
Do neostigmine and glycopyrrolate pass the placenta differently?
Glycopyrrolate and neostigmine, quaternary ammonium compounds, bearing a positively charged ionic nitrogen, pass the placenta with greater difficulty than nonionic compounds (e.g., atropine). We contend that the placental passage of neostigmine, which produces a pronounced pharmacologic effect, exceeds that of glycopyrrolate.
Does neostigmine affect the fetal heart rate during pregnancy?
The fetal heart rate slowed when glycopyrrolate was used, inasmuch as neostigmine passed the placenta to a greater extent than glycopyrrolate and there was insufficient placental transfer of the anticholinergic drug to prevent the fetal muscarinic effect of neostigmine.
Does neostigmine cross the blood–brain barrier?
Unlike physostigmine, neostigmine has a quaternary nitrogen; hence, it is more polar. It does not cross the blood–brain barrier and enter the CNS. However, it does cross the placenta. Its effect on skeletal muscle is greater than that of physostigmine.
What is the role of neostigmine and atropine in the treatment of bradycardia?
We suggest that neostigmine and atropine, rather than neostigmine and glycopyrrolate, be used to reverse nondepolarizing muscle relaxants in pregnant patients to ameliorate the pronounced bradycardia induced by the neostigmine. 1. Hon EH, Bradfield AH, Hess OW: The electronic evaluation of the fetal heart rate: V.
See more

Is neostigmine safe in pregnancy?
Neostigmine crosses the placenta and fetal bradycardia can occur, while glycopyrrolate does not. Opioids are highly lipid-soluble and readily cross the placenta. Although brief exposure is safe, long-term exposure will cause symptoms of withdrawal when the fetus is delivered.
What drugs Cannot cross the placenta?
DRUGS WHICH DO NOT CROSS THE PLACENTAAll paralytics.Glycopyrrolate.Insulin.Heparin.
Does atropine cross placenta?
It is well known that atropine will cross the placenta and that maternal administration results in an increase in fetal heart rate.
What medications pass through the placenta?
Drugs which have been shown to undergo significant placental metabolism include azidothymidine, dexamethasone, and prednisolone (van der Aa et al., 1998). The anticonvulsant oxcarbazepine (but not carbamazepine) is also metabolized to some extent by the human placenta (Pienimäki et al., 1997; Myllynen et al., 1998).
What Cannot pass through the placenta?
The immunoglobulin, which cannot pass through placenta and such foetus is IgM.
What substances pass from maternal to fetal blood?
In the placenta, carbon dioxide and waste products are released into the mother's circulatory system, and oxygen and nutrients from the mother's blood are released into the fetus' blood.
Why do you give atropine with neostigmine?
At the end of surgery, neostigmine has been given for the reversal of neuromuscular blocking agents with several adverse effects such as bradycardia and profuse secretion. Atropine has been used to prevent those side effects of neostigmine.
Does midazolam cross the placenta?
Midazolam is a commonly used sedative as it is fast-acting and of short duration, making it superior to other benzodiazepines. It is a lipophilic drug that can cross the placenta by passive diffusion. In large induction doses, midazolam and its metabolites cross the placenta in both animal[31] and human[14] studies.
Does propofol cross placenta?
Background: Propofol is an alternative to thiopental for induction of general anaesthesia for cesarean section. It crosses the placenta and induces vasodilatation of isolated vessels and may therefore alter fetal placental vascular resistance.
When do drugs cross the placenta?
Transplacental transfer of drugs increases in the third trimester due to increased maternal and placental blood flow, decreased thickness and increased surface area of the placenta[9].
Which of the following crosses the placental barrier?
Which of the following crosses the placental barriers? Oxygen.
Which category of drugs is contraindicated in pregnancy?
Category X: Contraindicated (studies in pregnant women have demonstrated a risk to the fetus, and/or human or animal studies have shown fetal abnormalities; risks of the drug outweigh the potential benefits).
Which category of drugs is contraindicated in pregnancy?
