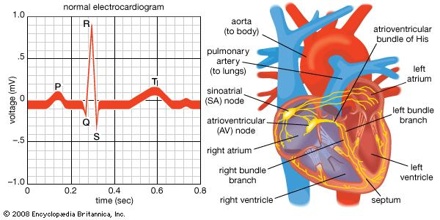
ECG can be normal in pulmonary embolism, and other recognised features of include sinus tachycardia
Tachycardia
A heart rhythm disorder with heartbeats faster than usual, greater than 100 beats per minute.
Which findings suggest pulmonary embolism?
transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiography may directly visualize embolized thrombi (right heart chambers or central pulmonary arteries) or show right heart hemodynamic changes that indirectly suggest pulmonary embolism.99indirect parameters such as unexplained right ventricular dilatation/dysfunction and marked tricuspid regurgitation, …
Is pulmonary embolism a deadly disease?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and potentially deadly form of venous thromboembolic disease. It is the third most common cause of cardiovascular death and is associated with multiple inherited and acquired risk factors as well as advanced age.
What are the risks for a pulmonary embolism?
- Older age (risk increases after age 40)
- Obesity ( body mass index [BMI] greater than 30kg/m 2)
- Recent surgery or injury (within 3 months)
- Use of estrogen-containing contraceptives (for example, birth control pills, rings,patches)
- Hormone replacement therapy (medical treatment in which hormones are given to reduce the effects of menopause)
Is autopsy a sure diagnosis of pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary thrombo-embolism (PTE) is a common cause of death but is frequently undetected by clinicians in spite of advanced diagnostic techniques. The autopsy has traditionally been used to identify the rate of PTE in hospital patients, but the decline in autopsy rates – especially in hospitals – has led to insufficient recent data from which to comment with confidence on the true rate of ...
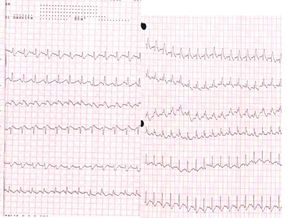
Why is pulmonary embolism so difficult to diagnose?
One of the main challenges in diagnosing a PE is that its symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness, are common in sev...
What tests do doctors use to diagnose pulmonary embolism?
A 2021 study suggests that computed tomographic pulmonary angiography is the “gold standard” test used to diagnose a PE. The screening combines a C...
Can I take an ECG at home?
There are a variety of at-home ECG monitors you can purchase. There are also portable monitors, such as a Holter monitor, that a doctor can prescri...
What are the changes in ECG in PE?
ECG changes in PE are related to: Dilation of the right atrium and right ventricle with consequent shift in the position of the heart. Right ventricular ischaemia. Increased stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system due to pain, anxiety and hypoxia.
What causes a cor pulmonale?
A similar spectrum of ECG changes may be seen with any cause of acute or chronic cor pulmonale (i.e. any disease that causes right ventricular strain / hypertrophy due to hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction).
What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
The main symptoms of pulmonary embolism are dyspnea, usually begin suddenly, and pleuritic chest pain. Pulmonary embolism may also present with pre-syncope or syncope, and in the most severe cases, with arterial hypotension and shock.
What is PE in electrocardiogram?
Electrocardiogram in Pulmonary Embolism. Acute pulmonary embolism (PE) is a relatively common medical emergency caused by occlusion of the pulmonary arteries. In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by a deep-vein thrombosis (DVT). The high effectiveness of the immediate treatment becomes vital early diagnosis, but sometimes it is difficult, ...
Can pulmonary embolism be suspected?
Pulmonary embolism should be suspected in patients with sudden dyspnea, chest pain or syncope, with predisposing factors. The electrocardiogram has an important role ruling out other diseases with similar symptoms ( acute myocardial infarction ). If the EKG changes previously described are present, suspicion of pulmonary embolism increases.
Is pulmonary embolism a DVT?
In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by a deep-vein thrombosis (DVT). The high effectiveness of the immediate treatment becomes vital early diagnosis, but sometimes it is difficult, because the clinical signs and symptoms are non-specific. Although the electrocardiogram in pulmonary embolism is not a test with high sensitivity ...
Is an electrocardiogram a sensitive test?
The electrocardiogram is not a sensitive test for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. In some cases appear certain changes that increase suspicion, helping in the diagnosis, but even in massive embolism, they are not always present 2.
Is pulmonary embolism a systemic thrombolytic therapy?
Pulmonary embolism without shock or hypotension often has better prognosis. Subcutaneous LMWH or fondaparinux is the treatment of choice. Systemic thrombolysis is not recommended in this patients. In patients with hemodynamic stability but with right ventricular dysfunction (intermediate-high-risk group) systemic thrombolytic therapy is indicated ...
What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms. The symptoms of pulmonary embolism are often non-specific, which include: Shortness of breath that is very severe and sudden. Chest pains that are sharp and get worse when breathing or coughing. Pink or foamy sputum.
Where does pulmonary embolism start?
