
What does oxalic acid do to your body?
Oxalic acid binds to minerals and reduces your absorption of both iron and calcium. Oxalic acid is also implicated in kidney stones. Garden greens tend to have high levels of this iron-binding substance.
What foods inhibit iron absorption in humans?
Animal proteins such as casein, whey, egg whites, and proteins from plants (soy protein) have been shown to inhibit iron absorption in humans. Oxalic acid is found in spinach, chard, beans, and nuts and acts to bind and inhibit iron absorption.
Does tea affect the absorption of iron from food?
If you consume large amounts of tea with your meals, you may not be receiving an adequate amount of iron from those foods, according to the website VeganHealth.org. Tea contains oxalates -- oxalic acid compounds that impair the absorption of non-heme iron.
What are the inhibitors and enhancers of iron absorption?
1 Inhibitors of iron absorption include phytate, which is a compound found in plant-based diets that demonstrate a... 2 Enhancers of iron absorption are dominated by the effect of ascorbic acid (vitamin C), which can overcome the effects of... More ...
Do oxalates inhibit iron absorption?
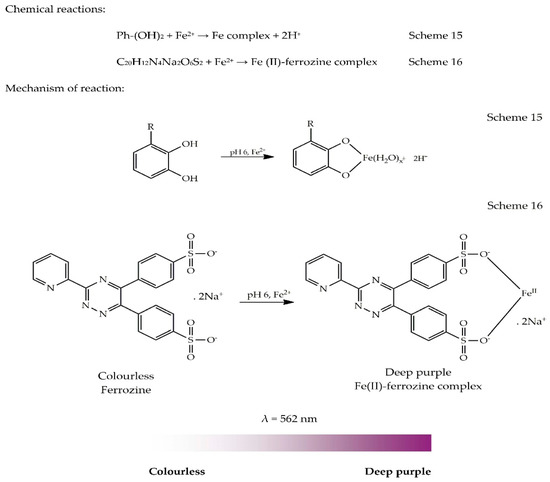
Oxalates impair the absorption of nonheme iron. Oxalates are compounds derived from oxalic acid and found in foods such as spinach, kale, beets, nuts, chocolate, tea, wheat bran, rhubarb, strawberries and herbs such as oregano, basil, and parsley.
What blocks the absorption of iron?
Animal proteins such as casein, whey, egg whites, and proteins from plants (soy protein) have been shown to inhibit iron absorption in humans. Oxalic acid is found in spinach, chard, beans, and nuts and acts to bind and inhibit iron absorption.
What can oxalic acid inhibit the absorption of?
Reduced mineral absorption. Oxalates block the absorption of calcium from the spinach but not from other sources like milk. Eating foods with fiber may further make it hard for the body to take in necessary nutrients.
Do oxalates bind to iron?
Indeed, oxalates can bind with both calcium and iron, partially limiting the absorption of these minerals during a meal.
What causes poor iron absorption?
Your body can't absorb iron. Conditions like celiac disease, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn's disease can make it harder for your intestines to absorb iron. Surgery such as gastric bypass that removes part of your intestines, and medicines used to lower stomach acid can also affect your body's ability to absorb iron.
Does turmeric inhibit iron absorption?
Turmeric is among the spices known to inhibit iron absorption by 20%-90% in humans, reducing iron absorption in a dose-dependent manner [10]. The stoichiometric qualities of turmeric indicate it could bind nearly all absorbable iron and cause iron deficiency, and it does so in mice [3].
What minerals do oxalates block?
Oxalates in green leafy vegetables, tea, beans, nuts, beets—can bind to calcium and prevent it from being absorbed. Phytates (phytic acid) in whole grains, seeds, legumes, some nuts—can decrease the absorption of iron, zinc, magnesium, and calcium.
Can your body absorb iron from spinach?
The iron absorption data are shown in Tables 2 and 3. Geometric mean iron absorption in study I was 8.4% from spinach and 11.0% from kale (absorption ratio A/B: 0.76, P=0.19). Geometric mean iron absorption in study II was 8.0% from spinach and 11.2% from kale plus OA (absorption ratio A/C: 0.72, P=0.16).
What does oxalic acid do to the body?
When oxalate levels are high, there's a greater chance it will bind to calcium, forming kidney stones. Because oxalates bind to minerals like calcium, they can prevent your body from absorbing beneficial nutrients in your digestive tract .
