What are the 4 stages of meiosis 1?
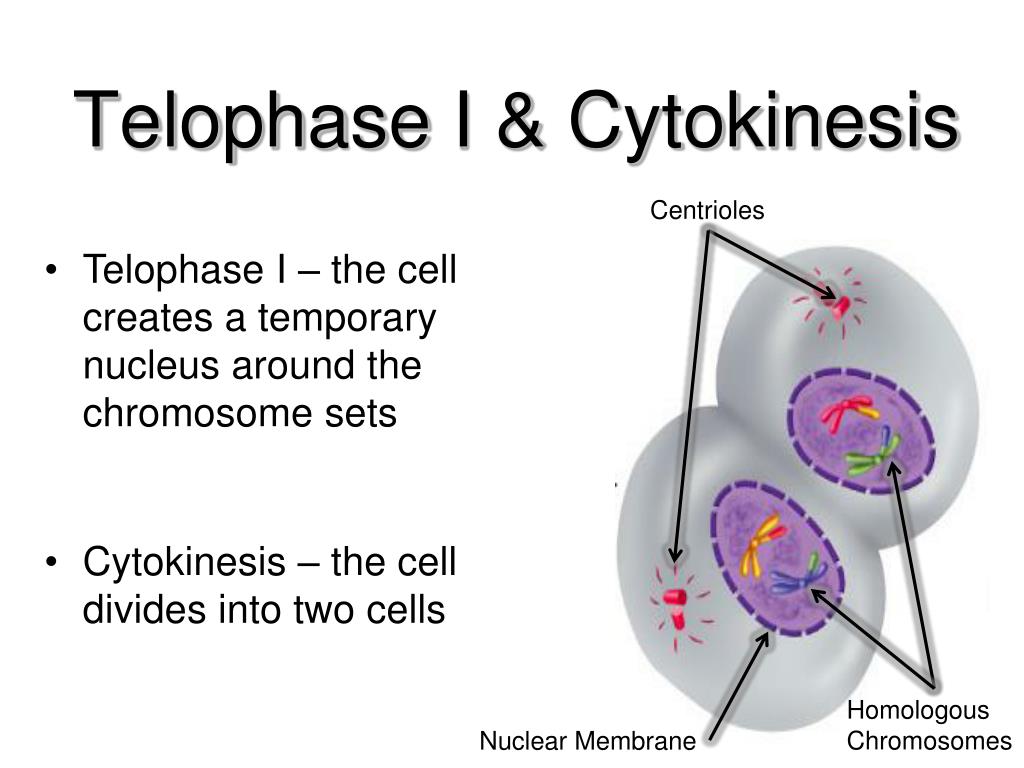
Feb 16, 2020 · Does meiosis 1 have cytokinesis? Telophase I and Cytokinesis Cytokinesis then divides the cell into two daughter cells. Each of the two daughter cells is now haploid (n), with half the number of chromosomes per nucleus as in meiosis I. In some species, the nuclear membrane briefly forms around the chromosomes, while in others it does not. Popular
What is the difference between telophase and cytokinesis?
May 26, 2020 · What happens in cytokinesis 1 of meiosis? The homologous chromosome pairs reach the poles of the cell, nuclear envelopes form around them, and cytokinesis follows to produce two cells. In animal cells, cytokinesis involves the formation of a cleavage furrow, resulting in the pinching of the cell into two cells. About Us Trending Popular Contact
Which event occurs during cytokinesis?
Feb 15, 2020 · Cytokinesis is the process whereby the cytoplasm of a parent cell is divided between two daughter cells produced either via mitosis or meiosis. This is also often known as cytoplasmic division or cell cleavage. Figure 1: Cytokinesis occurs in the late telophase of mitosis in an animal cell. What is an example of cytokinesis?
What phase does cytokinesis begin?
The process of Meiosis is divided into two parts: meiosis I and meiosis II which are further separated into Karyokinesis I and Cytokinesis I and Karyokinesis II and Cytokinesis II respectively. The preparatory steps that lead up to meiosis are similar in pattern and name to interphase of the mitotic cell cycle.
Does meiosis 1 and 2 have cytokinesis?
Meiosis I is NUCLEAR division which produces two NUCLEI. Cytokinesis between Meiosis I and Meiosis II forms TWO cells each with a HAPLOID number of chromosomes.
Does meiosis have cytokinesis?
