive reasoning has its place in the scientific method . Scientists use it to form hypotheses and theories. Deductive reasoning allows them to apply the theories to specific situations.
Why is abductive reasoning important?
Abductive reasoning is useful for forming hypotheses to be tested. Abductive reasoning is often used by doctors who make a diagnosis based on test results and by jurors who make decisions based on the evidence presented to them.
What is deductive reasoning?
Deductive reasoning, also known as deduction, is a basic form of reasoning. It starts out with a general statement, or hypothesis, and examines the possibilities to reach a specific, logical conclusion, according to Norman Herr, a professor of secondary education at California State University in Northridge The scientific method uses deduction to test hypotheses and theories, which predict certain outcomes if they are correct, said Dr. Sylvia Wassertheil-Smoller, a researcher and professor emerita at Albert Einstein College of Medicine.
What is scientific reasoning?
Another form of scientific reasoning that doesn't fit in with inductive or deductive reasoning is abductive . Abductive reasoning usually starts with an incomplete set of observations and proceeds to the likeliest possible explanation for the group of observations, according to Butte College. It is based on making and testing hypotheses using the best information available. It often entails making an educated guess after observing a phenomenon for which there is no clear explanation.
What is the interplay between inductive and deductive inference?
"In science, there is a constant interplay between inductive inference (based on observations) and deductive inference (based on theory), until we get closer and closer to the 'truth,' which we can only ...
What is the first step in deductive reasoning?
Deductive reasoning usually follows steps. First, there is a premise, then a second premise, and finally an inference. A common form of deductive reasoning is the syllogism, in which two statements — a major premise and a minor premise — reach a logical conclusion. For example, the premise "Every A is B" could be followed by another premise, "This C is A." Those statements would lead to the conclusion "This C is B." Syllogisms are considered a good way to test deductive reasoning to make sure the argument is valid.
What is deductive inference?
In deductive reasoning, if something is true of a class of things in general, it is also true for all members of that class. According to California State University, deductive inference conclusions are certain provided the premises are true. It's possible to come to a logical conclusion even if the generalization is not true.