
Does law of segregation occur in mitosis? Chromosome segregation is the process in eukaryotes by which two sister chromatids formed as a consequence of DNA replication, or paired homologous chromosomes, separate from each other and migrate to opposite poles of the nucleus. This segregation process occurs during both mitosis and meiosis Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsᵻs/ is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multicellular eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the l…Meiosis
Does segregation occur during mitosis or meiosis?
This segregation process occurs during both mitosis and meiosis. What is the rule of segregation? The Principle of Segregation describes how pairs of gene variants are separated into reproductive cells.
What is the law of segregation in biology?
The law of segregation ensures that a parent, with two copies of each gene, can pass on either allele. Both alleles will have the same chance of ending up in a zygote. In sexually reproducing organsisms, the genome is carried in two identical copies.
What is meant by chromosome segregation?
Chromosome segregation is the process in eukaryotes by which two sister chromatids formed as a consequence of DNA replication, or paired homologous chromosomes, separate from each other and migrate to opposite poles of the nucleus. This segregation process occurs during both mitosis and meiosis.
What is Mendel’s Law of segregation?
The Principle of Segregation describes how pairs of gene variants are separated into reproductive cells. The segregation of gene variants, called alleles, and their corresponding traits was first observed by Gregor Mendel in 1865. Where does Mendel’s law of segregation take place in meiosis?
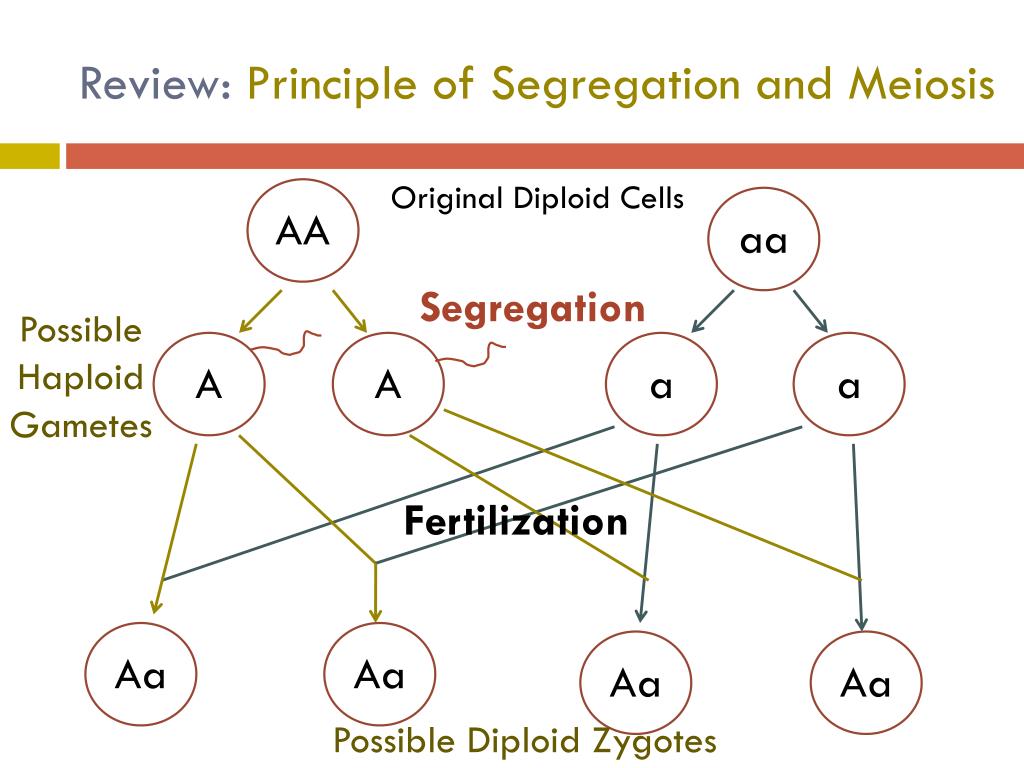
What stage of meiosis is law of segregation?
Mendel's Segregation law occurs in anaphase (I and II) of meiosis. It is a phase in the first meiotic division in which the homologous chromosomes are segregated into two daughter nuclei with their various versions of each gene.
Does law of segregation occur in meiosis?