The cell plasma membrane pinches, to leave two daughter cells with separate plasma membranes. In meiosis, cytokinesis must occur twice: once after telophase I and again, after telophase II....Memory Tricks.Mitosis StageChromosomesCytokinesisPinches to form two separate membranes around the two daughter cells.26 more rows•Nov 20, 2018
Does meiosis 2 have cytokinesis?
Telophase II and Cytokinesis The chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense. Nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes. Cytokinesis separates the two cells into four unique haploid cells. At this point, the newly formed nuclei are both haploid.
What does cytokinesis 1 do in meiosis?
During telophase I, the chromosomes are enclosed in nuclei. The cell now undergoes a process called cytokinesis that divides the cytoplasm of the original cell into two daughter cells.
What is difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2?
However, Meiosis I begins with one diploid parent cell and ends with two haploid daughter cells, halving the number of chromosomes in each cell. Meiosis II starts with two haploid parent cells and ends with four haploid daughter cells, maintaining the number of chromosomes in each cell.Mar 1, 2022
What happen in meiosis 1?
In meiosis I, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells. It is this step in meiosis that generates genetic diversity. DNA replication precedes the start of meiosis I. During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses, a step unique to meiosis.
Which phase comes after telophase 1 in meiosis?
After telophase 1 of meiosis 1 the cell will immediately enter into prophase 2 of meiosis 2.
What is the difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 quizlet?
Meiosis I is a reduction division where only one member of a homologous pair enters each daughter cell which becomes halploid. Meiosis II only splits up sister chromatids.
Is cytokinesis cell division?
Cytokinesis is the physical process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells. It occurs concurrently with two types of nuclear division called mitosis and meiosis, which occur in animal cells.
Is cytokinesis a part of mitosis?
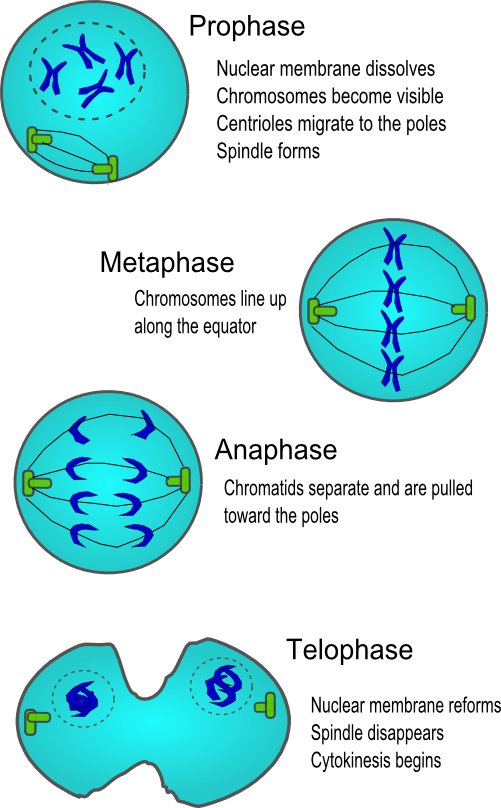
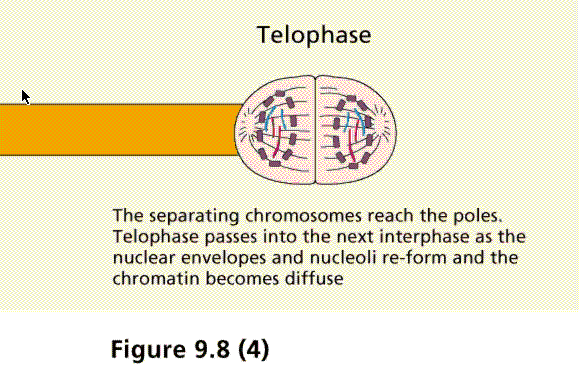
Cytokinesis is the final physical cell division that follows telophase, and is therefore sometimes considered a sixth phase of mitosis. All phases of mitosis, as well as the flanking periods of interphase and cytokinesis before and after, are shown in Figure 8.
In which phase of mitosis does cytokinesis occur?
Cytokinesis begins in anaphase in animal cells and prophase in plant cells, and terminates in telophase in both, to form the two daughter cells produced by mitosis.Mar 1, 2022
Which of the following distinguishes prophase 1 of meiosis from prophase of mitosis?
SolutionProphase-I of MeiosisProphase of MitosisProphase IChromosomes appear double from the very startProphase chromosomes do not look double in the beginningHomologous Chromosomes pair and often undergo crossing over in prophase-IThere is no pairing of homologous chromosomes, hence no chance of crossing over1 more row
1. How does meiosis help in mixing and matching the genes?
The gametes that are generated via meiosis are all haploid in nature and are not genetically identical. Each gamete that is produced will have a un...
2. Why is meiosis an important process in cell formation?
Meiosis is considered to be an important part of cell formation as it aids in three procedures as follows:1. It allows sexual reproduction of a dip...
3. How is Mitosis different from the process involved in Meiosis?
Mitosis is said to be the production of two genetically identical diploid gametes which arise from a diploid parent cell. Whereas on the other hand...
4. When meiosis and mitosis are compared with each other, which stages remain the same and which sta...
All of the stages of meiosis 1 except for the telophase 1 stage will be unique because homologous chromosomes are separated and not the sister chro...
5. Why is it important to learn about Meiosis 1 Stages and Process | Phases and Stages of Meiosis?
The act of fertilization includes two cells that fuse together in order to form a zygote. These two cells that fuse together are formed by specific...
What are the steps in meiosis?
Since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm). In each round of division, cells go through four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
How does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs in diploid cells. The chromosomes duplicate once, and through two successive divisions, four haploid cells are produced, each with half the chromosome number of the parental cell. Meiosis occurs only in sexually reproducing organisms.
What is the function of meiosis?
However, the primary function of meiosis is the reduction of the ploidy (number of chromosomes) of the gametes from diploid (2n, or two sets of 23 chromosomes) to haploid (1n or one set of 23 chromosomes).
What happens in meiosis I?
In meiosis I, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells. It is this step in meiosis that generates genetic diversity. DNA replication precedes the start of meiosis I. During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses, a step unique to meiosis.
How are gametes produced in meiosis?
Meiosis produces haploid gametes (ova or sperm) that contain one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes.
What is the definition of meiosis 2?
Definition. The second of the two consecutive divisions of the nucleus of eukaryotic cell during meiosis, and composed of the following stages: prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. Supplement. Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that ultimately gives rise to non-identical sex cells.
What happens in cytokinesis 2 of meiosis?
A nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes and cytokinesis occurs, producing four daughter cells, each with a haploid set of chromosomes. Cytokinesis takes place, producing four daughter cells (gametes, in animals), each with a haploid set of chromosomes.
What are the two parts of meiosis?
The process of Meiosis is divided into two parts: meiosis I and meiosis II which are further separated into Karyokinesis I and Cytokinesis I and Karyokinesis II and Cytokinesis II respectively. The preparatory steps that lead up to meiosis are similar in pattern and name to interphase of the mitotic cell cycle.
How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
Meiosis I isolate homologous chromosomes, each still made up of two sister chromatids, into two daughter cells, subsequently decreasing the chromosome number by half. In the process of meiosis II, sister chromatids decouple, and the resultant daughter chromosomes are segregated into four daughter cells. For diploid organisms, the daughter cells ...
What is the process of producing gametes?
Meiosis is the process of producing gametes—sex cells, or sperm and eggs in the human body. In a human being, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs. At the point when a sperm and an egg participate in of fertilization, the two haploid arrangements of chromosomes create a complete diploid set: another genome.
What is the longest stage of meiosis?
Prophase I is the longest stage of meiosis. During the phase of prophase, I, homologous chromosomes pair and exchange DNA (homologous recombination). This frequently results in a chromosomal hybrid. The new combination of DNA made during hybrid is a critical source of hereditary variation and result in new mixes of alleles, which might be beneficial. The combined and duplicated chromosomes are called bivalents or quadruplicates, which have two chromosomes and four chromatids, with one chromosome originating from each parent. The method of pairing the homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. At this stage, non-sister chromatids traverse at areas called chiasmata. Prophase I has historically been divided into sub-stages which are named as per the appearance of chromosomes.
What stage of meiosis do chromosomes assemble?
Chromosomes assemble further during the diakinesis stage; from Greek words signifying "moving through". This is the main point in meiosis where the four sections of the quadruplicates are really distinguishable. Regions of crossing-over entangle here, successfully covering, making chiasmata distinguishable.
What holds sister chromatids together?
The protein complex cohesin-holds sister chromatids together from the time of their replication until anaphase. In mitosis, the power of kinetochore microtubules pulling in opposite directions creates tension. The cell senses this strain and does not progress with anaphase until all the chromosomes are appropriately bi-situated in meiosis, building up strain requires something like one hybrid for each chromosome pair notwithstanding cohesin between the sister chromatids.
What are the stages of interphase?
