
How does water affect the concentration gradient?
Why do solutes move down the concentration gradient?
What is the effect of potassium on the neuron?
How can substances be moved against concentration gradients?
What is the process of ATP synthase?
Why do cells have ion gates?
Why do cells use concentration gradients?
See 4 more
About this website
Does osmosis move against concentration gradient?
Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a more concentrated solution, up a concentration gradient. This equalizes concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
Does osmosis go to higher or lower concentrations?
In osmosis, water moves from areas of low concentration of solute to areas of high concentration of solute.
Which process moves up a concentration gradient?
The process that uses proteins to move molecules against their concentration gradient is active transport. During active transport, molecules are moved from a low concentration to a high concentration, against their concentration gradient. This process requires energy, which is supplied by ATP.
How does osmosis relate to concentration gradient?
Osmosis occurs according to the concentration gradient of water across the membrane, which is inversely proportional to the concentration of solutes. Osmosis occurs until the concentration gradient of water goes to zero or until the hydrostatic pressure of the water balances the osmotic pressure.
Which statement about osmosis is correct?
Answer and Explanation: The statement that is true about osmosis is d. The greater the osmotic pressure of a solution, the greater the tendency for water to move into the solution.
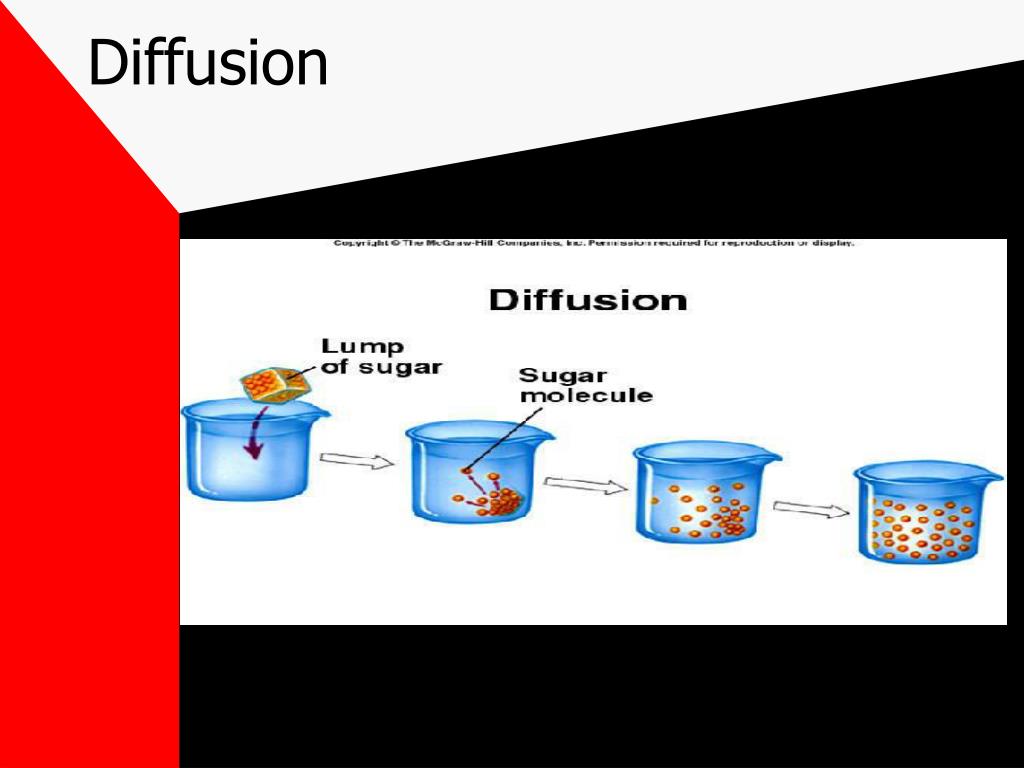
Does diffusion go from high to low concentration?
In the process of diffusion, a substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until its concentration becomes equal throughout a space.
What is difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Osmosis can only function in a liquid medium, but diffusion can occur in all three mediums (solid, liquid and gas). Furthermore, osmosis requires a semi-permeable membrane, while diffusion does not. The intake of water in plants is an example of osmosis.