FDA classifies various drugs used in pregnancy into five categories, categories A, B, C, D and X. Category A is considered the safest category and category X is absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy.
Does Tylenol cross the placenta?
Still, acetaminophen and its metabolites freely cross the placenta and have been found in cord blood, newborn urine, and fetal liver, suggesting the potential for direct fetal toxicity [5–7].
Does aspirin cross the placenta?
Aspirin crosses the placenta. Although aspirin has not been associated with other congenital anomalies, it has been associated with an increased risk of vascular disruptions, particularly gastroschisis and possibly premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Why does heparin not cross placenta?
H E P A R I N is a mucopolysaccharide with a molecular weight of about 16,000. Because of its molecular size, it was thought not to cross the placental barrier. lw3 Recently, we learned of a study by Stamm4 in which he concluded that there is no transport of heparin across the placenta.
How to administer neostigmine?
Neostigmine should be administered when the first twitch response of a peripheral nerve stimulator is substantially greater than 10% of baseline or when a second twitch is present. The drug is administered intravenously as a bolus. The drug is administered intravenously as a bolus. Intravenous (IV) dosage is 0.03 mg/kg to 0.07 mg/kg (up to 5 mg), with the higher dose for first twitch responses that are close to but not substantially greater than 10%. The peak effect (antagonism) occurs at approximately 7 to 10 minutes, and the duration of action is approximately 55 to 75 minutes. The principal route of excretion is the kidney. Neostigmine is typically administered along with an antimuscarinic agent like glycopyrrolate or atropine to attenuate the parasympathomimetic activity at other non-muscular acetylcholine receptor sites. [7][8]
What is neostigmine used for?
The use of neostigmine is primarily found in the context of the reversal of neuromuscular blockade during the administration of anesthesia to patients undergoing surgery that require muscle relaxation. After administration of neostigmine, the concentration of acetylcholine is increased in the neuromuscular junction, which allows for muscles to contract with full strength, and patients can breathe spontaneously and protect their airways safely after emergence from anesthesia. [1][2][3]
What is the clinical impact of Sugammadex?
Clinical Impact of Sugammadex in the Reversal of Neuromuscular Blockade.
Is neostigmine a reversal agent?
It is important to consider the relative duration of action of neuromuscular blocking agents when administering neostigmine as a reversal agent. Administering neostigmine after a relative degree of spontaneous recovery of neuromuscular function is important to prevent "recurarization," which can manifest as increased weakness in the post-operative recovery unit due to the lasting effect of the neuromuscular blocking drug. Of note, up to 70% of acetylcholine receptors may still be blocked with an apparently normal train of four from the peripheral nerve stimulator. The duration of action of neostigmine is increased in patients with renal failure as it is excreted by the kidneys.
Is neostigmine contraindicated?
Absolute contraindications of neostigmine include hypersensitivity to neostigmine and peritonitis or mechanical obstruction of the intestinal or urinary tract.[10] Neostigmine should also not be administered if zero twitches are observed on a peripheral nerve stimulator after the administration of a nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking drug. Neostigmine should be used with caution in patients with coronary artery disease, cardiac arrhythmias, recent acute coronary syndrome, and myasthenia gravis.
Can neostigmine cause bradycardia?
In pregnancy, neostigmine can cross the placenta and cause fetal bradycardia, and concurrent administration of atropine, which also crosses the placenta, should be considered in this situation. Another significant side effect of neostigmine and other anticholinesterase inhibitors is paradoxical anticholinesterase-associated muscle weakness. The clinical manifestation of muscle weakness includes decreases in upper airway dilator muscle tone, impairment of respiratory muscles like the diaphragm, and reductions in minute volume, which is the tidal volume multiplied by the respiratory rate. [9]
Does neostigmine affect the heart?
