
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of the plasma cells in bone marrow
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue which may be found within the spongy or cancellous portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production or hematopoiesis. It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bone…
What tests are used to diagnose multiple myeloma?
- Cytogenetics. Cytogenetics, which is the study of genetic changes in cells, and molecular studies may be performed on a tissue sample removed during a biopsy to find out how aggressive ...
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). ...
- Minimal residual disease (MRD) tests. ...
What imaging tests can help diagnose multiple myeloma?
X-rays can detect bone damage and lesions from multiple myeloma. Doctors may use X-rays and other imaging tests to diagnose and assess multiple myeloma. For example, MRI scans can provide detailed images that may help doctors detect multiple myeloma in its early stages.
Will a MRI or CT scan detect multiple myeloma?
• MRI and PET/CT have very close diagnostic value for the detection of bone marrow involvement in multiple myeloma. • MRI has a significantly higher sensitivity and better reproducibility. • PET/CT findings appear to have a higher impact on clinical decisions.
What are diagnostic criteria for multiple myeloma?
Diagnostic criteria. Diagnosis of multiple myeloma is based on the International Myeloma Working Group guidelines (Table 3). 10 The diagnosis rests on the presence of a monoclonal paraprotein together with marrow plasmacytosis and myeloma-related end-organ damage.
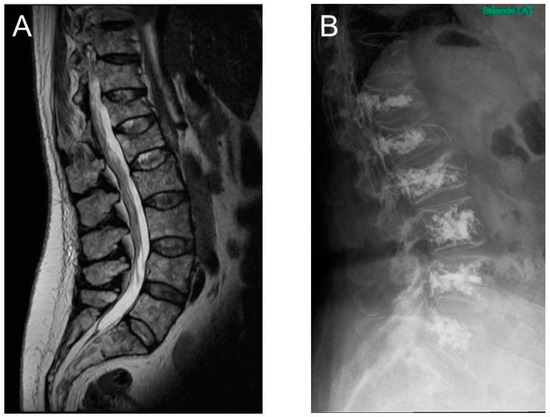
Can you see multiple myeloma on a bone scan?
MRI scans can detect myeloma in its early stages and show any abnormal sections of bone. MRI scans can also show plasmacytomas.
What is the most definitive test to confirm a diagnosis of multiple myeloma?
Bone marrow biopsy People with multiple myeloma have too many plasma cells in their bone marrow. The procedure used to check the bone marrow is called a bone marrow biopsy and aspiration. It can be done either at the doctor's office or at the hospital.
What imaging is needed for multiple myeloma?
MRI is the gold-standard imaging modality for detection of bone marrow involvement and the preferred imaging technique to rule out spinal cord compression in patients with multiple myeloma, whereas PET/CT provides valuable prognostic data and aids in assessment of response to therapy.
What tests indicate multiple myeloma?
Biopsy. This is a common test used to diagnose multiple myeloma. Your doctor will remove a piece of bone marrow or take a sample of cells from your body and check it in a lab under a microscope for signs of cancer.
What is usually the first symptom of multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma causes many symptoms, but bone pain often is the first symptom people notice. Other symptoms include: Weakness in your arms and legs and/or a sensation of numbness in your arms and legs. Multiple myeloma can affect the bones in your spine, causing them to collapse and press on your spinal cord.
Will a blood test show multiple myeloma?
Blood tests. Laboratory analysis of your blood may reveal the M proteins produced by myeloma cells. Another abnormal protein produced by myeloma cells — called beta-2-microglobulin — may be detected in your blood and give your doctor clues about the aggressiveness of your myeloma.
What blood levels indicate multiple myeloma?
If there are too many myeloma cells in the bone marrow, some of these blood cell levels can be low. The most common finding is a low red blood cell count (anemia2). Levels of blood creatinine, albumin, calcium, and other electrolytes will be checked. Creatinine levels show how well your kidneys are working.
Is multiple myeloma hard to diagnose?
Multiple myeloma can be difficult to diagnose because it's an uncommon type of cancer that usually has few or no symptoms in the early stages.
How does a person get multiple myeloma?
It's not clear what causes myeloma. Doctors know that myeloma begins with one abnormal plasma cell in your bone marrow — the soft, blood-producing tissue that fills in the center of most of your bones. The abnormal cell multiplies rapidly.
Is WBC high in multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma most commonly causes: Low red blood cell count (anemia), which can lead to fatigue and shortness of breath. Low white blood cell count, which makes you more likely to get infections. Low platelet count, which can lead to abnormal bleeding.
What virus causes multiple myeloma?
Human herpesvirus-8 has been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of KS, BCBL, and multicentric Castleman's disease. Evidence for its role in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma is accumulating. Human herpesvirus-8 is detectable in the nonmalignant bone marrow dendritic cells from most myeloma patients.
