Does meiosis or mitosis occur after fertilization?
The fertilized cell is a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitosis to form two identical cells that remain attached. This takes place about 36 hours after fertilization.
Does mitosis occur after fertilization?
During fertilization the sperm and egg unite to form a single cell called the zygote which contains chromosomes from both the sperm and egg. The zygote undergoes mitosis to begin development of the human embryo which eventually becomes a baby.
Does a fertilized egg undergo meiosis?
Following fertilization, the egg exits from meiosis and assembles a haploid pronucleus. At the same time the sperm genome, which enters the egg in a highly compact state, undergoes decompaction. Sperm protamines are replaced by histones and the male haploid pronucleus is formed.
At what stage does meiosis occur?
Meiosis can take place only in a diploid stage (post-zygotic stage) because the zygote is the only diploid cell in the life cycle of such organisms. This meiosis an case of haploid organisms will occur of the fertilization.
What process occurs after fertilization?
During fertilization, the sperm and egg unite in one of the fallopian tubes to form a zygote. Then the zygote travels down the fallopian tube, where it becomes a morula. Once it reaches the uterus, the morula becomes a blastocyst. The blastocyst then burrows into the uterine lining — a process called implantation.
How is meiosis related to fertilization?
Sexual life cycles involve an alternation between meiosis and fertilization. Meiosis is where a diploid cell gives rise to haploid cells, and fertilization is where two haploid cells (gametes) fuse to form a diploid zygote.
Does sperm and egg go through meiosis?
Meiosis is the type of cell division that creates egg and sperm cells. Mitosis is a fundamental process for life.
Why must meiosis occur prior to fertilization?
Because meiosis creates cells that are destined to become gametes (or reproductive cells), this reduction in chromosome number is critical — without it, the union of two gametes during fertilization would result in offspring with twice the normal number of chromosomes!
What stage happens before meiosis?
Before entering meiosis I, a cell must first go through interphase. As in mitosis, the cell grows during G 1start subscript, 1, end subscript phase, copies all of its chromosomes during S phase, and prepares for division during G 2start subscript, 2, end subscript phase.
When and where does meiosis happen?
Meiosis occurs in the primordial germ cells, cells specified for sexual reproduction and separate from the body's normal somatic cells. In preparation for meiosis, a germ cell goes through interphase, during which the entire cell (including the genetic material contained in the nucleus) undergoes replication.
Does a fertilized egg divide by mitosis?
Zygotes divide through a process known as mitosis, in which each cell doubles (one cell becomes two, two becomes four, and so on). This two-week stage is known as the germinal period of development and covers the time of fertilization (also called conception) to the implantation of the blastocyst in the uterus.
Why is mitosis important after fertilization?
Mitosis builds a person with an identical set of chromosomes in every cell. And meiosis generates reproductive cells with new combinations of gene variations. Chromosomes are sometimes gained, lost, or rearranged during meiosis and fertilization, causing people to have genetic disorders.
During which process does mitosis occur?
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. During cell division, mitosis refers specifically to the separation of the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus.
During which stage mitosis occurs?
Mitosis takes place in four stages: prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. You can learn more about these stages in the video on mitosis. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of the cell is split in two, making two new cells.
How does meiosis affect chromosomes?
In contrast to mitosis, meiosisresults in the division of a diploidparental cell into haploidprogeny, each containing only one member of the pair of homologous chromosomesthat were present in the diploid parent (Figure 14.32). This reduction in chromosome number is accomplished by two sequential rounds of nuclear and cell division (called meiosisI and meiosis II), which follow a single round of DNAreplication. Like mitosis, meiosis I initiates after S phasehas been completed and the parental chromosomes have replicated to produce identical sister chromatids. The pattern of chromosome segregation in meiosis I, however, is dramatically different from that of mitosis. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes first pair with one another and then segregate to different daughter cells. Sister chromatids remain together, so completion of meiosis I results in the formation of daughter cells containing a single member of each chromosome pair (consisting of two sister chromatids). Meiosis I is followed by meiosis II, which resembles mitosis in that the sister chromatids separate and segregate to different daughter cells. Completion of meiosis II thus results in the production of four haploid daughter cells, each of which contains only one copy of each chromosome.
When does meiosis II occur?
Meiosis II initiates immediately after cytokinesis, usually before the chromosomeshave fully decondensed. In contrast to meiosisI, meiosis II resembles a normal mitosis. At metaphaseII, the chromosomes align on the spindle with microtubules from opposite poles of the spindle attached to the kinetochores of sister chromatids. The link between the centromeres of sister chromatids is broken at anaphaseII, and sister chromatids segregate to opposite poles. Cytokinesis then follows, giving rise to haploiddaughter cells.
What is the role of MPF in meiosis?