There are a number of adverse effects of neostigmine that can affect multiple organ systems, most of which are related to the cholinergic side effects of the drug. Cardiac muscarinic effects that can be seen include bradyarrhythmias like junctional escape rhythms, complete heart block, and even asystole. A potentially life-threatening adverse effect of neostigmine is bronchoconstriction. Neostigmine, along with other anticholinesterase inhibitors, can stimulate the muscarinic receptors in the airway smooth muscle, potentially leading to bronchospasm. This adverse effect can be mostly attenuated with concurrent administration of an anticholinergic agent like glycopyrrolate. Other adverse effects include increased secretions, miosis, nausea, and increased peristalsis. [9]
Why do hospitals give neostigmine?
Hospitals sometimes administer a solution containing neostigmine intravenously to delay the effects of envenomation through snakebite. Some promising research results have also been reported for administering the drug nasally as a snakebite treatment.
What is the shift of Neostigmine?
Neostigmine's 1 H NMR Spectroscopy reveals shifts at: 7.8, 7.7, 7.4, 7.4, 3.8, and 3.1 parts per million. The higher shifts are due to the aromatic hydrogens. The lower shifts at 3.8 ppm and 3.1 ppm are due to the electronic withdrawing nature of the tertiary and quaternary nitrogen, respectively.
How does neostigmine affect muscarinic receptors?
By interfering with the breakdown of acetylcholine, neostigmine indirectly stimulates both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Unlike physostigmine, neostigmine has a quaternary nitrogen; hence, it is more polar and does not cross the blood–brain barrier and enter the CNS, but it does cross the placenta. Its effect on skeletal muscle is greater than that of physostigmine. Neostigmine has moderate duration of action – usually two to four hours. Neostigmine binds to the anionic and ester site of cholinesterase. The drug blocks the active site of acetylcholinesterase so the enzyme can no longer break down the acetylcholine molecules before they reach the postsynaptic membrane receptors. This allows for the threshold to be reached so a new impulse can be triggered in the next neuron. In myasthenia gravis there are too few acetylcholine receptors so with the acetylcholinesterase blocked, acetylcholine can bind to the few receptors and trigger a muscular contraction.
What is neostigmine used for?
Neostigmine is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used together with atropine to end the effects of neuromuscular blocking medication of the non-depolarizing type, reversing the full-body paralysis generally required during major surgery.
How long does neostigmine work?
Neostigmine has moderate duration of action – usually two to four hours. Neostigmine binds to the anionic and ester site of cholinesterase. The drug blocks the active site of acetylcholinesterase so the enzyme can no longer break down the acetylcholine molecules before they reach the postsynaptic membrane receptors.
When was neostigmine invented?
Neostigmine was patented in 1931 . It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The term is from Greek neos, meaning "new", and "-stigmine", in reference to its parent molecule, physostigmine, on which it is based.
What is the compound that is made from physostigmine?
Neostigmine, which can be viewed as a simplified analog of physostigmine, is made by reacting 3-dimethylaminophenol with N -dimethylcarbamoyl chloride, which forms the dimethylcarbamate, and its subsequent alkylation using dimethyl sulfate forming the desired compound.
What is the placenta?
The placenta is a disc-shaped organ which provides the sole physical link between mother and fetus. During pregnancy, the placenta grows to provide an ever-larger surface area for materno-fetal exchange. At term, the placenta weighs almost 500 g, has a diameter of 15–20 cm, a thickness of 2–3 cm, and a surface area of almost 15 m 2. 1
Why do local anaesthetics accumulate in the fetus?
Local anaesthetics can accumulate in the fetus due to ‘ion trapping’ if the fetus becomes acidotic. Ion trapping occurs when the decreased pH in the fetus produces an increased proportion of ionized drug which is then unable to cross the placenta. 3
How much does the placenta weigh?
At term, the placenta weighs almost 500 g , has a diameter of 15–20 cm, a thickness of 2–3 cm, and a surface area of almost 15 m 2. 1. The basic structural unit of the placenta is the chorionic villus. The villi are vascular projections of fetal tissue surrounded by chorion.
What is the function of the placenta?