How fast does myeloma progress?
The risk of myeloma progressing is highest in the first 5 years after diagnosis. About 50 out of 100 people (50%) with smouldering myeloma develop symptoms and need treatment within the first 5 years. However, after 5 years the risk decreases and some people never develop symptoms or need treatment.
How myeloma is diagnosed?
Myeloma is diagnosed using information gathered from a number of different tests. These include a physical examination, blood tests, urine tests, a bone marrow biopsy, x-rays and other more specialised bone imaging tests.
What does SPEP and UPEP test for?
SPEP and UPEP tell us how MUCH monoclonal protein there is, but not the type. Monoclonal protein is the output of myeloma cells in most people with myeloma. Yet, every person's myeloma is unique. The output of monoclonal protein can vary from patient to patient.
How high is IgG in multiple myeloma?
In people with multiple myeloma, 70% have high levels of IgG protein, 20% have high levels of IgA and 5–10% produce only immunoglobulin light chains (Bence-Jones proteins).
How high is IgM in multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma is characterized by the neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells preferentially in the bone marrow producing a monoclonal immunoglobulin in the blood and/or urine. The abnormal immunoglobulin can be IgG (52%), IgA (21%), IgD (2%), kappa or lambda light chains only (16%), biclonal (2%), or IgM (0.5%).
How to diagnose multiple myeloma?
Diagnosing Multiple Myeloma. Multiple myeloma is often diagnosed based on tests, the patient’s symptoms and the doctor’s physical exam of the patient. A diagnosis of multiple myeloma requires either: 1. A plasma cell tumor (proven by biopsy) OR at least 10% plasma cells in the bone marrow AND. 2.
What is the test for multiple myeloma?
This test measures the blood levels of the different antibodies ( also called immunoglobulins). There are several different types of antibodies in the blood: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM. The levels of these immunoglobulins are measured to see if any are abnormally high or low. In multiple myeloma, the level of one type may be high while the others are low.
Why is MRI important?
Because MRI can find plasmacytomas that can’t be seen on regular x-rays, they can be helpful if the patient has pain in a bone but nothing abnormal is seen on the x-ray. MRI can also be used to look at the bone marrow in patients with multiple myeloma.
How long does it take for a cytogenetic test to show a chromosome?
Finding these changes can sometimes help in to predicting a person’s prognosis (outlook). Cytogenetic testing usually takes about 2 to 3 weeks to get a result.
What is a routine urine test for myeloma?
Urine tests. A routine urine sample is typically taken to look for myeloma protein that has filtered through the kidney. You most likely also will be asked to give a sample of urine that has been collected over a 24-hour period, so it can measure how much myeloma protein is present.
Why is myeloma abnormal?
The antibody produced by myeloma cells is abnormal because it is monoclonal (all the exact same ). Serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) is a test that measures the antibodies in the blood and can find a monoclonal antibody.
What test is used to determine the type of antibody?
Another test, called immunofixation or immunoelectrophoresis, is used to determine the exact type of abnormal antibody (IgG. IgA or some other type). Finding a monoclonal antibody in the blood may be the first step in diagnosing multiple myeloma.
How to detect myeloma?
X-rays are the oldest and least sensitive method to detect myeloma-caused bone damage. A full skeletal X-ray survey can show. X-rays are simple and quick procedures. Insurance covers most X-rays. While they are widely available, other imaging studies often are more precise than X-rays. X-rays can detect bone damage only after 30% or more ...
What is a CT scan for myeloma?
Whole-body low-dose computed tomography (WBLDCT) is the new standard for evaluating myeloma bone disease. Computerized axial tomography (CT or CAT) scan uses X-ray technology to create a three-dimensional digital image of the body that is more precise than X-ray. Also, a CT scan can provide clear, detailed images of bone lesions.
What is a non secretory myeloma PET scan?
a patient has non-secretory myeloma (myeloma cells that secrete no monoclonal protein) PET scans. cover the whole body. are sensitive in detecting potential tumor activity. are the only "real-time" imaging study. detect early changes in the bone marrow before there is destruction of bone.
What is the most common symptom of multiple myeloma?
Bone disease is a common symptom of multiple myeloma: 70%–80% of patients are found to have bone disease at diagnosis. Imaging studies that assess the status of a patient's bones and/or bone marrow at diagnosis and relapse are. X-rays. CT scans.
What is MRI in medical terms?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive way to produce a detailed two- or three-dimensional image of structures inside the body.