What enhances iron absorption?
vitamin CConsuming heme iron sources alongside non-heme sources will improve the absorption of non-heme iron. Take vitamin C with your source of iron. Vitamin C increases absorption of both heme and non-heme iron absorption. Four ounces (1/2 cup) of orange juice is enough to increase iron absorption.
How can I absorb iron better?
You can enhance your body's absorption of iron by drinking citrus juice or eating other foods rich in vitamin C at the same time that you eat high-iron foods. Vitamin C in citrus juices, like orange juice, helps your body to better absorb dietary iron.
Does oatmeal block iron absorption?
The present studies showed that oat bran and oat porridge markedly inhibited the absorption of non-haem iron. The inhibition can be explained by the high phytate content of oat products.
Does magnesium inhibit iron absorption?
Although in vitro studies show that iron absorption can be inhibited by magnesium laxatives such as magnesium oxide, taking oral iron supplements with magnesium laxatives is not considered a clinical problem.
How can I absorb iron better?
You can enhance your body's absorption of iron by drinking citrus juice or eating other foods rich in vitamin C at the same time that you eat high-iron foods. Vitamin C in citrus juices, like orange juice, helps your body to better absorb dietary iron.
Does vitamin C inhibit iron absorption?
Ascorbic acid is a powerful enhancer of nonheme iron absorption and can reverse the inhibiting effect of such substances as tea and calcium/phosphate. Its influence may be less pronounced in meals of high iron availability--those containing meat, fish, or poultry.
Do eggs stop iron absorption?
Eggs. Eggs block iron absorption because they contain phosvitin, a protein compound that binds iron molecules together and prevents the body from absorbing iron from foods. One boiled egg can reduce iron absorption by as much as 28 percent, per the Iron Disorders Institute.
What is oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid (OA) is a common constituent of plant foods such as green leafy vegetables, rhubarb, parsley, beetroot, carrots, potatoes, cocoa and tea ( Zarembski and Hodgkinson, 1962; Chai and Liebman, 2005 ). Concentrations vary depending on season, variety, age, soil conditions, maturity and part of the plant ( Kasidas and Rose, 1980 ). The largest amounts, up to 1–2 g/100 g wet weight, are found in rhubarb ( Honow and Hesse, 2002) and spinach, mangold and purslane ( Chai and Liebman, 2005 ). OA may be present in foods as insoluble calcium or magnesium oxalate crystals or as soluble sodium or potassium oxalate. Relative contributions of these two fractions to total OA seem to vary widely within and between plant species. Zarembski and Hodgkinson analysed OA contents of 80 food items commonly used in English homes and hospitals and calculated the average daily intake to be 118 mg in the household setting and to range between 70 and 150 mg in six hospital diets ( Zarembski and Hodgkinson, 1962 ). This compares to results from a small study including five subjects, in which mean daily OA intake was estimated to be 152 mg (range 44–351 mg) ( Holmes and Kennedy, 2000 ). Additionally, the human body is itself able to synthesize OA, with ascorbic acid and glycine being the major precursors ( Hodgkinson and Zarembski, 1968 ).
Does iron absorption decrease with OA?
The reason why OA has no influence on iron absorption but decreases absorption of calcium ( Heaney et al., 1988; Heaney and Weaver, 1989 ), magnesium ( Bohn, 2003) and zinc ( Kelsay and Prather, 1983) is presumably related to the respective solubility and complex stability constants ( Table 4 ). The poor water solubility of calcium and zinc oxalate (<1 mg/100 ml) could explain the inhibitory effect of oxalate on zinc and calcium absorption. Magnesium oxalate is more soluble but the solubility is still only 70 mg/100 ml. Both ferrous and ferric iron form stable oxalate complexes ( KS >4.7); however, ferrous oxalate is rather insoluble (22 mg/100 ml) compared to ferric oxalate which is described as very soluble ( Hodgkinson and Zarembski, 1968 ). Presumably, most of the meal iron in the present study was in the ferric form in the gastric and duodenal phases of digestion. It is possible that when iron is in the ferrous form, as in meals high in ascorbic acid, OA may inhibit iron absorption by forming the more insoluble ferrous oxalate. It could also be speculated that in the present study, meal iron in the gastrointestinal tract was equally in the ferrous and ferric form and whereas OA increased the absorption of ferric iron, it reduced the absorption of ferrous iron, so the net effect would be no influence on iron absorption. Some support to this last theory is given by Caco-2 cell experiments, which have reported a fivefold enhancing effect of OA on the uptake of ferric iron but a 20% decrease in the uptake of ferrous iron, both given as the pure iron salts ( Salovaara et al., 2002 ).
Does potassium oxalate affect iron absorption?
