
What are the common causes of metabolic acidosis?
What is metabolic acidosis?
- Produces too much acid
- Doesn’t get rid of enough acid
- Doesn’t have enough base to neutralize the acid
How does the body compensate for metabolic acidosis?
Those in metabolic acidosis may exhibit deep, rapid breathing called Kussmaul respirations which is classically associated with diabetic ketoacidosis. Rapid deep breaths increase the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled, thus lowering the serum carbon dioxide levels, resulting in some degree of compensation.
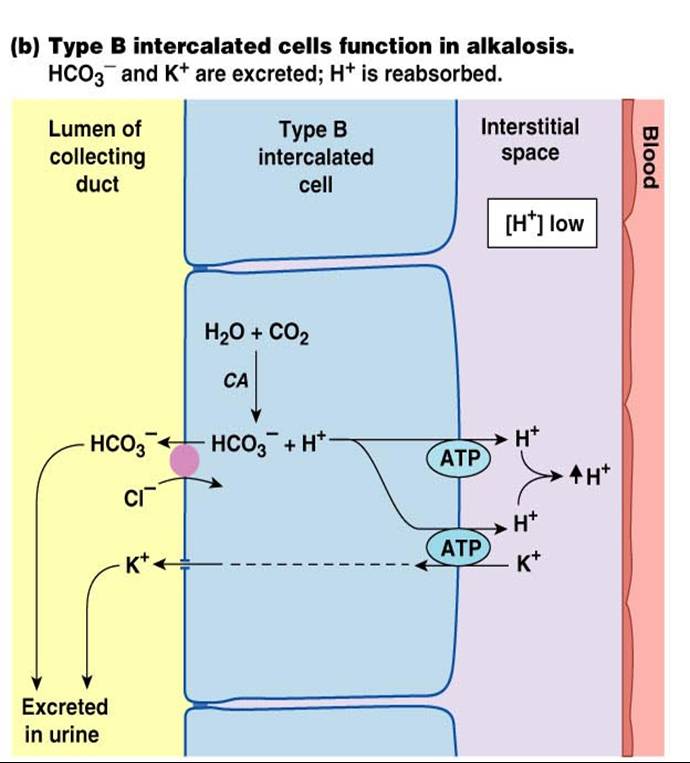
What are the different causes of metabolic alkalosis?
The four types of alkalosis
- Respiratory alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there isn’t enough carbon dioxide in your bloodstream.
- Metabolic alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis develops when your body loses too much acid or gains too much base.
- Hypochloremic alkalosis. ...
- Hypokalemic alkalosis. ...
What is the compensation for metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic Acidosis If the kidneys are also functioning, the renal compensation for acidosis is to excrete acidic urine. Chronically, the renal excretion of H+ is enhanced as the renal ability to produce ammonium from glutamine is induced.
Does hyperventilation cause metabolic acidosis?
In general, the kidneys compensate for respiratory causes and the lungs compensate for metabolic causes. Therefore, hyperventilation may be a cause of respiratory alkalosis or a compensatory mechanism for metabolic acidosis.
What does respiratory alkalosis cause?
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when you breathe too fast or too deep and carbon dioxide levels drop too low. This causes the pH of the blood to rise and become too alkaline. When the blood becomes too acidic, respiratory acidosis occurs.
How do metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis differ?
Metabolic acidosis: patients who are acidotic and have a HCO3– <22 (base excess <–2); Respiratory acidosis: patients who are acidotic with a PaCO2 >6; Metabolic alkalosis: patients who are alkalotic with a HCO3– >28 (base excess >+2); Respiratory alkalosis: patients who are alkalotic with a PaCO2 <4.7.
What happens in response to respiratory alkalosis?
In response to acute respiratory alkalosis, the HCO3− decreases by 1 to 3 mmol/L for every 10–mm Hg decrease in Paco2. The kidney compensates in response to respiratory alkalosis by reducing the amount of new HCO3− generated and by excreting HCO3−. The process of renal compensation occurs within 24 to 48 hours.