The physical basis of Mendel's law of segregation is the first division of meiosis in which the homologous chromosomes with their different versions of each gene are segregated into daughter nuclei.
Where in mitosis and or meiosis does the principle of segregation occur?
Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate during metaphase I of meiosis. The homologous chromosomes, with their different versions of each gene, are randomly segregated into daughter nuclei, resulting in a variety of possible genetic arrangements.
Where does law of Independent Assortment occur in meiosis?
What stage of meiosis does independent assortment occur? Independent assortment in meiosis takes place in eukaryotes during metaphase I of meiotic division. It produces a gamete carrying mixed chromosomes. Gametes contain half the number of regular chromosomes in a diploid somatic cell.
Does independent assortment occur in mitosis?
When Does Independent Assortment Occur? Independent assortment occurs during the process of meiosis. Meiosis is similar to mitosis, only the final product is gamete cells.
Does independent assortment occur in meiosis 2?
Homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I. Sister chromatids separate in meiosis II. Independent assortment of genes is due to the random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I.
In which phases of mitosis are the principles of segregation?
In which phases of mitosis and meiosis are the principles of segregation and independent assortment at work? In anaphase I of meiosis, each pair of homologous chromosomes segregate independently of all other pairs of homologous chromosomes. The assortment is dependent on how the homlogs line up during metaphase I.
What is being divided during mitosis?
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. During cell division, mitosis refers specifically to the separation of the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus.
What is independent segregation in meiosis?
When cells divide during meiosis, homologous chromosomes are randomly distributed to daughter cells, and different chromosomes segregate independently of each other. This called is called independent assortment. It results in gametes that have unique combinations of chromosomes.
During which phase of the cell cycle does the law of Independent Assortment occur?
During which phase of the cell cycle does the law of independent assortment occur? anaphase I. (Homologous chromosomes separate during anaphase I.
How does meiosis lead to segregation and independent assortment?
During meiosis, the pairs of homologous chromosome are divided in half to form haploid cells, and this separation, or assortment, of homologous chromosomes is random. This means that all of the maternal chromosomes will not be separated into one cell, while the all paternal chromosomes are separated into another.
Is law of segregation supported by events in mitosis and meiosis?
The law of segregation is present in meiosis only.
What is chromosome segregation in meiosis?
Chromosome segregation is the process in eukaryotes by which two sister chromatids formed as a consequence of DNA replication, or paired homologous chromosomes, separate from each other and migrate to opposite poles of the nucleus. This segregation process occurs during both mitosis and meiosis.
How do the laws of segregation and independent assortment relate to meiosis?
The law of segregation describes how homologous chromosomes (and hence allele pairs) are separated in meiosis I. The law of independent assortment describes how homologous pairs align randomly (as bivalents) during metaphase I.
Which of the following events happens in meiosis?
It occurs only in germ cells to produce gametes....Major Events in Meiosis.StageMajor EventsProphase IChromosomes condense , homologous chromosomes synapse, crossing over takes place, nuclear envelope break down and mitotic spindle forms.Metaphase IHomologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate.11 more rows
What is the law of segregation?
The law of segregation ensures that a parent, with two copies of each gene, can pass on either allele.
What happens to the chromosomes in meiosis?
As meiosis begins, the chromosomes condense and align with their homologous pairs. Homologous chromosomes are those which contain identical portions of DNA, originally inherited from different parents. During prophase I of meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes bind together. Special sections of the DNA can overlap, causing breakages in the DNA.
What happens during meiosis?
During prophase I of meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes bind together. Special sections of the DNA can overlap, causing breakages in the DNA. Due to the similarity of the DNA, the breaks simply exchange segments in a process called crossing-over. This crossing-over helps establish both the randomness of allele inheritance and also the separation of different genes. The separation of different genes during meiosis is known as the law of independent assortment. During metaphase I of meiosis I, these bonded homologous pairs are aligned in the middle of the cell and separated. In doing this, the different alleles for each gene are affectively separated. During meiosis II, the copies of the alleles will be separated into individual gametes. This insures that each allele makes it to a new gamete, giving it an essentially equal chance of finding a gamete to fuse with and create a new organism.
Why is each allele equal to a new gamete?
This insures that each allele makes it to a new gamete, giving it an essentially equal chance of finding a gamete to fuse with and create a new organism. Due to the law of segregation each allele is its own entity and always has an equal chance of being passed on to the next generation.