Potassium oxalate did not influence iron absorption in humans from a kale meal and our findings strongly suggest that OA in fruits and vegetables is of minor relevance in iron nutrition.
Does kale affect iron absorption?
The added OA (1.26 g) therefore did not influence iron absorption.
Does spinach lower iron?
In our study, there was a 24% lower iron absorption from spinach than from kale which failed to reach statistical significance. It would be expected from the literature that spinach inhibits iron absorption ( Gillooly et al., 1983; Brune et al., 1989 ), most likely owing to the high polyphenol ( Brune et al., 1989) and calcium ( Hallberg et al., 1991) contents, which were twofold and tenfold higher, respectively, in the spinach meals compared to the kale meals used in the present study. The lack of statistical significance can be explained by the study design which aimed to detect a 30% difference at 80% power. We would like to emphasize that although most subjects had lower iron absorption from spinach than from kale, two subjects in each study had much lower iron absorption from kale than from spinach. Owing to the higher variability in iron absorption values than we observe normally in comparable studies with comparable subject dropout numbers, we would have needed a 42–49% reduction in iron absorption from spinach compared to kale meals to reach statistical significance.
What are some ways to reduce iron absorption?
Eggs and Iron. Eggs are a common inhibitor of iron absorption. Eggs contain phosvitin, a protein compound that binds iron molecules together and prevents the body from absorbing iron from foods. According to the Iron Disorders Institute, one boiled egg can reduce iron absorption by as much as 28 percent. Advertisement.
What is the role of iron in the body?
Iron, an essential vitamin, is responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body, according to the National Institutes of Health. There are two types of dietary iron: heme iron and non-heme iron.
Why is iron deficiency anemia common?
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when red blood cells do not contain an adequate amount of iron due to pregnancy, blood loss, a diet low in iron, or poor absorption of iron by the body. Knowing what foods inhibit iron can help keep the body functioning efficiently.
What foods contain phenolic acid?
Phenolic acid can also be found in apples, peppermint and some herbal teas, spices, walnuts, blackberries, raspberries and blueberries. It is important to note that these foods should not be consumed two hours prior to, or following, your main iron-rich meal. Advertisement.
Does tea help with iron?
If you consume large amounts of tea with your meals, you may not be receiving an adequate amount of iron from those foods, according to the website VeganHealth.org. Tea contains oxalates — oxalic acid compounds that impair the absorption of non-heme iron. Oxalates can also be found in spinach, kale, beets, nuts, chocolate, wheat bran, rhubarb, strawberries and herbs such as oregano, basil and parsley.
Does milk affect iron absorption?
Calcium-Rich Foods. Milk can also work as an inhibitor of iron absorption, potentially affecting your iron levels. Milk contains calcium, an essential mineral and the only known substance to inhibit absorption of both non-heme and heme iron. One cup of milk contains approximately 300 mg of calcium. Calcium has little or no effect on iron absorption ...
Does walnut help absorb iron?
Foods High in Phytates. Walnuts can reduce the amount of iron your body absorbs from iron-rich foods. Walnuts contain phytates — compounds found in soy protein and fiber. Even low levels of phytates have a strong inhibitory effect on your body's ability to absorb iron from foods.
Where does iron absorption occur?
The absorption of most dietary iron occurs in the duodenum and proximal jejunum and depends heavily on the physical state of the iron atom. At physiological pH, iron exists in the oxidized, ferric (Fe3+) state. To be absorbed, iron must be in the ferrous (Fe2+) state or bound by a protein such as heme.
Why is iron not absorbed in the body?
One reason for the lack of adequate iron absorption is that upon exposure to oxygen, iron forms highly insoluble oxides, which are unavailable for absorption in the human gastrointestinal tract. Human enterocytes contain apical membrane-bound enzymes whose activity can be regulated and which function to reduce insoluble ferric (Fe3+) to absorbable ferrous (Fe2+) ions.
What are the two types of absorbable iron?
There are two types of absorbable dietary iron: heme and non-heme iron.
What is the mechanism of iron excretion?
The mechanism of iron excretion is an unregulated process arrived at through loss in sweat, menstruation, shedding of hair and skin cells, and rapid turnover and excretion of enterocytes. In the human body, iron exists mainly in erythrocytes as the heme compound hemoglobin (approximately 2 g of iron in men and 1.5 g in women), ...
Which molecule has ferroxidase activity?