What causes metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis is caused by a build-up of too many acids in the blood. This happens when your kidneys are unable to remove enough acid from your blood.
What are the complications of respiratory alkalosis?
Possible Complications Arrhythmias (heart beating too fast, too slow, or irregularly) Coma. Electrolyte imbalance (such as low potassium level)
Can you have respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis at the same time?
Acidemia has a respiratory cause if the PCO2 is greater than 44 mm Hg. It has a metabolic cause if the bicarbonate level is less than 25 mEq/L. A PCO2 greater than 44 mm Hg concurrent with a bicarbonate level less than 25 mEq/L suggests that respiratory and metabolic acidosis coexist.
Does hyperventilation result in acidosis or alkalosis?
Alveolar hyperventilation leads to hypocapnia and thus respiratory alkalosis whereas alveolar hypoventilation induces hypercapnia leading to respiratory acidosis.
Is High HCO3 acidosis or alkalosis?
pH is in the normal range, so use 7.40 as a cutoff point, in which case it is <7.40, acidosis is present. The PaCO2 is elevated, indicating respiratory acidosis, and the HCO3 is elevated, indicating a metabolic alkalosis. The value consistent with the pH is the PaCO2. Therefore, this is a primary respiratory acidosis.
What best describes respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition marked by a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood due to breathing excessively.
Does respiratory alkalosis cause hypokalemia?
Persistent respiratory alkalosis can induce secondary hypocalcemia and hypokalemia that may cause cardiac arrhythmias, conduction abnormalities, and various somatic symptoms such as paresthesia, hyperreflexia, convulsive disorders, muscle spasm and tetany [2].
Why is bicarbonate high in respiratory alkalosis?
Alveolar hyperventilation leads to a decreased partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2). In turn, the decrease in PaCO2 increases the ratio of bicarbonate concentration to PaCO2 and, thereby, increases the pH level; thus the descriptive term respiratory alkalosis.
Does respiratory alkalosis cause hyperventilation?
Respiratory alkalosis involves an increase in respiratory rate and/or volume (hyperventilation). Hyperventilation occurs most often as a response to hypoxia, metabolic acidosis, increased metabolic demands (eg, fever), pain, or anxiety.
How does alkalosis affect the body?
Metabolic alkalosis can have central nervous system manifestations ranging from confusion to coma, peripheral neuropathic symptoms of tremor, tingling and numbness, muscle weakness and twitching, and arrhythmias, particularly when associated with hypokalemia and hypocalcemia.
Which symptom is associated with respiratory alkalosis?
Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis may include muscle spasms, irritability, dizziness, and nausea. Respiratory alkalosis is one possible classification of an acid-alkaline imbalance in the body. The human body normally works to maintain a pH level of around 7.35–7.45 .
Why does alkalosis cause hyperexcitability?
Alkalosis causes H+ to move out from the cells and K+ to move in to the cell, leading to hypokalemia. This leads to a higher concentration gradient between intracellular and extracellular K+ leading to more K+ exiting the cell through leakage channels leading to hyperpolarization of the cell.
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when high levels of carbon dioxide disrupt the blood’s acid-base balance. It often occurs in people who experience rapid, uncontrollable breathing (hyperventilation). Treatment includes supplemental oxygen and therapies to reduce the risk of hyperventilation.
Why is respiratory alkalosis important?
The condition is not life-threatening. Nor does it have lingering effects on your health. But it’s important to seek medical care for respiratory alkalosis because it’s often a sign of another medical condition. Some people need treatment with supplemental oxygen. Addressing what’s causing you to hyperventilate lowers your risk of future episodes.
Why does alkalosis occur?
Your body is continuously working to maintain the blood’s acid-base (alkali) balance. Alkalosis occurs when there’s too much alkali and not enough acid. Chemical changes in the acid-base balance can reflect changes in metabolism or breathing.
What causes rapid uncontrolled breathing?