What is the process of meiosis?
Meiosis occurs in specialized cells known as gametocytes, which form haploid cells from diploid cells. In order for the ploidy of the cell to be reduced, the chromosomes in the cell must be equally divided. To start the process, all of the DNA in a cell is duplicated. This creates two copies of each allele.
How many copies of the same allele are there in an organism?
3. An organisms has two copies of the same allele, one from each parent. Since the alleles are the same, can the law of segregation take place in this gene, for this organisms?
How many copies of the genome are there in a sexually reproducing organism?
In sexually reproducing organsisms, the genome is carried in two identical copies. A copy was inherited from each parent, in the form of a gamete. These organisms are known as diploid when they have both copies of the genome, and haploid when they are gametes and have only one copy.
Where does the law of segregation occur in meiosis?
Where does the Law of Segregation occur in meiosis? During Anaphase II and Telophase II and Cytokinesis, when the sister chromatids separate so that there is 1 allele per gamete.
What is the principle of segregation?
The Principle of Segregation describes how pairs of gene variants are separated into reproductive cells. The segregation of gene variants, called alleles, and their corresponding traits was first observed by Gregor Mendel in 1865. From his data, Mendel formulated the Principle of Segregation. …
What is an example of Mendel’s law of segregation?
For example, the gene for seed color in pea plants exists in two forms. There is one form or allele for yellow seed color (Y) and another for green seed color (y). … When the alleles of a pair are different (heterozygous), the dominant allele trait is expressed, and the recessive allele trait is masked.
What are the 3 laws of inheritance?
The Mendel’s laws of inheritance include law of dominance, law of segregation and law of independent assortment.
What is the relationship between Mendel’s Law of Segregation and meiosis quizlet?
Explain the relationship between Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment and Meiosis: Meiosis divides the chromosomes into groups of four. Each allele for one trait has a 50% chance of being passed on.
What do you mean by Law of Independent Assortment?
The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop. Independent assortment of genes and their corresponding traits was first observed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 during his studies of genetics in pea plants.
Who first proposed the existence of genes?
But did we always know those things? Not by a long shot! About years ago, a monk named Gregor Mendel published a paper that first proposed the existence of genes and presented a model for how they were inherited. Mendel's work was the first step on a long road, involving many hard-working scientists, that's led to our present understanding of genes and what they do.
How did Mendel find his model of inheritance?
One thing I find pretty amazing is that Mendel was able to figure out his entire model of inheritance simply from his observations of pea plants. This wasn't because he was some kind of crazy super genius, but rather, because he was very careful, persistent, and curious, and also because he thought about his results mathematically (for instance, the ratio). These are some of the qualities of a great scientist—ones that anyone, anywhere, can develop!
What happens when an egg and sperm join in fertilization?
When an egg and a sperm join in fertilization, they form a new organism, whose genotype consists of the alleles contained in the gametes. The diagram below illustrates this idea:
What is the dominant allele in Mendel's model?
In Mendel's model, parents pass along “heritable factors," which we now call genes, that determine the traits of the offspring. Each individual has two copies of a given gene, such as the gene for seed color ( Y gene) shown below. If these copies represent different versions, or alleles, of the gene, one allele—the dominant one—may hide the other allele—the recessive one. For seed color, the dominant yellow allele Y hides the recessive green allele y.
What trait did Mendel call the trait that was visible in the generation?
Conventional wisdom at that time would have predicted that the hybrid flowers should be pale violet—that is, that the parents' traits should blend in the offspring. Instead, Mendel’s results showed that the white flower trait had completely disappeared. He called the trait that was visible in the generation (violet flowers) the dominant trait, and the trait that was hidden or lost (white flowers) the recessive trait.
What results did Mendel find in his crosses for flower color?
When he gathered and planted the seeds produced in this cross, Mendel found that percent of the plants in the next generation, or generation, had violet flowers.
Does Mendel's model include genes?
Not quite! We've seen all of Mendel's model for the inheritance of single genes. However, Mendel's complete model also addressed whether genes for different characteristics (such as flower color and seed shape) influence each other's inheritance. You can learn more about Mendel's model for the inheritance of multiple genes in the law of independent assortment article.