The placenta is the interface between mother and fetus. Functions of the placenta include gas exchange, metabolic transfer, hormone secretion, and fetal protection. Nutrient and drug transfer across the placenta are by passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and pinocytosis. Placental drug transfer is dependent on ...
Why do we give drugs to mothers?
In some cases, this transplacental transfer may be beneficial and drugs may be deliberately administered to the mother in order to treat specific fetal conditions. For example, steroids may be given to the mother to promote fetal lung maturation and cardiac drugs may be given to control fetal arrhythmias.
How does oxygen transfer to the fetus?
Oxygen transfer to the fetus is enhanced by the Bohr effect. At the materno-fetal interface, maternal blood takes up carbon dioxide and becomes more acidotic. This causes a rightward shift of the maternal oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve which favours oxygen release to the fetus. At the same time, fetal blood releases carbon dioxide and becomes more alkalotic. This leads to a leftward shift of the fetal curve, favouring fetal uptake of oxygen. This phenomenon is called the ‘Double Bohr Effect’. The transfer of oxygen from mother to fetus is also favoured by the presence of fetal haemoglobin which shifts the fetal oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve further to the left. 3
Where do drugs transfer from the maternal to the fetal?
Drugs which transfer from the maternal to the fetal blood must be carried into the intervillous space and pass through the syncytiotrophoblast, fetal connective tissue, and the endothelium of fetal capillaries. The rate-limiting barrier for placental drug transfer is the layer of syncytiotrophoblast cells covering the villi. Factors affecting drug transfer across the placenta are listed in Table 1.
Is intra-abdominal anesthesia safe?
Intra-abdominal procedures for inflammation immediately adjacent to the uterus are more likely to result in uterine irritability, and the risk of preterm labour or abortion is significantly higher. The anaesthetist must provide safe anaesthesia to the mother while minimizing the risks to the developing fetus.
Is regional anaesthesia necessary during pregnancy?
Regional anaesthesia is highly desirable, although there are particular considerations during pregnancy. Obesity and oedema can obscure anatomical landmarks. Interspinal ligaments are hormonally softened, causing difficulty with epidural loss of resistance techniques. The spread of the local anaesthetic within the epidural or spinal space is greater in pregnancy, and lower doses are required. This may be due to both the mechanical effect of the enlarging uterus and hormonal changes, increasing sensitivity to local anaesthetic agents. Albumin concentration is reduced, with lower plasma binding and a higher risk of local anaesthetic toxicity.
What drugs cross the placenta?
All inhalational agents and most intravenous agents used by anesthesiologists will cross the placenta – inhalational agents cause very little fetal depression if used at < 1 MAC and delivery occurs within 10 mins of induction. Thiopental, propofol, benzodiazepines, and ketamine all cross the placenta, although only benzodiazepines are noted to produce significant fetal effects. Opiates all cross the placenta to some extent (amount is variable) – from a respiratory standpoint, newborns are most sensitive to maternal morphine. Fentanyl appears to be safe if given at < 1 ucg/kg. Epidural opiates produce minimal effects. Ephedrine, B-blockers, vasodilators, metoclopramide, and atropine cross the placenta, although glycopyrrolate (which also does not pass the blood-brain barrier) does not
Why is a pregnant woman hypoosmotic?
While pregnant women are hypoosmotic due to decreased plasma protein concentrations , the fetus still has 50% less protein than its mother. The implications of this in terms of placental transfer are unclear, however it is certain that highly protein-bound drugs (ex. bupivacaine) are found in higher maternal (as opposed to fetal) concentrations
Do non-ionized drugs cross the placenta?
Non-ionized drugs tend to cross the placenta more easily than ionized drugs, however the fetus usually has a lower pH than the mother, leading to “ion trapping.”
Can ephedrine be used in spinal cord?
Some authors have suggested that ephedrine, which causes NE release and can produce tachyphylaxis, may need to be avoided in spinal patients as it is theoretically possible for ephedrine to reduce the potency of epinephrine if used prior to EPI administration in an emergency situation.
Does MW 1000 cross the placenta?
