See more

Does sodium chloride affect your blood pressure?
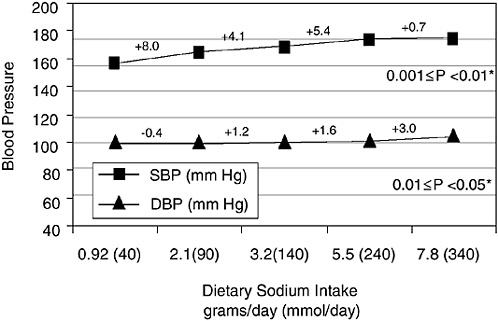
Among the environmental factors that affect blood pressure, dietary sodium chloride has been studied the most, and there is general consensus that increased sodium chloride intake increases blood pressure.
What IV fluids raise BP?
Saline is a commonly used intravenous solvent, however, its excessive infusion may increase drug-induced sodium intake. To investigate the effects of saline infusion on blood pressure variability (BPV) in patients with hypertension, a retrospective study was performed in 1010 patients with hypertension.
Is saline good for high blood pressure?
The water potential in blood will decrease due to the increase solutes and blood osmotic pressure will increase. While the kidney reacts to excrete excess sodium and chloride in the body, water retention causes blood pressure to increase. Saline water causes an increase in blood pressure not decrease in blood pressure.
Can Too Much IV fluids cause high blood pressure?
When you have too much excess fluid, it can cause health complications such as swelling, high blood pressure, heart problems and more.
Which IV fluid is best for low BP?
Isotonic crystalloid solutions are typically given for intravascular repletion during shock and hypovolemia.
Can dehydration cause high blood pressure?
When your body is dehydrated, it releases higher amounts of a chemical called vasopressin. Vasopressin helps your kidneys retain water, which can prevent you from losing more water through urination. At the same time, it causes your blood vessels to constrict, which then causes your blood pressure to increase.
How do IV fluids help blood pressure?
If a patient is suffering from fluid (volume) depletion, then his or her heart rate will increase to improve cardiac output and raise blood pressure, hereby maintaining tissue oxygenation. Blood pressure only falls after the intravascular volume has dropped by 20–30 per cent.
How does sodium chloride IV work?
A sodium chloride IV is a mixture of fluids and sodium chloride administered intravenously to restore fluid balance. This cocktail is used to treat patients with fluid loss and those unable to take fluids and nutrients by mouth.
Does Ringer's lactate increase blood pressure?
Lactated Ringer's injection is used to replace water and electrolyte loss in patients with low blood volume or low blood pressure. It is also used as an alkalinizing agent, which increases the pH level of the body. This medicine is to be given only by or under the supervision of your doctor.
Can dextrose saline increase blood pressure?
Saline and dextrose infusion had neutral effects on BP and FMD. The co-administration of lipid and dextrose decreased FMD by 2.4% ± 2.1% (p = 0.002) from baseline, but did not significantly increase systolic or diastolic BP.
Do IV fluids help low blood pressure?
Treating hypotension directly usually happens in one of three ways: Increasing blood volume. This method, also known as fluid resuscitation, involves infusing fluids into your blood. Examples of this include intravenous (IV) fluids, plasma or blood transfusions.
What is sodium chloride solution-intravenous, and how does it work (mechanism of action)?
These molecules play a vital role in maintaining proper fluid balance and keeping our tissues hydrated. Additionally, sodium is involved in many cell processes such as muscle contraction, transmission of nerve impulses, and kidney function. Chloride ions are responsible for maintaining the acid-base balance. To sustain life it's very important to maintain these ions within a narrow therapeutic range.
What is the dosage for sodium chloride solution-intravenous?
Dosing of sodium chloride intravenous solution varies. Total volume of administration depends on many factors including condition being treated, laboratory results, and other patient specific characteristics.
What is sodium chloride solution?
Sodium chloride solution (intravenous) normal saline (NS), 1/2 NS is a prescription intravenous medication used to replenish fluids with dehydration and other medical conditions that require additional fluids.
What temperature should sodium chloride be stored at?
Sodium chloride preparations should be stored at room temperature between 59 F to 86 F (15 C to 30 C).
What is the role of sodium in the body?
Additionally, sodium is involved in many cell processes such as muscle contraction, transmission of nerve impulses, and kidney function. Chloride ions are responsible for maintaining the acid-base balance. To sustain life it's very important to maintain these ions within a narrow therapeutic range.
How to report side effects of prescription drugs?
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
When was sodium chloride first approved?
