What breaks down sugar to release energy in a cell?
Sugar is a type of carbohydrate that the body breaks down to release energy. The process starts in the digestive tract and continues in the cells. Read more in detail here: what breaks down sugar to release energy in a cell. Sugar is broken down into ATP through respiration of cells with the assistance of oxygen (energy molecule).
How is glucose broken down into ATP?
Sugar is broken down into ATP through respiration of cells with the assistance of oxygen (energy molecule). The process of cellular respiration in mitochondria converts sugar into energy that plant cells may utilize to survive and develop. People often wonder how glucose is broken down to release energy.
What happens when mitochondria stop working?
When mitochondria stop functioning, the cell they are in is starved of energy. So, depending on the type of cell, symptoms can vary widely. As a general rule, cells that need the largest amounts of energy, such as heart muscle cells and nerves, are affected the most by faulty mitochondria.
What is the main function of mitochondria in the cell?
They generate the majority of our adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria are also involved in other tasks, such as signaling between cells and cell death, otherwise known as apoptosis.

Does the mitochondria release energy from sugar?
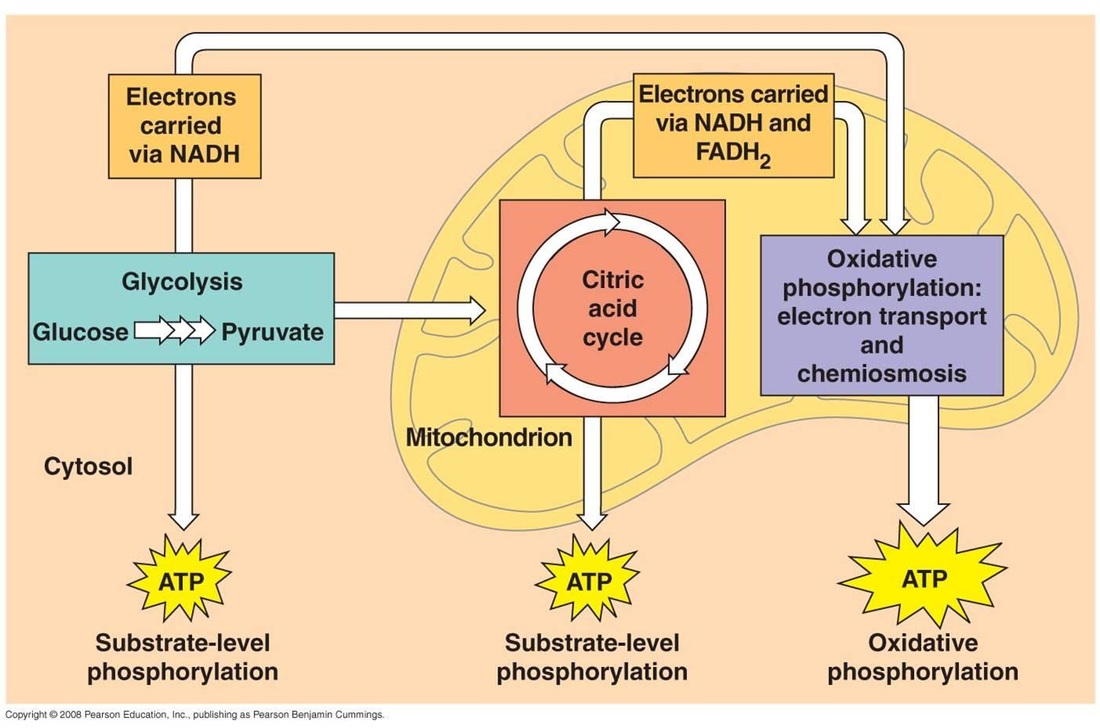
In the mitochondria, the metabolism of sugars is completed, and the energy released is harnessed so efficiently that about 30 molecules of ATP are produced for each molecule of glucose oxidized. By contrast, only 2 molecules of ATP are produced per glucose molecule by glycolysis alone.
Does a mitochondria break down sugar?
Mitochondria break down sugar molecules and produce energy in the form of molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
How does the mitochondria release energy?
The process is called oxidative phosphorylation and it happens inside mitochondria. In the matrix of mitochondria the reactions known as the citric acid or Krebs cycle produce a chemical called NADH. NADH is then used by enzymes embedded in the mitochondrial inner membrane to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Does the mitochondria break down food to release energy?
Mitochondria are tiny organelles inside cells that are involved in releasing energy from food. This process is known as cellular respiration. It is for this reason that mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell.