Does PET scan detect myeloma?
are the only imaging study that detect extramedullary disease, which is myeloma that grows outside the bone marrow. The IMWG's consensus statement on assessment of response to treatment includes PET scanning. The IMWG states that PET scans are required, along with either Next-Generation Flow (NGF) or Next-Generation DNA Sequencing ...
Can you use gadolinium on an MRI?
Before scheduling an MRI, discuss the use of contrast agent gadolinium with your oncologist. In December 2017, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) required "a new class warning and other safety measures for all gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) concerning gadolinium remaining in patients’ bodies, including the brain, for months to years after receiving these drugs," according the FDA's website.
Multiple Myeloma Diagnosis
Diagnosing multiple myeloma includes blood work, a 24-hour urine collection, a bone marrow biopsy, imaging studies (such as x-rays, MRIs, PET scans) and bone density tests. It sounds like a lot (and it is!) but none are that invasive or painful, with the exception of the bone marrow biopsy, but even that isn’t so bad.
All Myeloma is Not the Same
Did you know that not all myeloma is the same? There are various sub-types of myeloma, some being more aggressive and some being less aggressive. The tests will help to determine your myeloma sub-type and how best to treat it.
An Accurate Multiple Myeloma Diagnosis
Results of any single test are not enough to make a diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Diagnosis is based on a combination of factors, including the patient’s description of symptoms, the doctor’s physical examination and the results of a variety of tests. The diagnosis of multiple myeloma requires either:
Smoldering Myeloma
This term used to mean early myeloma that is not causing any symptoms or problems. Those with smoldering myeloma have normal blood counts, normal calcium levels, normal kidney function, and no bone or organ damage.
Laboratory Tests
If symptoms suggest that a person might have multiple myeloma, lab tests on blood and/or urine, x-rays of the bones, and a bone marrow biopsy are usually done.
Blood Counts
The complete blood count (CBC) is a test that measures the levels of red cells, white cells, and platelets in the blood. If myeloma cells occupy too much of the bone marrow, levels of these blood cells will be low and anemia will be common.
Free light chains (blood test)
This test measures the amount of light chains in the blood. This is most helpful in the rare cases of myeloma in which no M protein is found by SPEP. Since the SPEP measures the levels of intact (whole) immunoglobulins, it cannot measure the amount of light chains.
What percentage of myeloma patients have osteolytic lesions?
About 80–90% of myeloma patients suffer from osteolytic lesions during the course of disease affecting axial and appendicular skeleton. As a result of MBD, patients may suffer from bone pain (70–80%), fractures (50–60%), hypercalcemia (15%), spinal cord compression (2–3%), decreased quality of life, and poor mobility. 80
What is the role of MM cells in osteoblastic activity?
On the other hand, MM cells inhibit the osteoblastic activity by production of inhibitory cytokines and reduced OPG production. 20
What is the intermediate phase of smoldering multiple myeloma?
Some patients experience an intermediate phase called smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM), characterized by higher levels of abnormal immunoglobulins and more plasma cells in the bone marrow. Most cases of SMM progress to MM over 15 years.
What is the second most common hematologic cancer?
Bone Tumors: Multiple Myeloma. Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignancy of bone marrow plasma cells that produce abnormal immunoglobulins. It is the second most common hematologic cancer and typically is diagnosed in individuals ages 65 to 74 years.
What imaging is used to diagnose multiple myeloma?
Various types of imaging studies are used to diagnose and monitor bone disease in multiple myeloma: X-ray: Despite its many limitations, conventional skeletal survey with x-ray remains the standard of care to diagnose bone disease in patients with suspected myeloma. CT (computed tomography): Current NCCN (National Comprehensive Cancer Network) ...
What is the best CT scan for myeloma?
CT (computed tomography): Current NCCN (National Comprehensive Cancer Network) guidelines list skeletal survey or whole-body low-dose CT scan as the preferred studies for diagnosing myeloma bone disease, giving doctors the choice to do the more sensitive (and more expensive) CT study if insurance reimbursement is available.
What Are Focal Lesions?
Focal lesions are early, abnormal areas in the bone marrow that signal the development of a lytic lesion within the next 18-24 months. An otherwise asymptomatic patient whose MRI scan shows more than 1 focal lesion of at least 5 mm in size has what is called a "myeloma-defining event," and should be treated for active disease.
What is the minimum amount of bone damage that requires therapy?
The official International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) definition of the minimal amount of bone damage that requires therapy is: more than one focal lesion of at least 5 mm in size on MRI, or. one or more lytic bone lesions detected on CT scan, including whole-body low-dose CT or PET/CT.
How does multiple myeloma affect osteoclasts?
Multiple myeloma upsets the osteoclast-osteoblast balance by uncoupling their functions. Myeloma cells produce osteoclast-activating factors, signaling osteoclasts to break down bone uncontrollably. At the same time, they prevent bone repair by inhibiting the formation of osteoblasts. The result is too much bone breakdown ...