Interphase is partitioned into three stages: • Growth 1 (G1) phase: In this very active phase, the cell synthesizes its vast range of proteins, including the enzymes and structural proteins it will require for development and growth. • Synthesis (S) phase: The hereditary material is replicated; each of the cell's chromosomes duplicates ...
What is the mechanism of meiosis?
Meiosis uses similar mechanisms as those employed during mitosis to accomplish the separation and redistribution of chromosomes. However, several features, namely, the pairing and genetic recombination between homologous chromosomes, are unique to meiosis.
What is the process by which replicated chromosomes undergo two nuclear divisions to produce four haploid
MEIOSIS I. Meiosis is the process by which replicated chromosomes undergo two nuclear divisions to produce four haploid cells, also called meiocytes (sperms and eggs). Diploid (2 n) organisms rely on meiosis to produce meiocytes, which have half the ploidy of the parents, for sexual reproduction. Halving the ploidy in meiocytes is essential ...
How are chromosomes arranged in metaphase?
In metaphase I, each pair of bivalents (two chromosomes, four chromatids total) align on the metaphase plate. This is different from metaphase in mitosis, where all chromosomes align single file on the metaphase plate. The position of each chromosome in the bivalents is random - either parental homolog can appear on each side. This means that there is a 50-50 chance for the daughter cells to get either the mother's or father's homolog for each chromosome (see figure below). As shown in the below figure, during metaphase I, bivalents from either parent can align on either side of the cell. In an organism with two sets of chromosomes, there are four ways in which the chromosomes can be arranged, resulting in differences in chromosomal distribution in daughter cells after meiosis I. (A diploid organism with 2 n chromosomes will have 2 n possible combinations or ways of arranging its chromosomes during metaphase I.)
What happens during prophase 1?
At this time they are said to be in synapsis. During synapsis, crossovers – cross-connections that form from breakage and rejoining between sister chromatids – can occur between the paired bivalents, leading to genetic recombination (exchange of genetic material) between the strands involved. The point where a crossover occurs is called a chiasma (plural chiasmata) (see below figure). In figure below, following crossing over, the blue and red chromosomes, which originally carried AA and aa alleles, respectively, now carry Aa alleles in both chromosomes at the end of prophase I. Note that these bivalents have two chromosomes and four chromatids, with one chromosome originating from each parent.
What happens in anaphase I?
Anaphase I. In anaphase I, homologous chromosomes separate. Homo logous chromosomes, each containing two chromatids, move to separate poles. Unlike in mitosis, the centromeres do not split and sister chromatids remain paired in anaphase I.
Is a daughter cell haploid?
Each of the two daughter cells is now haploid ( n ), with half the number of chromosomes per nucleus as in meiosis I. In some species, the nuclear membrane briefly forms around the chromosomes, while in others it does not. The cell now proceeds into meiosis II, with the chromosomes remaining condensed.
What is the phase of meiosis?
Interphase. Ed Reschke/Getty Images. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II. Before a dividing cell enters meiosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA.
How many daughter cells are produced in meiosis?
Cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm and the formation of two distinct cells) occurs. At the end of meiosis II, four daughter cells are produced. Each cell has one-half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
Where do chromosomes line up in meiosis?
The chromosomes line up at the metaphase II plate at the cell's center. The kinetochore fibers of the sister chromatids point toward opposite poles. At the end of metaphase II of meiosis, the cell enters into anaphase II.
What happens to chromosomes in meiosis?
Chromosomes thicken and detach from the nuclear envelope. Similar to mitosis, the centrioles migrate away from one another and both the nuclear envelope and nucleoli break down. Likewise, the chromosomes begin their migration to the metaphase plate. At the end of prophase I of meiosis, the cell enters into metaphase I.
What is the function of microtubules in meiosis?
Similar to mitosis, microtubules such as the kinetochore fibers interact to pull the chromosomes to the cell poles. Unlike in mitosis, sister chromatids remain together after the homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles. At the end of anaphase I of meiosis, the cell enters into telophase I.
What happens at the end of telophase?
At the end of telophase I and cytokinesis, two daughter cells are produced, each with one-half the number of chromosomes of the original parent cell. Depending on the kind of cell, various processes occur in preparation for meiosis II. There is, however, a constant: The genetic material does not replicate again.
What happens during prophase 2?
In prophase II of meiosis, the following events occur: The nuclear membrane and nuclei break up while the spindle network appears. Chromosomes do not replicate any further in this phase of meiosis. The chromosomes begin migrating to the metaphase II plate (at the cell's equator).