Sodium chloride was initially approved by the FDA in 1951.
What happens if you have too much sodium in your blood?
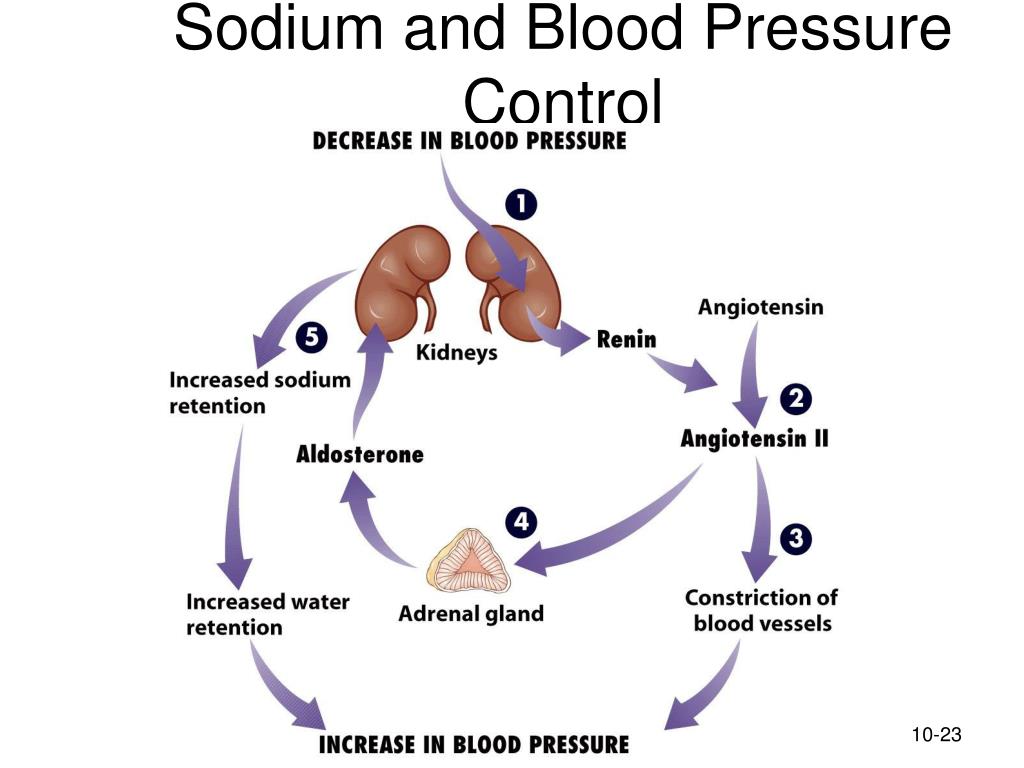
When there’s too much sodium in your bloodstream, your brain signals your kidneys to release more water into your blood circulation. This leads to an increase in blood volume and blood pressure. Decreasing your sodium intake can lead to less water being absorbed into the bloodstream. The result is a lower blood pressure.
What is the compound that the body uses to make salt?
Sodium chloride (NaCl), also known as salt, is an essential compound our body uses to: Salt is an inorganic compound, meaning it doesn’t come from living matter. It’s made when Na (sodium) and Cl (chloride) come together to form white, crystalline cubes. Your body needs salt to function, but too little or too much salt can be harmful to your health.
How much sodium is in a teaspoon of salt?
Many companies and restaurants use salt to preserve, season, and flavor their food. Since one teaspoon of salt has about 2,300 milligrams (mg) of sodium, it’s easy to go over the daily value.
What is saline solution?
Sodium chloride mixed with water creates a saline solution, which has a number of different medical purposes. Medical uses for a saline solution include: It’s important to consult a doctor and only use medical saline products (excluding over-the-counter products like contact solution) as prescribed.
What are the two electrolytes that are in the fluid?
Sodium and potassium are electrolytes in the fluid outside and inside your cells. The balance between these particles contributes to how your cells maintain your body’s energy. It’s also how nerves send signals to the brain, your muscles contract, and your heart functions.
What is sodium deficiency?
Sodium deficiency is usually a sign of an underlying disorder. The name for this condition is hyponatremia. It can be due to: inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (ADH), caused by disorders that affect hormone balance, certain drugs, and certain medical conditions. excessive water intake.
Is sodium chloride a hazard?
For the most part, sodium chloride isn’t a health hazard, but in excessive amounts it can irritate your:
What is the role of NKCC1 in hypertension?