What causes holes in bones?
Bone Disease. Myeloma bone disease can cause the bones to become thinner and weaker (osteoporosis), and it can make holes appear in the bone (lytic lesions). The weakened bone is more likely to break under minor pressure or injury (pathologic fracture). The bones most commonly affected are the spine, pelvis, ribs, skull, ...
What is the best treatment for multiple myeloma?
1) effective treatment of the myeloma. 2) use of a supportive "bone-modifying" treatment to prevent further bone loss. Currently, three such bone-modifying agents (BMAs) are available for multiple myeloma. They are not chemotherapy, and they do not treat MM.
What is bone imaging?
Bone imaging is a critical aspect of care for patients with multiple myeloma (MM), and recent advances in imaging modalities have improved detection of lytic lesions and bone marrow involvement. “Bone Imaging Can Make or Break…”.
Why is MRI used for back pain?
Dr Vij also noted that it is used “to evaluate any episode of back pain because it is the best test to rule out spinal cord compression.”
What are the two classes of agents available for the treatment of bone disease in MM?
There are 2 classes of agents available for the treatment of bone disease in MM: bisphosphates and an anti-RANKL antibody . These agents inhibit osteoclast activity, thereby preventing new osteolytic lesions, pathologic fractures, and hypercalcemia…
What is the most accurate technique for detecting extramedullary disease?
FDG-PET/CT detects bone lesions with a sensitivity and specificity between 80% and 100% and is the most accurate technique for detecting extramedullary disease. It can also be used for prognostication, as the number and metabolism of focal lesions prior to stem cell transplantation has been established as an independent prognostic factor. FDG-PET/CT is also the preferred modality for monitoring metabolic response to MM treatment…
What can be used to diagnose a patient?
Imaging studies such as PET scans and x-rays can offer diagnostic information that should be a part of the conversation.
Does Emerson have a plasmycytoma?
To quote my oncologist, Nathan A. Berger M.D. in his lab report dated 2/28/94, “Mr. Emerson clearly had a single plasmycytoma of bone which has been removed and repaired with a bone graft. He has no evidence of systemic myeloma…I told the family that there is no demonstration that systemic adjuvant therapy is effective in early myeloma (chemo doesn’t help a single plasmacytoma).”
Is bisphosphonate better than denosumab?
Selection between bisphosphonates and de nosumab comes down to cost and renal disease. Bisphosphonate are “literally a tenth of the cost of denosumab, but denosumab has little in the way of renal side effects,” Dr Vij said. This is important given that many patients with MM have renal dysfunction at diagnosis or develop it as their disease progresses. For these patients, “denosumab is certainly the best option,” he said, “but to give it to everybody, is certainly not something that most physicians or opinion leaders currently recommend because of the cost.”
What is the median age of diagnosis for multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma is a common malignancy in patients above 40 (70% of cases are diagnosed between ages 50 and 70 with a median age of diagnosis being 69 years) with a male predilection (M: F 2:1) 7,12.
What is the medical term for multiple myeloma?
As per the WHO classification of tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, multiple myeloma is called plasma cell myeloma. Historically, it was sometimes known as Kahler disease or myelomatosis 13.
What is a smoldering multiple myeloma?
Smoldering multiple myeloma refers to a form that falls on the spectrum between monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS) and active multiple myeloma. Patients are asymptomatic, with worse biochemistry than MGUS but without the end-organ damage of active multiple myeloma 9.
Why is a skeletal survey important?
A skeletal survey is essential not only for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma but also in pre-empting potential complications (e.g. pathological fracture) and assessing response to therapy. ~40% bone destruction is required for lesion detection, thus giving the skeletal survey a high false-negative rate of ~50% (range 30-70%) 12 .
What is the most common bone neoplasm in adults?
Multiple myeloma, also known as plasma cell myeloma, is a monoclonal gammopathy and is the most common primary malignant bone neoplasm in adults. It arises from red marrow due to the monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells and manifests in a wide range of radiographic abnormalities. Multiple myeloma remains incurable.
What are the causes of renal failure in multiple myeloma?
most common cause of renal failure in multiple myeloma. direct nephrotoxicity of Bence Jones proteins on the epithelial cells of the renal tubules. hypercalcemia and dehydration. hyperuricemia and urate nephropathy due to high cell turnover. amyloidosis (AL type) increased risk of renal infection.
Is diffuse multiple myeloma normal?
Disseminated multiple myeloma has two common radiological appearances, although it should be noted that initially, radiographs may be normal, despite the presence of symptoms. The two main diffuse patterns are 12:
