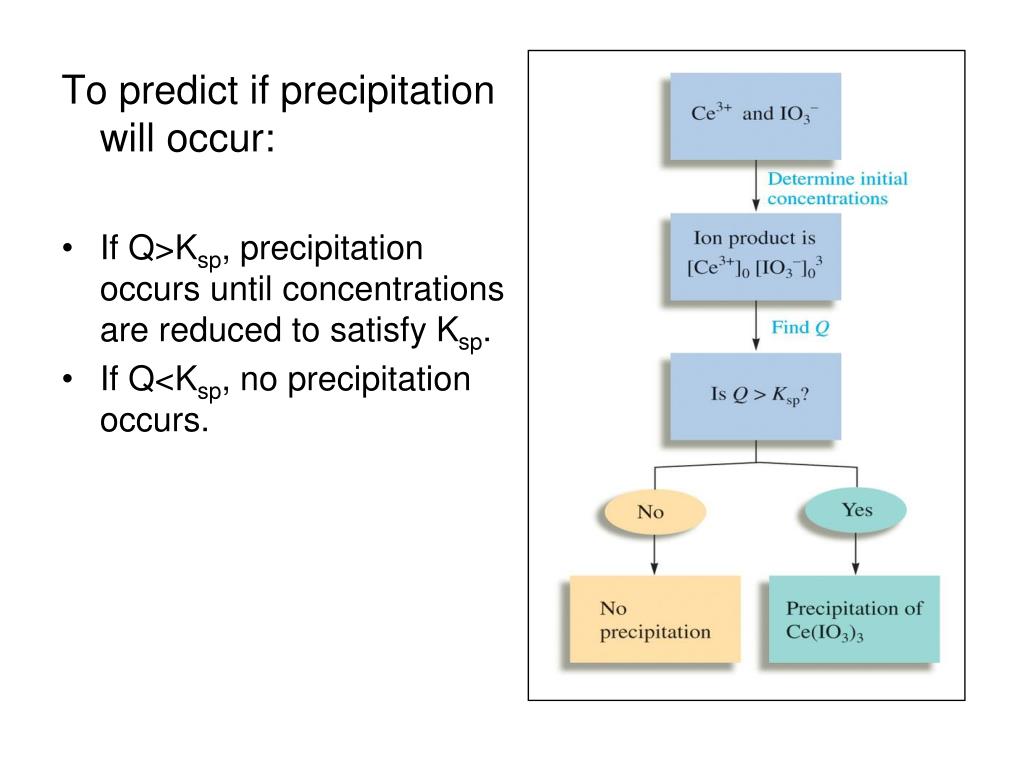
If Q > Ksp, a precipitate will form. Note that precipitation may not happen immediately if Q is equal to or greater than Ksp. A solution could be supersaturated for some time until precipitation occurs. Click to see full answer. People also ask, will a precipitate form? The solid is called a precipitate.
Full Answer
What is the relationship between precipitate forming and KSP?
Apr 13, 2020 · If Q = Ksp, a precipitate will form. If Q > Ksp, a precipitate will form. Note that precipitation may not happen immediately if Q is equal to or greater than Ksp. A solution could be supersaturated for some time until precipitation occurs. Click to see full answer. People also ask, will a precipitate form? The solid is called a precipitate.
What is a precipitate and how does it form?
Apr 25, 2018 · Explanation: 1) If Solubility product is larger than the ionic product then no precipitate will form on adding more solute because unsaturated solution is formed. 2) If Solubility product is smaller than the ionic product then excess solute will precipitate out because of the formation of super saturated solution. 3) If Solubility product is equal to the ionic …
What are the points for Ksp of an ionic compound?
We can compare Q vs Ksp to predict whether a precipitate forms. Q= K sp Q< K sp Q> K sp Saturated solution Unsaturated solution No precipitate Supersaturated solution Precipitate will form Compare Q spvs K sp. Ag 2CO 3(s)2Ag+(aq)+ CO 3 2-(aq) K sp= [Ag+]2[CO 3 Q = [Ag+]2[CO2] 2-] before equilbrium after equilbrium
What will happen if q > KSP?
Feb 09, 2021 · When we know the K s p value of a solute, we can figure out if a precipitate will occur if a solution of its ions is mixed. Below are the two rules that determine the formation of a precipitate. Ionic product > K s p then precipitation will occur Ionic product < K s p then precipitation will not occur To Understand the Common Ion Effect

How do you know if a precipitate forms KSP?
0:075:15Determining Whether a Precipitate Will Form (Solubility Equilibrium #3)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIf the queue again is greater than the KSP. Then you know that a precipitate will form if the queueMoreIf the queue again is greater than the KSP. Then you know that a precipitate will form if the queue is less than the KSP you know that it's going to dissolve.
Will a precipitate form Q vs KSP?
12:1626:47Solubility Equilibrium: Will a Precipitate form and more - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou do see a precipitate Q is equal to KSP you're at equilibrium the solution is saturated. There isMoreYou do see a precipitate Q is equal to KSP you're at equilibrium the solution is saturated. There is no precipitate if Q is less than KSP.
Which KSP will precipitate first?
2:146:58Which Precipitates First? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd what we find is that the KSP for barium chromate it's 1.2 times 10 to the minus 10 while the KSPMoreAnd what we find is that the KSP for barium chromate it's 1.2 times 10 to the minus 10 while the KSP for strontium chromate is 2.2 times 10 to the minus.
What is the difference between Q and Ksp?