Most drugs with MW < 500 Da cross the placenta, and most drugs with MW > 1000 Da do not cross the placenta (ex. heparin, protamine, insulin). Neither succinylcholine (highly ionized) or non-depolarizing NMBDs (high molecular weights) cross the placenta.
Does epinephrine prolong lidocaine?
Epinephrine has a differential effect on various anesthetics, substantially prolonging both lidocaine and mepivacaine and having a relatively minor effect (if any) on bupivacaine and ropivacaine.
Can maternal stress increase NE?
Data from pregnant sheep suggest that matern al stress can lead to increased native NE production and subsequently reduced uterine blood flow [Shnider SM et al. Anesthesiology 50: 524, 1979], suggesting that a regional technique may help preserve oxygen delivery to the fetus
Definition
According to animal (sheep) studies, peak maternal/fetal levels of atropine are 8x higher than glycopyrrolate after intravenous maternal administration.
Sources
S H Murad, K A Conklin, K M Tabsh, C R Brinkman, R Erkkola, B Nuwayhid Atropine and glycopyrrolate: hemodynamic effects and placental transfer in the pregnant ewe. Anesth. Analg.: 1981, 60 (10);710-4
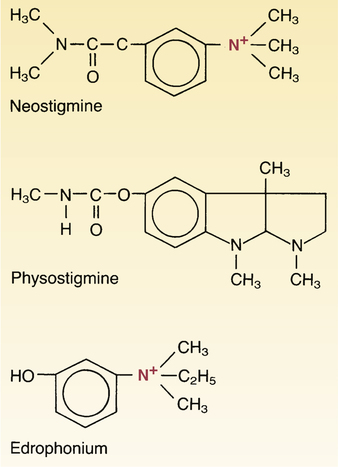
Overview
Pharmacology
By interfering with the breakdown of acetylcholine, neostigmine indirectly stimulates both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Unlike physostigmine, neostigmine has a quaternary nitrogen; hence, it is more polar. It does not cross the blood–brain barrier and enter the CNS. However, it does cross the placenta. Its effect on skeletal muscle is greater than that of physostigmine. Neostigmine has moderate duration of action – usually two to four hours. Neostigmine binds to the anionic and e…
Medical uses
It is used to improve muscle tone in people with myasthenia gravis, and also to reverse the effects of non-depolarizing muscle relaxants such as rocuronium and vecuronium at the end of an operation.
Another indication for use is the conservative management of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction, or Ogilvie's syndrome, in which patients get massive colonic dilatation in the absence of a true mec…
Side effects
Neostigmine can induce generic ocular side effects including: headache, brow pain, blurred vision, phacodonesis, pericorneal injection, congestive iritis, various allergic reactions, and rarely, retinal detachment. Neostigmine is often prescribed for underactive urinary bladder.
Neostigmine has a wide variety of side-effects such as reduced heart rate (bradycardia), due to the increase of acetylcholine at nerve terminals. For this reason it is usually given along with an a…
Chemistry
Neostigmine, which can be viewed as a simplified analog of physostigmine, is made by reacting 3-dimethylaminophenol with N-dimethylcarbamoyl chloride, which forms the dimethylcarbamate, and its subsequent alkylation using dimethyl sulfate forming the desired compound.
Neostigmine shows notable UV/VIS absorption at 261 nm, 267 nm, and 225 nm.
Neostigmine's H NMR Spectroscopy reveals shifts at: 7.8, 7.7, 7.4, 7.4, 3.8, and 3.1 parts per milli…
History
Neostigmine was first synthesized by Aeschlimann and Reinert in 1931 and was patented by Aeschlimann in 1933.
Neostigmine is made by first reacting 3-dimethylaminophenol with N-dimethylcarbamoyl chloride, which forms a dimethylcarbamate. Next, that product is alkylated using dimethyl sulfate, which forms neostigmine.
External links
• "Neostigmine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
• "Neostigmine methylsulfate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
• "Neostigmine bromide". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.