People who experience intense bouts of stress, anxiety, panic or anger are at higher risk for respiratory alkalosis. These conditions can lead to rapid, uncontrolled breathing (hyperventilation).
What happens when you breathe faster?
Your body releases carbon dioxide when you exhale. When you breathe faster, the lower carbon dioxide level in your blood can lead to respiratory alkalosis.
Can a lung disease cause shortness of breath?
Any lung disease that leads to shortness of breath can also cause respiratory alkalosis (such as pulmonary embolism and asthma).
What causes respiratory alkalosis?
These include central causes, hypoxemic causes, pulmonary causes, and iatrogenic causes. Central sources are a head injury, stroke, hyperthyroidism, anxiety-hyperventilation, pain, fear, stress, drugs, medications such as salicylates, and various toxins. Hypoxic stimulation leads to hyperventilation in an attempt to correct hypoxia at the expense of a CO2 loss. Pulmonary causes include pulmonary embolisms, pneumothorax, pneumonia, and acute asthma or COPD exacerbations. Iatrogenic causes are primarily due to hyperventilation in intubated patients on mechanical ventilation. [6][7]
How to treat metabolic alkalosis?
Treatment of metabolic alkalosis is targeted at treating the underlying pathology. In anxious patients, anxiolytics may be necessary. In infectious disease, antibiotics targeting sputum or blood cultures are appropriate. In embolic disease, anticoagulation is necessary. Ventilator support may be necessary for patients with acute respiratory failure, acute asthma, or acute, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation if they show signs of respiratory fatigue. In ventilator controlled patients, it may be necessary to reevaluate their ventilator settings to reduce respiratory rate. If hyperventilation is intentional, monitor the arterial or venous blood gas values closely. In severe cases, pH may be directly reduced using acidic agents. However, this is not routinely done. [14][15][16]
How does HCO3 affect alkalosis?
HCO3 functions as an alkalotic substance. CO2 (carbon dioxide) functions as an acidic substance. Therefore, Increases in HCO3 (bicarbonate) or decreases in CO2 will make blood more alkalotic . The opposite is also true where decreases in HCO3 or an increase in CO2 will make blood more acidic. CO2 levels are physiologically regulated by the pulmonary system through respiration, whereas the HCO3 levels are regulated through the renal system with reabsorption rates. Therefore, respiratory alkalosis is a decrease in serum CO2. While it is theoretically possible to have decreased CO2 production, in every scenario this illness is a result of hyperventilation where CO2 is breathed away. [2][3][4]
What is the normal pH of the blood?
Respiratory alkalosis is 1 of the 4 basic classifications of blood pH imbalances. Normal human physiological pH is 7.35 to 7.45. A decrease in pH below this range is acidosis, an increase above this range is alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis is by definition a disease state where the body’s pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some respiratory or pulmonary process.[1]
What is the primary pH buffer system in the human body?
The primary pH buffer system in the human body is the HCO3/CO2 chemical equilibrium system. Where:
Is respiratory alkalosis an acute or chronic process?
Respiratory alkalosis may be an acute process or a chronic process. These are determined based on the level of metabolic compensation for the respiratory disease. Excess HCO3 levels are buffered to reduce levels and maintain a physiological pH through the renal decrease of H secretion and increasing HCO3 secretion; however, this metabolic process occurs over the course of days whereas respiratory disease can adjust CO2 levels in minutes to hours. Therefore, acute respiratory alkalosis is associated with high bicarbonate levels since there has not been sufficient time to lower the HCO3 levels and chronic respiratory alkalosis is associated with low to normal HCO3 levels. [8][1][9]
Is respiratory alkalosis a disease?
Respiratory alkalosis is the most common acid-base abnormality with no discrimination between genders. The exact frequency and distribution of disease are dependent upon the etiology. Likewise, the morbidity and mortality rates are dependent on the etiology of the disease. [5]
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is a primary decrease in carbon dioxide partial pressure (P co2) with or without compensatory decrease in bicarbonate (HCO 3− ); pH may be high or near normal. Cause is an increase in respiratory rate or volume (hyperventilation) or both. Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic.