Like the M phaseof somatic cells, the meiosisof oocytes is controlled by MPF. The regulation of MPF during oocyte meiosis, however, displays unique features that are responsible for metaphaseII arrest (Figure 14.38). Hormonal stimulation of diplotene-arrested oocytes initially triggers the resumption of meiosis by activating MPF, as at the G2to M transition of somatic cells. As in mitosis, MPF then induces chromosome condensation, nuclear envelopebreakdown, and formation of the spindle. Activation of the anaphase-promoting complexB then leads to the metaphase to anaphase transition of meiosis I, accompanied by a decrease in the activity of MPF. Following cytokinesis, however, MPF activity again rises and remains high while the egg is arrested at metaphase II. A regulatory mechanism unique to oocytes thus acts to maintain MPF activity during metaphase II arrest, preventing the metaphase to anaphase transition of meiosis II and the inactivation of MPF that would result from cyclin B proteolysisduring a normal M phase.
What happens to the chromosomes in metaphase I?
At metaphaseI, the bivalent chromosomesalign on the spindle. In contrast to mitosis(see Figure 14.27), the kinetochores of sister chromatids are adjacent to each other and oriented in the same direction, while the kinetochores of homologous chromosomes are pointed toward opposite spindle poles (Figure 14.36). Consequently, microtubules from the same pole of the spindle attach to sister chromatids, while microtubules from opposite poles attach to homologous chromosomes. Anaphase I is initiated by disruption of the chiasmataat which homologous chromosomes are joined. The homologous chromosomes then separate, while sister chromatids remain associated at their centromeres. At completion of meiosisI, each daughter cell has therefore acquired one member of each homologous pair, consisting of two sister chromatids.
What is the first regulatory point in oocyte meiosis?
The first regulatory point in oocyte meiosisis in the diplotenestage of the first meiotic division (Figure 14.37) . Oocytes can remain arrested at this stage for long periods of time—up to 40 to 50 years in humans. During this diplotene arrest, the oocyte chromosomesdecondense and are actively transcribed. This transcriptional activity is reflected in the tremendous growth of oocytes during this period. Human oocytes, for example, are about 100 μm in diameter (more than a hundred times the volume of a typical somatic cell). Frog oocytes are even larger, with diameters of approximately 1 mm. During this period of cell growth, the oocytes accumulate stockpiles of materials, including RNAs and proteins, that are needed to support early development of the embryo. As noted earlier in this chapter, early embryonic cell cycles then occur in the absence of cell growth, rapidly dividing the fertilized egg into smaller cells (see Figure 14.2).
When do oocytes resume meiosis?
Oocytes of different species vary as to when meiosisresumes and fertilization takes place. In some animals, oocytes remain arrested at the diplotenestage until they are fertilized, only then proceeding to complete meiosis. However, the oocytes of most vertebrates (including frogs, mice, and humans) resume meiosis in response to hormonal stimulation and proceed through meiosis I prior to fertilization. Cell division following meiosis I is asymmetric, resulting in the production of a small polar bodyand an oocyte that retains its large size. The oocyte then proceeds to enter meiosis II without having re-formed a nucleusor decondensed its chromosomes. Most vertebrate oocytes are then arrested again at metaphaseII, where they remain until fertilization.
When is meiosis arrested?
Meiosis of vertebrate oocytes. Meiosis is arrested at the diplotene stage, during which oocytes grow to a large size. Oocytes then resume meiosis in response to hormonal stimulation and complete the first meiotic division, with asymmetric cytokinesis (more...)
When does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs before fertilization, since it’s the process that makes the cells that fertilize. In other words, it’s like asking if smelting metal occurs after or before casting a sword.
What happens to the chromosomes in meiosis?
At this point, certain enzymes get activated that randomly the cut the chromosomes at various locations between genes and then stitch them together again crossways. This ends up swapping some of the gene variants between the two choromosomes in a pair. This is the process known as crossover. Then the pairs of chromosomes are divided up, and the cell splits into two haploid cells that each have only a single chromosome from the pair. These then replicate their chromosomes and divide once more to produce four haploid gametes.
How many chromosomes are in a human egg?
Meiosis is necessary to reduce the number of chromosomes to half: from 46 chromosomes in our regular cells to 23 chromosomes in the egg or sperm. The other half in the baby will come from the other partner to create genetic diversity.
What happens to calcium ion release in the cell?
Calcium ion release throughout the cell triggers the next series of changes, resulting in completion of meiosis II and the expulsion of the polar body.
When does meiosis occur in diploid organisms?
In diploid organism meiosis occurs before fertilization that is during the production of gamets and the original diploid number is restored after fertilization
How long does it take for a female pronucleus to divide?
Subsequent division each take about 24 hours, so if that hold here, the process must begin by 12 hours.
What are the stages of interphase?