What moves from low to high concentration?
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower concentration solution (i.e., higher concentration of water) to an area of higher concentration solution (i.e., lower concentration of water). Water moves into and out of cells by osmosis.
What is moving down a concentration gradient?
Moving down the concentration gradient means that a molecule moves from a high concentration to a low concentration. This occurs during passive transport and does not require energy. For example, during diffusion molecule move directly across the membrane from a high to low concentration without using energy.
Why does water move from high to low concentration?
The process by which water particles move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane is called osmosis, but movement of water particles across the concentration gradient ie., from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration requires ...
Why does the rate of osmosis increase with concentration?
Increasing the concentration of solute reduces the space available for water molecules, which reduces their numbers. This in turn increases the tendency of the water to flow into that side from the other side.
What is higher concentration and lower concentration?
Here,Concentration mean amount of substance (solute) in a solvent or solution.Solution which contain more solute is highly concentrated solution while less solute,low concentration.
Why does a higher concentration increase the rate of osmosis?
Increasing the concentration of solute reduces the space available for water molecules, which reduces their numbers. This in turn increases the tendency of the water to flow into that side from the other side.
Does osmotic pressure increase with concentration?
Osmotic pressure is affected by concentration and temperature. Concentration of solute and temperature each affect the amount of pressure created by the movement of water across a membrane. Higher concentrations and higher temperatures increase osmotic pressure.
What is difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Osmosis only allows solvent molecules to move freely, but diffusion allows both solvent and solute molecules to move freely. 4. Osmosis happens when molecules move from higher to lower concentrations, but diffusion happens when it is reversed.
Is reverse osmosis high to low?
Osmosis is water moving through a semipermeable membrane from lower to higher concentrations. Reverse osmosis, also called ultrafiltration, is water moving through a semipermeable membrane from higher to lower concentrations.
Concentration gradient | definition of concentration gradient by ...
concentration gradient: a solution in which the concentration (density) of a solute increases in a continuous fashion from top to bottom, or end to end, of a container (for example, the centrifuge tube in density-gradient centrifugation). Synonym(s): concentration gradient
Concentration Gradient - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Exercise 10.1 Concentration Gradients (a) Make a mathematical model to describe the diffusion of a solute (call it’s concentration u) in water through a permeable membrane idealized as a cross section of a tube (perhaps an idealized blood vessel) with one closed end.Suppose the tube radius is a, its length is L, and the membrane is placed at a distance pL (for some 0 < p < 1) from the open ...
Concentration gradient Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com
Concentration gradient definition, the gradual difference in concentration of a dissolved substance in a solution between a region of high density and one of lower density. See more.
Concentration Gradient: Examples - Study.com
Learn the definition of a concentration gradient and read about different types of diffusion. Explore real world examples of concentration...
What is the principle of diffusion in osmosis?
A principle of diffusion is that the molecules move around and will spread evenly throughout the medium if they can.
How does diffusion work?
A principle of diffusion is that the molecules move around and will spread evenly throughout the medium if they can. However, only the material capable of getting through the membrane will diffuse through it. In this example, the solute cannot diffuse through the membrane, but the water can. Water has a concentration gradient in this system. Therefore, water will diffuse down its concentration gradient, crossing the membrane to the side where it is less concentrated. This diffusion of water through the membrane— osmosis —will continue until the concentration gradient of water goes to zero. Osmosis proceeds constantly in living systems.
What is hypotonic water?
In a hypotonic solution, such as tap water, the extracellular fluid has a lower concentration of solutes than the fluid inside the cell, and water enters the cell.
What is the process of transporting water through a semipermeable membrane?
Passive Transport: Osmosis. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane according to the concentration gradient of water across the membrane. Whereas diffusion transports material across membranes and within cells, osmosis transports only water across a membrane and the membrane limits the diffusion of solutes in the water.
What is the measure of the tonicity of a solution?
The measure of the tonicity of a solution, or the total amount of solutes dissolved in a specific amount of solution, is called its osmolarity. Three terms—hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic—are used to relate the osmolarity of a cell to the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid that contains the cells.
What happens when a cell is hypertonic?
In a hypertonic solution (the prefix hyper – refers to the extracellular fluid having a higher concentration of solutes than the cell’s cytoplasm), the fluid contains less water than the cell does , such as seawater. Because the cell has a lower concentration of solutes, the water will leave the cell. In effect, the solute is drawing the water out of the cell. This may cause an animal cell to shrivel, or crenate.
Why does water leave the cell?
Because the cell has a lower concentration of solutes, the water will leave the cell. In effect, the solute is drawing the water out of the cell. This may cause an animal cell to shrivel, or crenate. In an isotonic solution, the extracellular fluid has the same osmolarity as the cell.
What does it mean to move against a concentration gradient?
Moving against a concentration gradient means that the substance is moving from a low concentration to a high concentration. Moving down (descending) a concentration gradient means ...
What is the difference between facilitated diffusion and active transport?
The difference between facilitated diffusion and active transport is that facilitated distribution occurs down a concentration gradient and active transport occurs against a concentration gradient. I understand that, as a result of these differences, active transport uses ATP so that it can bind to the carrier protein, however I don't know what is meant by going against a concentration gradient or down a concentration gradient.
What happens during osmosis?
Osmosis, the diffusion of water, occurs to reach equilibrium. The sugar molecules were not able to diffuse through the semi permeable membrane, therefore the number did not change
Why do isotonic solutions pass in and out of the semi-permeable membrane?
Isotonic solutions want an equal amount of molecules on both sides. So, the molecules pass in and out of the semi-permeable membrane in order to maintain a balance.
Why does water decrease in a hypertonic solution?
It decreases because water is leaving the cell and going to the hypertonic solution where there is less water than solute.
What happens when water comes into an animal cell?
Osmosis will occur and water will come into the cell, possibly causing the animal cell to lyse (burst).
Why is the membrane in a U-shaped tube similar to the membrane in a cell?
The membrane in the U-shaped tube is similar to the membrane in a cell because it is semi-permeable, letting only certain solutes pass into and out of the cell.
Do molecules come in and out of the cell?
Yes because the molecules never stop moving, so they come in and out of the cell maintaining equilibrium.
How does water affect the concentration gradient?
So, the concentration gradient can be alleviated by adding water to a highly concentrated membrane compart ment (or cell ). Organisms that need to move a substance in or out of their cells may use the movement of one substance down its concentration gradient to transport ...
Why do solutes move down the concentration gradient?
Over time, solutes always move down their concentration gradient to “try” to produce an equal concentration throughout the whole solution. So, the concentration gradient above would eventually disappear as the ions of salt diffused throughout the entire tank.
What is the effect of potassium on the neuron?
Neurons and the Sodium/Potassium Pump. Neurons spend a huge amount of energy – about 20-25% of all the body’s calories, in humans – pumping potassium into their cells, and sodium out. The result is an extremely high concentration of potassium inside of nerve cells and a very high concentration of sodium outside. Since potassium.
How can substances be moved against concentration gradients?
A is correct. Substances can only be moved against their concentration gradients by expending energy. In this case, cells break down glucose and expend huge amounts of ATP to make the sodium/potassium concentration gradient possible. In the process, they move the larger system toward randomness, in keeping with the laws of thermodynamics.
What is the process of ATP synthase?
ATP synthase – the protein that produces ATP – relies on a concentration gradient of hydrogen ions. As the ions pass through ATP synthase to cross the membrane and alleviate the gradient, ATP synthase transfers the energy into adding a phosphate group to ADP, thereby storing the energy in the newly formed bond.
Why do cells have ion gates?
The sodium/potassium concentration differences are so strong that the ions “want” to instantly rush out of the cell. Because ions are electrically charged, this actually changes the electrical charge of the cell.
Why do cells use concentration gradients?
Concentration gradients are used by many cells to complete a wide variety of tasks. In fact, there is energy stored in a concentration gradient because the molecules want to reach equilibrium. So, this energy can be utilized to accomplish tasks.