In the VSMC, loop diuretics decrease the concentration of intracellular chloride, hyperpolarize the sarcolemma, and attenuate Ca2+influx though voltage-gated channels, indicating a putative mechanism by which NKCC1 contributes to hypertension via elevation of vascular tone [68, 70]. NKCC1-null mice have decreased baseline BP but exhibit augmented BP increment evoked by high-salt diets. NKCC1 deficiency causes approximately threefold elevation in plasma renin concentrations and attenuates high-ceiling diuretics-induced renin production [68, 70].
What is the intracellular concentration of cl?
The intracellular concentration of Cl−is much lower than its plasma concentration and depends on the resting membrane potential of the cell and ranges from 2–4 mEq/L in muscle cells and 100–120 mEq/L in smooth muscle cells and red blood cells [4, 29]. The Cl−channels in other tissues include (1) the ClC family of Cl−channels that are often voltage-gated, (2) the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), a member of the ABC transporter family, (3) the ligand-gated GABA and glycine-activated Cl−channels, (4) the calcium-activated Cl−channels and bestrophins, and (5) the transmembrane protein 16 (TMEM16)/anoctamin (ANO) [20, 92].
What is the mechanism of electrolyte homeostasis?
There is evidence of extrarenal regulatory mechanisms for electrolyte homeostasis with the finding of Na+and Cl−sequestration in the skin interstitium which appear to be regulated by the mononuclear phagocyte system [56, 57, 98]. Macrophages infiltrate to the sites of Na+and Cl−overload in the skin which display a hypertonic microenvironment and subsequently upregulate the transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 (NFAT5) [31]. The induction of NFAT5 in macrophages of the skin was shown to directly govern the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C), resulting in the hyperplasia of lymph capillaries via and interaction with the VEGF receptor 3 (VEGFR3) [98]. Failure of this local extrarenal macrophage-dependent control mechanism to regulate interstitial electrolyte and water homeostasis resulted in arterial hypertension and massive disturbances in skin electrolyte composition [98]. Moreover, when NFAT5/VEGF-C axis was knocked out in experimental models, there was selective Cl−accumulation in the skin, a direct correlation between skin Cl−content and blood pressure increases, and no relationship between Na+and water content and blood pressure [98].
Is clone hypertension a direct role?
A direct role for Cl−on hypertension is not established currently. However, evidence from monogenic syndromes, dietary and animal studies on renal Cl−balance, and Cl−transporters in vascular tissues point to a critical role for Cl−in mechanisms that contribute to blood pressure regulation.
Does low Cl increase mortality?
The mechanism by which low serum Cl–increases mortality or cardiovascular events is unclear [23]. The risk associated with low serum Cl–appears to be independent of serum Na+, K+, or anion gap [59]. This also suggests that dietary Cl–and serum Cl–exert different effects and perhaps the regulation of serum Cl–is not entirely related to dietary intake and renal mechanisms. Emerging evidence that the immune system plays an extrarenal regulatory role in Na+homeostasis and the intriguing finding that when this immune mechanism was blocked there was selective Cl−accumulation in the skin salt-sensitive hypertension would support this hypothesis [56, 57, 98].
Is a lower circulating cl good for cardiovascular disease?
Large epidemiologic studies curiously show that lower circulating levels of Cl−are associated with higher cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. De Bacquer et al. [19] studied 9106 participants from the Belgian Interuniversity Research on Nutrition and Health (BIRNH) study who were followed up for 10 years. They showed serum Cl−<100 mEq/L was associated with an increased risk of all-cause, cardiovascular disease, non-cardiovascular disease, and coronary heart disease mortality after adjustment for age, body mass index (BMI), and serum Na+levels. Serum Cl−<100 mmol/L was found to be a strong predictor (RR 1.77; 95 % CI 1.22–2.5), in multivariate analysis, of total, cardiovascular, and non-cardiovascular mortality independent of other classic risk factors and larger than the effects of diabetes (RR 1.46; 95 % CI 0.81–2.63), smoking status (RR 1.50; 95 % CI 1.10–2.05), BMI (RR 1.20; 95 % CI 0.85–1.67), and cholesterol levels (RR 1.16; 95 % CI 0.88–1.54).
Does sodium chloride increase blood pressure?