Interphase consists of three stages: the G1 stage, the S stage, and the G2 stage. During the G1 phase all the internal organelles of the plant cell are replicated, during the S phase (the longest phase) all the DNA of the plant cell is replicated, and during the G2 phase the replicated DNA is checked for mutations. This process is necessary prior to mitosis to ensure that the cell has twice the usual amount of organelles and twice the usual amount of DNA to ensure that two genetically identical diploid cells can be produced when the cell divides by equatoral division in mitosis.
What stage of meiosis do follicles grow?
Untill puberty the follicles grown from primordial to antral stage (secondary folliccle) and oocytes are arrested in diplotene of profase I of meiosis I, without polar body, with a nucleous called germinative vesicle. After puberty, with gonadotrophis, they can grow more and ovulate. With LH surge they are stimulated to continuing meiosis and they lose the nucleous and became metafase I oocytes (MI) and extrude the first polar body to became secondary oocytes (MII oocytes) just before ovulation. So, the Graaf folicle, last stage of follicular development, has a secondary oocyte arrested in metafase II. Only after ovulation and with fecundation it is possible to escape from MII arrest and extrude the second polar body.
How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
At the end of meiosis I females have two daughter cells and meiosis II only occurs if and when fertilization occurs by a sperm cell.
What stage of meiosis is the oocyte arrested?
Meiosis, as you know, have two stages, Meiosis I and II. The oocyte is arrested during metaphase II of MEOISIS II. This arrest is facilitated by a complex called "Cytostatic Factor" (CSF). After fertilization, the sperm induces a rise in intracellular calcium ion which activates and enzyme, Calmodulin Kinase II.
What happens to an egg after ovulation?
After ovulation, each oocyte continues to metaphase of meiosis II. Meiosis II is completed only if fertilization occurs, resulting in a fertilized mature ovum and the second polar body. So in short, the egg is stuck in metaphase II until fertilization. Share. Improve this answer.
What happens to sperm before it can fuse with an egg?
Sperm must ignite some process in female that puts female meiosis II going on before sperm can fuse with egg.
What is the process of fertilization?
The process of fertilization involves a sperm fusing with an ovum.
What phase is the egg stuck in?
So in short, the egg is stuck in metaphase II until fertilization.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
When egg and sperm form, they go through a special type of cell division called meiosis. One purpose of meiosis is to reduce the number of chromosomes by half. The other is to create genetic diversity.
What happens to the chromosomes before a cell divides?
Before a cell divides to make two cells, it copies all of its chromosomes. These copies, called sister chromatids, are identical. Until the cell divides, the identical copies stay connected with each other by their middles (centromeres.) When the cell divides, the copies are pulled apart, and each new cell gets one identical copy of each chromosome.
What is the process called when homologous chromosomes exchange?
But unlike in mitosis, homologous chromosome pairs line up and exchange pieces-a process called recombination. Remember, homologous chromosomes have the same genes but with slight differences. Recombination increases genetic diversity by putting pieces of slightly different chromosomes together.
How many chromosomes are in an egg?
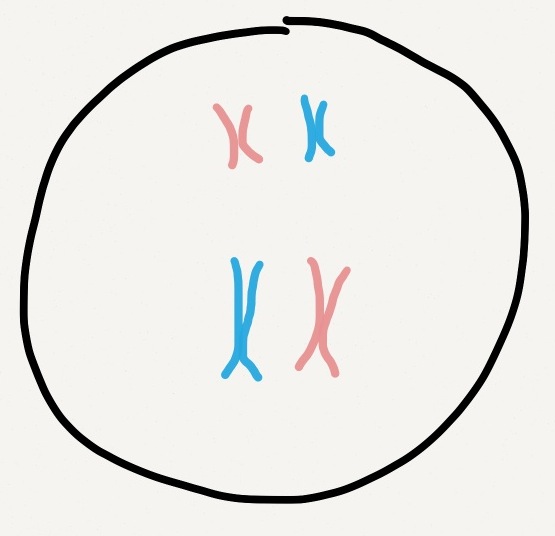
Egg and sperm cells have just 23 chromosomes each. That's half as many chromosomes as regular cells. Through the process of fertilization, egg and sperm join to make a cell with 46 chromosomes (23 pairs), called a zygote.
How many chromosomes are produced in mitosis?
This type of cell division is called mitosis, and it produces cells with a total of 46 chromosomes. Beginning soon after fertilization (see below), all of the cells in your body were made this way. Thus, every cell in your body has an identical set of chromosomes.
When cells divide to make more cells, what is the process called?
When cells divide to make more cells (mitosis) or reproductive cells (meiosis), and when reproductive cells join to make a new individual (fertilization), it is important that the new cells get the proper number of chromosomes. Read on to learn more about these processes.
Do homologous chromosomes have the same genes?
For each chromosome pair, one homologous chromosome came from each parent. They have the same genes arranged in the same order, but there are small variations in the DNA letters of those genes.