The key difference between Ksp and Qsp is that Ksp indicates the solubility of a substance whereas Qsp indicates the current state of a solution. The solubility product is the product of concentrations of ionic species present in a solution when a substance is dissolved in a solvent such as water.Mar 29, 2018
How do you know if a precipitate forms?
If the rules state that an ion is soluble, then it remains in its aqueous ion form. If an ion is insoluble based on the solubility rules, then it forms a solid with an ion from the other reactant. If all the ions in a reaction are shown to be soluble, then no precipitation reaction occurs.Dec 10, 2021
How do you determine if a precipitate will form without Ksp?
If the value of the ion product is less than the value of the Ksp, then the solution will remain unsaturated. No precipitate will form because the concentrations are not high enough to begin the precipitation process. If the value of the ion product is greater than the value of the Ksp, then a precipitate will form.
How is molar solubility related to Ksp?
The relation between solubility and the solubility product constants is that one can be used to find the other. In other words, there is a relationship between the solute's molarity and the solubility of the ions because Ksp is literally the product of the solubility of each ion in moles per liter.
How do you tell if a precipitate will form when mixing two solutions?
If the rules state that an ion is soluble, then it remains in its aqueous ion form. If an ion is insoluble based on the solubility rules, then it forms a solid with an ion from the other reactant. If all the ions in a reaction are shown to be soluble, then no precipitation reaction occurs.Dec 3, 2021
What is entropy in chemistry?
Entropy is a measure of energy dispersal in a chemical system. Energy tends to be dispersed over a larger number of “ quantum states” in a system of molecules rather than dispered over fewer states. Increasing the volume decreases energy level spacing increasing entropy by populating more.
What is internal energy?
Microscopic: Internal energy is distributed over all the quantized translational, vibronic and rotational energy states in molecules and atoms. The quantized energy levels are of different energy. Rotational gaps are on the order of the energy of microwave radiation. Vibrational spacing is higher in energy (IR).
What is Henry's law?
Henry's law states that the solubility of a gas is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas. Henry’s law is written as p = kc, where. p is the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid. k is Henry’s law constant. c is the concentration of gas in the liquid.
Is a solvent more soluble than a particle?
Generally, solutes with smaller molecules are more soluble than ones with molecules particles. It’s easier for the solvent to surround smaller molecules, so those molecules can be dissolved faster than larger molecules.
What is the difference between k and c?
k is Henry’s law constant. c is the concentration of gas in the liquid. Henry’s law shows that, as partial pressure decreases, the concentration of gas in the liquid also decreases, which in turn decreases solubility. So less pressure results in less solubility, and more pressure results in more solubility. You can see Henry’s law in action ...
What is the common ion effect?
The common ion effect states that when two solutions that share a common ion are mixed, the solute with the smaller K s p value will precipitate first. For example, say BiOCl and CuCl are added to a solution.
What is the solubility product constant?
Although some chemical compounds are classified as insoluble, most "insoluble" compounds are actually very slightly soluble. The solubility process reaches a dynamic equilibrium described by an equilibrium constant. This equilibrium constant is called the solubility product constant, and is given the symbol Ksp. The solubility product can be calculated given a compound's solubility. The solubility constant can be used to calculate whether a precipitate will form given the concentrations of ionic species. Compounds having a common ion but different solubility constants can be separated by fractional precipitation.
How does pH affect solubility?
pH and Solubility. If one of the ions appearing in a solubility equilibrium is the conjugate base of a weak acid, then pH can affect the concentrations of ions in the solubility equilibrium. The magnitude of this effect can be estimated from the solubility product. Example: Consider two slightly soluble salts, ...
Can metal ions react with ligands?
In addition to forming precipitates, some metal ions in solution can react with ligands to form soluble complex ions . The metal ions, ligands, and complex ions are in dynamic equilibrium described by a formation constant. The solubility of normally insoluble metal salts can be increased by the formation of complex ions.
What is fractional precipitation?
Fractional precipitation is a technique that separates ions from solution based on their different solubilities. For example, consider an aqueous solution that contains initially Ba 2+ and Sr 2+ ions. Suppose that an aqueous solution of potassium chromate (K 2 CrO 4 ) is added slowly. Two precipitates can form: BaCrO 4 with Ksp of 1.2 x 10 -9 M , and SrCrO 4 with Ksp of 3.5 x 10 -5 M. (Since all potassium salts are soluble, the potassium ion of the aqueous solution of K 2 CrO 4 is a spectator ion and does not need to be considered in the solubility equilibrium.) Because Ksp for SrCrO 4 is smaller than for BaCrO 4, SrCrO 4 will precipitate first. If K 2 CrO 4 is added to the solution so that the ion product for BaCrO4 is not exceeded, then only SrCrO 4 will precipitate. The resulting solution can be filtered and the Sr 2+ isolated from the original solution as the chromate salt.
Solubility as an Equilibrium Process
When you were learning your solubility rules for ionic compounds dissolving in water at 25°C, you were probably taught that barium sulfate is insoluble.
Example : Calculating the solubility of an ionic compound (MA)
Question: Calculate how much silver bromide in moles will dissolve in 1 L of water at 25°C given K sp = 5.0 x 10 -13 at 25 o C.
Example : Calculating the solubility of an ionic compound (MA 2)
Question: Calculate how much strontium fluoride in moles per litre will dissolve in 1 L of water given K sp = 2.5 × 10 -9 at 25 o C.
Example : Deciding whether a precipitate will form
Question: Will a precipitate form if 25.0 mL of 1.4 × 10 -9 mol L -1 NaI and 35.0 mL of 7.9 × 10 -7 mol L -1 AgNO 3 are mixed?