Among the environmental factors that affect blood pressure, dietary sodium chloride has been studied the most, and there is general consensus that increased sodium chloride intake increases blood pressure. There is accruing evidence that chloride may have a role in blood pressure regulation which may perhaps be even more important than that of Na+. Though more than 85 % of Na+is consumed as sodium chloride, there is evidence that Na+and Cl−concentrations do not go necessarily hand in hand since they may originate from different sources. Hence, elucidating the role of Cl−as an independent player in blood pressure regulation will have clinical and public health implications in addition to advancing our understanding of electrolyte-mediated blood pressure regulation. In this review, we describe the evidence that support an independent role for Cl−on hypertension and cardiovascular health.
What other drugs will affect Sodium Chloride,?
Tell your doctor about all medicines you use, and those you start or stop using during your treatment with Sodium Chloride,, especially:
How is Sodium Chloride, given?
Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not use this medicine in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended .
What is Sodium Chloride,?
Sodium Chloride, is the chemical name for salt. Sodium Chloride, can reduce some types of bacteria in certain body secretions, such as saliva.
What should I avoid while using Sodium Chloride,?
Follow your doctor's instructions about any restrictions on food, beverages, or activity.
What is the mask used to inhale sodium chloride?
A mouthpiece or face mask is then attached to the drug chamber, along with an air compressor. To prepare for inhaling sodium chloride through a nebulizer, you may be given another inhaled medication to prevent bronchospasm (muscle contractions within the airways of the lungs).
How to store sodium chloride?
If you store Sodium Chloride, at home, keep it at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
What is potassium supplement?
potassium supplements; a diuretic or "water pill"; a steroid such as prednisone, fluticasone, mometasone, dexamethasone, and others; blood pressure medication; or. medication that contains sodium, such as Alka-Seltzer or Zegrid ( omeprazole and sodium bicarbonate ). This list is not complete. Other drugs may interact with sodium chloride, ...
How long to use sodium chloride solution before surgery?
In our study, patients with essential hypertension (including stage 1, stage 2, and stage 3 hypertension) who used 0.9% sodium chloride solution as an intravenous solvent before surgery for continuous 3 to 5 days and were served with low-salt diet at the same time in the department of orthopedics of Zhongnan Hospital from March 2014 to January 2018 were involved. Meanwhile, patients with all kinds of tumor, renal disfunction, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, hyponatremia, various types of water loss, or more than 5 kinds of severe combined diseases were excluded. Finally, 1010 patients were selected to meet the criterion. Then age, sex, blood pressure (BP), anti-hypertensive medication, and medical history were retrospectively collected. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University.
Why are patients with a history of cardiovascular events prone to water and sodium retention?
Patients with a history of cardiovascular events had pathological changes in their heart and blood vessels, and the cardiac load and vascular elasticity were not as well as physiological status. Under the condition of high salt intake, due to hemodynamic changes and the activation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the patients were prone to water and sodium retention and larger BPV. [32–34]
What does BPV 20 mean?
BPV ≤20 mm Hg indicates a physiological phenomenon, while abnormal BPV was conformed when BPV > 20 mm Hg, and it would get severe abnormal when the BPV > 30 mm Hg. [17]
How long should saline be infused?
Our study suggests that it would have an adverse effect for blood pressure control if the saline infusion was >500 mL per day during continuous for 3 to 5 days. Furthermore, patients with diabetes and cardiovascular events are supposed to limit the volume of saline infusion per day, or receipt other solvents such as glucose or xylitol solution in case of organ damage caused by abnormal BPV. Except for the diet control, the drug-induced salt intake such as saline, sodium bicarbonate tablets, and injection should be taken enough attention by doctors and the hypertensive.
What is the best blood pressure for orthopedic surgery?
Even through the blood pressure below 180/110 mm Hg does not affect the orthopedic operation, there is still the best control range of blood pressure during the perioperative period: for patients younger than 60 years or patients with diabetes or chronic kidney disease, the aim blood pressure is below 140/90 mm Hg; for patients older than 60 years, the aim blood pressure is blow 150/90 mm Hg. [38] Even so, we still found that 4 of the inpatients with severe abnormal BPV had to receive the delayed surgery because of the poor control of blood pressure before the scheduled time for surgery. It will not only increase the suffering of patients but also aggravate their economic burden, resulting in waste of medical resources, which were not what expected. [39,40]
What is salt sensitivity?
Some of them have difficulty in excreting too much salt, leading to a significant increase in blood pressure, which is called salt sensitivity. [8] . And high blood pressure associated with salt sensitivity is called salt sensitive hypertension. [9] .
Is saline safe for hypertension?
Therefore, the use of saline in patients with hypertension, especially in patients with salt-sensitive hypertension, has been a controversial issue. Meanwhile, it is unclear whether there is correlation ...