What do mitochondria break down?
Known as the “powerhouses of the cell,” mitochondria produce the energy necessary for the cell's survival and functioning. Through a series of chemical reactions, mitochondria break down glucose into an energy molecule known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used to fuel various other cellular processes.
What part of the cell breaks down sugar?
MitochondriaMitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. They are organelles that act like a digestive system which takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy rich molecules for the cell. In cellular respiration sugar with the help of oxygen is broken down into ATP (energy molecule).
What are the 3 functions of mitochondria?
What do mitochondria do?Producing energy. ATP, a complex organic chemical found in all forms of life, is often referred to as the molecular unit of currency because it powers metabolic processes. ... Cell death. Cell death, also called apoptosis, is an essential part of life. ... Storing calcium. ... Heat production.
What are 5 functions of the mitochondria?
Here we take a look at 5 roles that mitochondria have been shown to play in cells, and what can happen when these processes are disturbed.Production of ATP. ... Calcium Homeostasis. ... Regulation of Innate Immunity. ... Programmed Cell Death. ... Stem Cell Regulation.
What is the primary function of the mitochondria?
The classic role of mitochondria is oxidative phosphorylation, which generates ATP by utilizing the energy released during the oxidation of the food we eat. ATP is used in turn as the primary energy source for most biochemical and physiological processes, such as growth, movement and homeostasis.
What does the mitochondria do with glucose?
Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) convert chemical energy into energy that our cells can actually use. This process is called cellular respiration. The mitochondria use it to turn glucose and oxygen into a high-energy molecule called ATP. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the money of the cell world.
Do mitochondria need glucose?
Basic mitochondrial function is typically taught based on how glucose is used to make energy, but proteins and fats are used to make energy as well. To really break it down, this whole process is really all about moving electrons.
Which of the following is not a function of mitochondria?
So, the correct answer is 'Polysaccharide degradation'
What does sugar do to the mitochondria?
Not only is sugar considered detrimental to our waistline and to our teeth, it's also the enemy of our mitochondria and contributes to many metabolic health issues. Consuming excess sugar puts the mitochondria under stress, causing them to emit free radicals. This is called oxidative damage.
How does sugar effect mitochondria?
Researchers have now found evidence that excessive sugar consumption may be detrimental to mitochondria, organelles that are known as cellular powerhouses. High sugar levels may reduce their efficiency and energy output. The findings have been published in Cell Reports.
What sort of energy does glucose store?
The bonds between sugar molecules store chemical energy. A burst of energy is produced when the links between sugar molecules are broken, which the cell may utilize.
What causes glucose to be broken down?
When food is digested in the stomach, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the meal is broken down into glucose, a different kind of sugar. The glucose is absorbed by the stomach and small intestines before being released into the circulation.
What are glycolysis’s byproducts?
Glycolysis produces two pyruvate, two NADH, and two ATP as net end products (A special note on the “two” ATP later).
What is the mechanism through which the body expels energy?
Your body cells acquire energy from the food you consume by breathing oxygen. Cellular respiration is the name for this process. The cell utilizes oxygen to break down sugar during cellular respiration. When a cell utilizes oxygen to break down sugar, it consumes oxygen, produces carbon dioxide, and releases energy.
What is the purpose of ATP?
The nucleotide adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the “molecular currency” of intracellular energy transfer in biochemistry; that is, ATP can store and transmit chemical energy inside cells. ATP is also necessary for the production of nucleic acids.
How do plants make use of the energy they get from respiration?
In plants, the process of respiration includes combining the sugars generated during photosynthesis with oxygen to provide energy for plant development. Respiration is the polar opposite of photosynthesis in many respects. Plants generate their own nourishment to live in the natural world.
What is the process of converting food into energy?
The energy in meals is transformed into energy that the body’s cells may utilize via the process of cellular respiration. Glucose and oxygen are transformed to carbon dioxide and water during cellular respiration, and the energy is transferred to ATP.
Where does glucose break down?
Glycolysis is the first step where glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. This occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
How many molecules of ATP are broken down in the process of glucose?
By the end of the process, a molecule of glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide, water and up to around 32 molecules of ATP.
What happens when glucose is oxidized?
When glucose is oxidized, electrons are transferred to a lower energy state. Some of this energy is available for the production of ATP.
Which organelle produces ATP?
The organelle where this process occurs is the mitochondria where ATP is produced as a result of respiration . ATP is a high energy compound that...