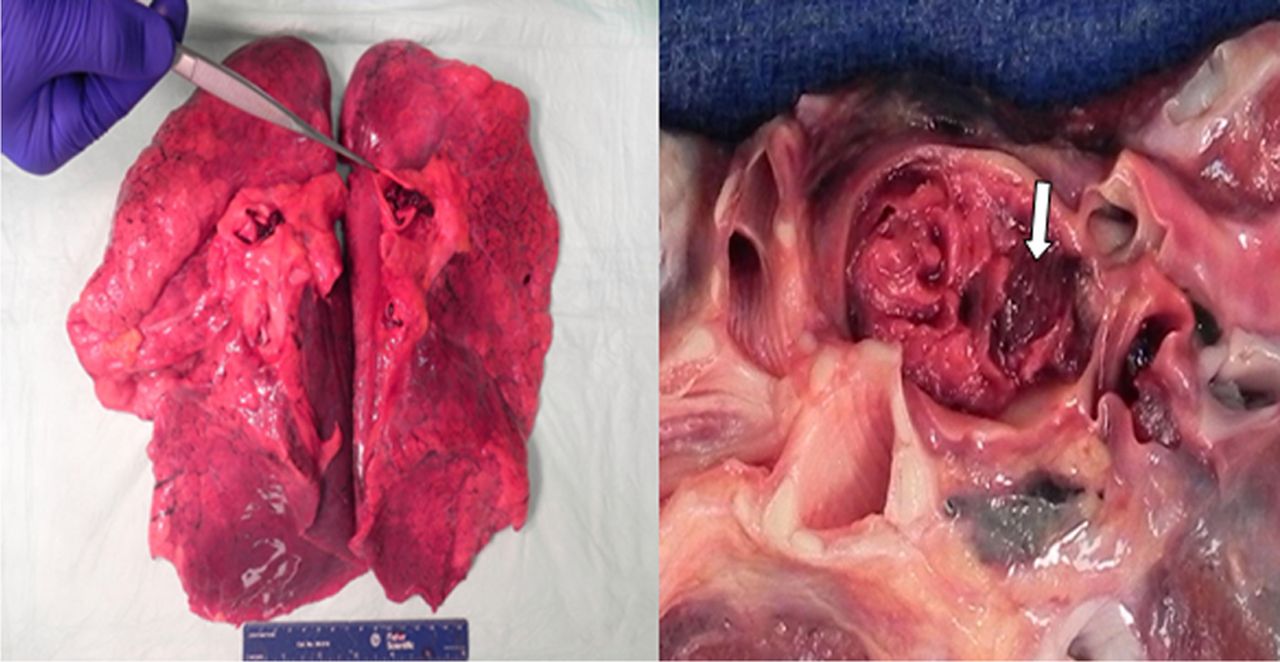
A pulmonary embolism is caused by a blood clot blocking one of the arteries in the lungs. This most often starts in one of the deep veins way down in the legs , which travels up into the smaller arteries in the lungs. Less commonly, clots can start out in the pelvic area or even the arms.
What causes a right ventricular strain pattern?
One of the causes is PE, but it can also be caused by congenital heart defects, hypertension, and heart disease. Right Ventricular Strain Pattern – This is an acute right heart syndrome that happens to around 34% of patients that have PE.
Can ECG be used to diagnose pulmonary embolism?
ECG fingdings can be very helpful in diagnosing Pulmonar y Embolism. A pulmonary embolism happens with a blood clot closes off one of the main arteries that sends blood back and forth between the heart and the lungs. When CT scans cannot effectively diagnose a pulmonary embolism, ECG can be very helpful if there are changes.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause a clot?
Tiny blood clots that start within a surface vein rarely cause blood clots. Other causes of blood clots and pulmonary embolism include infections, fat embolism, air bubbles in the blood, or tumors caused by cancer. Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms. The symptoms of pulmonary embolism are often non-specific, which include:
What are the symptoms of acute PE?
Symptoms suggestive of an acute PE include dyspnoea at rest or upon exertion, pleuritic chest pain, cough, orthopnoea, and calf or thigh pain or swelling. Signs include tachypnoea, tachycardia, rales, decreased breath sounds, an accentuated pulmonic component of the second heart sound and jugular venous distention.
How long does a massive PE last?
Massive PE results in hypotension, and should be considered if the patient has hypotension lasting more than 15 minutes or requiring inotropic support, with elevated central venous pressure that has no other attributable cause, or if hypotension is associated with profound bradycardia or pulselessness.
Can ECG be used to predict disease?
However, there is increasing interest in the prognostic use of ECG, as well as evidence to suggest that certain ECG findings can play a role in predicting which patients have a more complicated disease or worse prognosis , and hence require more invasive testing and earlier aggressive treatment. ECG features.
Is PE considered low risk?
Patients without the above clinical features of adverse prognosis are considered to have low-risk PE. Management of patients with PE depends on the severity of the disease. After resuscitation and stabilisation of the patient, anticoagulation therapy should be started for all eligible patients.
Does submassive PE cause hypotension?
In submassive PE, patients do not have hypotension; however, there is evidence of right ventricular strain in the form of right ventricular dilatation, elevation of serum brain natriuretic peptide, ECG changes or myocardial necrosis. This population of patients is at increased risk for adverse short-term outcomes.