What causes cellular acidosis in the arterial blood?
Exhalation of large amounts of CO 2 causes respiratory alkalosis in arterial blood (hence on ABG measurements), but poor systemic perfusion and cellular ischemia cause cellular acidosis, leading to acidosis of venous blood.
What are the symptoms of P co2?
Acute respiratory alkalosis causes light-headedness, confusion, peripheral and circumoral paresthesias, cramps, and syncope. Mechanism is thought to be change in cerebral blood flow and pH. Tachypnea or hyperpnea is often the only sign; carpopedal spasm may occur in severe cases due to decreased levels of ionized calcium in the blood (driven inside cells in exchange for hydrogen ion [H + ]).
Why does ventilation increase?
Ventilation increase occurs most often as a physiologic response to hypoxia (eg, at high altitude), metabolic acidosis , and increased metabolic demands (eg, fever) and, as such, is present in many serious conditions. In addition, pain and anxiety and some central nervous system (CNS) disorders (eg, stroke, seizure [post-ictal]) ...
What is the primary cause of aldosteronism?
Primary aldosteronism is caused by autonomous production of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex due to hyperplasia, adenoma, or carcinoma. Which of the following is an uncommon symptom of this disorder?
Which ion is most reactive in acid-base regulation?
Acid-Base Regulation Metabolic processes continually produce acid and, to a lesser degree, base. Hydrogen ion (H+) is especially reactive; it can attach to negatively charged proteins and, in high concentrations... read more
Is alkalosis life threatening?
Treatment is directed at the underlying disorder. Respiratory alkalosis is not life threatening, so no interventions to lower pH are necessary. Increasing inspired carbon dioxide through rebreathing (such as from a paper bag) is common practice but may be dangerous in at least some patients with CNS disorders in whom the pH of cerebrospinal fluid may already be below normal.
What causes acidosis in the respiratory system?
The only cause of respiratory acidosis is alveolar hypoventilation, which causes global respiratory failure ,. We’ll repeat some causes here. Not all of these warrant an explanation, but some of them do. CNS disturbances damage or depress the respiratory centre, which decreases the respiratory drive.
What is the pH of respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis. In respiratory acidosis we have: pH below 7.35. When kidney compensation kicks in, after around 24 hours, will we also have: Because it is respiratory is it caused by a primary increase in pCO 2, due to inadequate ventilation. This decreases the pH.
What causes hyperventilation?
Hypoxaemia causes hyperventilation as a compensatory reaction. If the arterial pO 2 falls below 60 mmHg the hypoxaemia start to stimulate ventilation.
What happens if there are multiple conditions present in the same person, where one would cause an alkalosis and?
What happens if there are multiple conditions present in the same person, where one would cause an alkalosis and the other an acidosis? The answer is that they could cancel each other out to some degree. pH may even become normal. That doesn’t mean that everything is fine – other components of the conditions could be dangerous.
Why does pCO2 increase?
Because it is respiratory, it’s caused by a primary increase in pCO 2, due to inadequate ventilation. This decreases the pH. When pCO 2 increases will actual HCO 3– also increase because they’re in an equilibrium. We’ll get to the compensation later.
Can hypercapnia cause hypoxia?
Chronic hypercapnia is well tolerated, but it causes the respiratory centre to be less sensitive to CO 2, potentially causing breathing to be driven by hypoxia instead. If the acidosis is severe will the consequences be similar as for metabolic acidosis.
Can alkalosis and metabolic alkalosis be at the same time?
We can also have respiratory alkalosis and metabolic alkalosis at the same time, where they worsen each other. The same goes for acidosis.
Why does blood K go down in acidosis?