Monomers of the ferritin molecule have ferroxidase activity (Fe3+ ↔ Fe2+), allowing the mobilization of Fe2+ ions out of the ferrihydrite mineral lattice structure enabling its subsequent efflux out of the enterocyte via ferroportin and into circulation across the basolateral membrane of the enterocyte.
Which protein is the only efflux route of cellular iron?
The transmembrane protein ferroportin is the only efflux route of cellular iron and is regulated almost exclusively by hepcidin levels. High levels of iron, inflammatory cytokines, and oxygen lead to increased levels of the peptide hormone hepcidin.
What is iron found in?
Iron is also found bound to proteins (hemoprotein) and non-heme enzymes involved in oxidation-reduction reactions and the transfer of electrons (cytochromes and catalase) .[1][2][3] Iron is an essential element of various metabolic processes in humans, including DNA synthesis, electron transport, and oxygen transport.
Should You Worry Or Bother?
The oxalic acid obsession is most important for people relying on oxalate foods for their mineral content or people prone to kidney stones. We took care to reduce oxalic acid in our green soups because we were making gallons of concentrated greenness. Some people have raw green smoothies every day with no issue at all. If that is you — fantastic.
How Do You Ferment Vegetable Juice or Vegetables?
You can ferment your juice or vegetables using a vegetable starter like Caldwell, saving a start from your first batch to inoculate subsequent batches.
Why is oxalic acid important?
The oxalic acid obsession is most important for people relying on oxalate foods for their mineral content or people prone to kidney stones. We took care to reduce oxalic acid in our green soups because we were making gallons of concentrated greenness. Some people have raw green smoothies every day with no issue at all. If that is you — fantastic. There is so much goodness in greens any way that you prepare them, that we all really need to find more ways to eat them that meet our own specific circumstances. Fermentation is just one possibility.
Does fermentation reduce oxalic acid?
As a result, the evidence suggests that both fermentation and boiling are fairly effective strategies to reduce oxalic acid in your food. Of course, the key benefit of fermentation is that the food can stay raw, giving you all of the benefits of rawness with the mineral binders.
What foods inhibit iron absorption?
Low Iron Foods With Iron Inhibitors. This category of food contains primarily beverages: milk, coffee, black tea, and red wine. These beverages typically offer minimal iron but will actually inhibit your absorption of iron in foods you eat in the same meal. Breakfast cereal is a great example: many cereal manufacturers pack your processed breakfast ...
How to get rid of oxalic acid in spinach?
For vegetables high in oxalic acid, your best strategy is to boil them and discard the boiling water. (I describe the research in more detail here as it relates to calcium but it applies to iron as well.) Eating foods high in vitamin C along with your vegetables may help as well, especially if you are boiling all of the vitamin C out of your spinach.
How to reduce phytic acid in food?
The best way to reduce phytic acid in food comes down to one word: soak and ferment. If you place the food in warm water for hours (or even for a day), the content of phytic acid will decrease or may disappear entirely. There are some exceptions for which it is difficult to remove the phytic acid (notably, soy and corn which I will leave to other discussions). For much of the rest of the food world, you can improve the phytic acid reduction by soaking a ground version of the food (cracked or ground grains, chopped nuts). You can also improve your iron absorption by eating these foods with high vitamin C foods such as tomatoes, peppers, and oranges. There are more tricks to improving your iron absorption from high phytic acid food that I will add to this website. The tricks and exceptions are described in detail in my digital books on iron rich foods and phytic acid.
What foods have iron inhibitors?
High Iron Foods With Iron Inhibitors. In this category, we have high iron classics: spinach, soybeans, and corn. The iron in vegetables is blocked primarily by oxalic acid. Phytic acid is the culprit in grains, legumes, nut, and seeds.
Why is iron an interesting mineral?
Iron inhibitors: Foods that reduce your iron absorption. Iron is an interesting mineral because other foods can enhance or inhibit our iron absorption. It is not enough to look at the iron content of food on a label, we need to look at our whole meal to get a sense of how iron-rich the meal is.
Can you drink milk with iron?
For this group of inhibitors, it is best to avoid consuming them with your iron-rich meal. I realize you are not going to give up your coffee, but you can plan an iron-rich dinner well after your early afternoon cup of coffee. You may also rely on milk for calcium like I do. If you are like me, drink the milk a couple of hours before or after your iron-rich meal. I give my son warm milk at night as a sleep aid and a calcium boost rolled into one.
Can you eat spinach with iron?
I get some flack from spinach lovers over this point and the fact is that I am a big fan of raw spinach salads but if you need the spinach for iron, your best strategy is to boil it and eat it mushy.