Acidosis is caused BY the build up of H+ ion. Not VV. A higher H+ is buffered by moving into cells in exchange for K moving out our cells. Thus higher blood K. Alkalosis is due to not enough H+ in blood. Cells "let out" H+ to help bring up low H+ in blood. As the H+ moves out of cell, K+ from blood enters the cell. Thus blood K goes down.
What happens to potassium during alkalosis?
The body strives to maintain normal concentrations of potassium, acid, as well as electrical charge. Acidosis causes a build up of hydrogen and cells will shift hydrogen and potassium to prevent acid buildup as a result potassium goes up, the reverse occurs when alkalosis happens
Can cystic fibrosis cause lung damage?
Possible but small %: Many people with cystic fibrosis have aspergillus (a fungus) in their airway, but in the vast majority of cases it does not cause disease. In a small percent of patients it may cause allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (abpa), and that can lead to lung damage. Abpa can usually be treated.
How to treat respiratory alkalosis?
Treatment is aimed at the condition that causes respiratory alkalosis. Breathing into a paper bag — or using a mask that causes you to re-breathe carbon dioxide — sometimes helps reduce symptoms when anxiety is the main cause of the condition. In anxious patients, anxiolytics may be necessary.
What is the cause of alkalosis in the kidneys?
People with healthy kidneys and lungs do not usually have serious alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis is caused by a low carbon dioxide level in the blood.
Why is respiratory alkalosis iatrogenic?
Iatrogenic causes are primarily due to hyperventilation in intubated patients on mechanical ventilation. Respiratory alkalosis may be an acute process or a chronic process. These are determined based on the level of metabolic compensation for the respiratory disease.
What happens when the body returns the acid-base balance to normal?
Compensated alkalosis occurs when the body returns the acid-base balance to normal in cases of alkalosis, but bicarbonate [HCO3 –] and carbon dioxide (CO2) levels remain abnormal. Untreated alkalosis or alkalosis not treated properly, complications may include any of the following:
What causes alkaline pH?
Alkalosis may have respiratory causes such as hyperventilation (respiratory alkalosis) and pneumonia or metabolic causes such as prolonged vomiting and severe dehydration (metabolic alkalosis). Decreased carbon dioxide (an acid) level or increased bicarbonate (a base) level makes the body too alkaline. There are different types of alkalosis. These are described below.
What is the pH of blood?
Normal blood pH must be maintained within a narrow range, typically 7.35-7.45 (average 7.40), to ensure the proper functioning of metabolic processes and the delivery of the right amount of oxygen to tissues. Acidosis refers to an excess of acid in the blood that causes the pH to fall below 7.35, and alkalosis refers to an excess of base in the blood that causes the pH to rise above 7.45. Many conditions and diseases can interfere with pH control in the body and cause a person’s blood pH to fall outside of healthy limits.
How to treat alkalosis?
To treat alkalosis, your doctor needs to first find the underlying cause. For alkalosis caused by hyperventilation, breathing into a paper bag allows you to keep more carbon dioxide in your body, which improves the alkalosis. If your oxygen level is low, you may receive oxygen.
How does metabolic acidosis affect the body?
The person may be confused or experience nausea, vomiting, and lethargy, and could develop rapid breathing or take long, deep breaths at a normal rate as the lungs attempt to remove excess CO2. Long, deep breaths, known as Kussmaul breathing, is most common in severe and late-stage metabolic acidosis. In severe cases, metabolic acidosis can lead to arrhythmias, hypotension, shock, or death. Doctors may treat this issue using dialysis or, in severe cases, bicarbonate replacement via IV.
Why does metabolic acidosis occur?
The most common cause is excessive vomiting or other gastrointestinal loss. The condition can also be caused by kidney disease, severe dehydration, and poisoning, most commonly from ethylene glycol, which is in antifreeze or develops from an overdose of aspirin.
What causes C02 to drop in blood?
Metabolic Acidosis. Metabolic acidosis occurs when the kidneys are unable to produce enough bicarbonate to counter the level of pH in the blood or if there is a loss of bicarbonate for some other reason. This causes C02 to accumulate, dropping the pH.
What is respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory Acidosis. Respiratory acidosis occurs when the lungs cannot remove enough CO2 and can be chronic or acute. The chronic type develops over a long period, as the kidneys compensate for the increased amount of CO2 in the blood.
How does the body compensate for respiratory acidosis?
The brain increases the rate of ventilation so that the lungs blow off more CO2, which raises the blood pH. To compensate for respiratory acidosis, the kidneys adjust the level of bicarbonate to counter the increased CO2 and raise the pH.
How does the brain affect the pH of the blood?
The brain increases the rate of ventilation so that the lungs blow off more CO2, which raises the blood pH. To compensate for respiratory acidosis, the kidneys adjust the level of bicarbonate to counter the increased CO2 and raise the pH. Advertisement.
How does acidosis occur?
The body maintains this through a variety of intricate chemical processes. Essentially, too much CO2 in the blood increases acidity , leading to acidosis. The lungs remove CO2 from the body during exhalation and, by varying the respiratory rate, control how much CO2 is excreted. Acidosis can also be corrected by the kidneys, which facilitate the production of bicarbonate. This natural chemical is a buffer, helping to maintain a stable blood pH.
Which organ is responsible for maintaining acid-base homeostasis?
Alongside the kidneys and lungs, the liver has been recognised as an important regulator of acid-base homeostasis. While respiratory alkalosis is the most common acid-base disorder in chronic liver disease, various complex metabolic acid-base disorders may occur with liver dysfunction.
Which organ regulates acid-base homeostasis?
Alongside the kidneys and lungs, the liver has been recognised as an important regulator of acid-base homeostasis. While respiratory alkalosis is the most common acid-base disorder in chronic liver disease, various complex metabolic acid-base disorders may occur with liver dysfunction. While the standard variables of acid-base equilibrium, ...
Why is cirrhosis a fragile equilibrium?
When patients with liver cirrhosis become critically ill (e.g., because of sepsis or bleeding ), this fragile equilibrium often tilts towards metabolic acidosis, which is attributed to lactic acidosis and acidosis due to a rise in unmeasured anions.
Can liver disease cause multiple acid-base abnormalities?
In conclusion, patients with liver diseases may have multiple co-existing metabolic acid-base abnormalities. Thus, knowledge of the pathophysiological and diagnostic concepts of acid-base disturbances in patients with liver disease is critical for therapeutic decision making.
Can liver failure cause acid-base disorder?
Interestingly, even though patients with acute liver failure show significantly elevated lactate levels, often, no overt acid-base disorder can be found because of the offsetting hypoalbuminaemic alkalosis. In conclusion, patients with liver diseases may have multiple co-existing metabolic acid-base abnormalities.
Is liver acid-base disorder a metabolic disorder?
Acid-base disorders in liver disease. Alongside the kidneys and lungs, the liver has been recognised as an important regulator of acid-base homeostasis. While respiratory alkalosis is the most common acid-base disorder in chronic liver disease, various complex metabolic acid-base disorders may occur with liver dysfunction. While the sta ….
What are the effects of hypoxia on the body?
Hypoxia and Its Acid-Base Consequences: From Mountains to Malignancy. Hypoxia, depending upon its magnitude and circumstances, evokes a spectrum of mild to severe acid-base changes ranging from alkalosis to acidosis, which can alter many responses to hypoxia at both non-genomic and genomic levels, in part via altered hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) ...
What is the spectrum of acid-base changes?
Hypoxia, depending upon its magnitude and circumstances, evokes a spectrum of mild to severe acid-base changes ranging from alkalosis to acidosis, which can alter many responses to hypoxia at both non-genomic and genomic levels, in part via altered hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) metabolism.
Is acidosis cytoprotective?
Although conventionally considered to be injurious and deleterious to cell function and survival , both acidoses may be cytoprotective by various anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic mechanisms which limit total hypoxic or ischemic-reperfusion injury.
