The sucrose in the molasses is hydrolyzed to glucose and fructose by invertase. The reducing sugars are then degraded by NaOH, the alkali being neutralized by the sugar acids produced, resulting in an increase of the ionic strength and consequently depression of the freezing point of the resulting solution.
What is the reaction between sucrose and NaOH and KMnO4?
Reaction between Sucrose, NaOH and KMnO4 - YouTube See the amazing colour changes when KMnO4 is added to NaOH and Sucrose solution. This is due to manganese is being reduced from 7+ to 3+. See the amazing colour changes when KMnO4 is added to NaOH and Sucrose solution. This is due to manganese is being reduced from 7+ to 3+.
What happens when sucrose is hydrolyzed with sulphuric acid?
Answer Wiki. Since sucrose is a disaccharide, hot dilute sulphuric acid catalyses the hydrolysis of sucrose into a mixture of glucose and fructose according to the following equation;- However, if concentrated (98%) sulphuric acid is used, the reaction is firstly dehydration of the sucrose to give carbon;- ….
Why is HCl used in hydrolysis of sucrose?
- Chemistry Stack Exchange Why is HCl used in hydrolysis of sucrose? I am aware that H C l can be used to help speed up the hydrolysis of sucrose but I haven't really been able to find out why. I've read somewhere that the glycosidic link in sucrose is broken off and that the H X + ions from the H C l is responsible for this.
What is the reaction between HCOOH and concentrated sulphuric acid?
Concentrated sulphuric is a powerful dehydrating agent, it protonates H2O which removes it from the equilibrium of reactions, this means that HCOOH is readily dehydrated to CO, carbon monoxide. The reaction would need to use small quantities, be carried out in a fume cupboard.

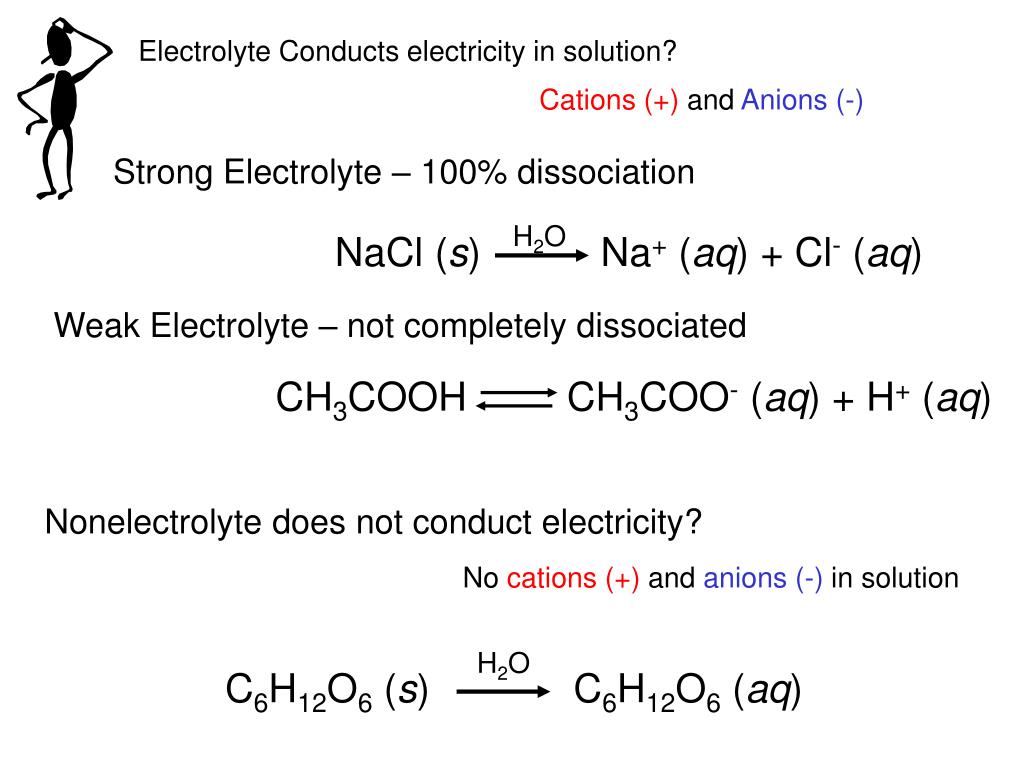
Does sugar react with NaOH?
Hint: When glucose is treated with dilute NaOH, it converts the aldehyde group of glucose into the ketone group, so a ketose sugar forms. When the ketose sugar is treated with NaOH an epimer of glucose forms or again glucose can also form. All the reactions are reversible.
What happens when NaOH is added to glucose?
Solution : When glucose is treated with dilute NaOH, it forms a mixture of D-glucose, D-fructose and D-mannoseD-mannoseMannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › MannoseMannose - Wikipedia due to reversible isomerisation. This reaction is generally known as Lobry de Bruyn-van Ekenstein. Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams.
What can react with NaOH?
Sodium hydroxide reacts with strong acids (hydrochloric, sulfuric or nitric), water, and moisture to rapidly release heat. Sodium hydroxide reacts with metals (aluminum, lead, tin or zinc) to form flammable and explosive hydrogen gas.
What reacts with sucrose?
Sucrose can undergo a combustion reaction to yield carbon dioxide and water. When reacted with chloric acid, this compound yields hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide, and water. Upon hydrolysis, the glycosidic bond linking the two carbohydrates in a C12H22O11 molecule is broken, yielding glucose and fructose.
Is starch soluble in NaOH?
experimental results revealed that starch could dissolve in urea (2–20 wt %) and NaOH (10–1 wt %) aqueous solutions at tempera- ture ranging from 212 to 25 8C, where the optimized dissolution condition was in the aqueous solution of mixed urea 14% and NaOH 4% at 0 8C for 30 min or above.
Does glucose react with HCl?
The introduction of HCl lowers the reaction rate of glucose-to-fructose isomerization but enhances the reaction rate of fructose dehydration. Higher loading of HCl (1.0 M) leads to increased direct dehydration of glucose to humins and results in lower selectivity to HMF.
What does not react with sodium hydroxide?
Aluminium does not react with sodium hydroxide.
Which metals does not react with NaOH?
question. Gold and platinum are the metals which do not react with sodium hydroxide. Gold and platinum are noble metals.
What reacts with NaOH to form a precipitate?
Description: AgNO3 reacts with NaOH. When 0.25M solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3) is added to 1M solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), dark brown precipitate composed of various hydrated silver oxidessilver oxidesSilver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Silver_oxideSilver oxide - Wikipedia (Ag2O xH2O) is produced.
Does sucrose react with sulfuric acid?
In the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid sucrose is dehydrateddehydratedIn chemistry, a dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes, the reverse of a hydration reaction.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dehydration_reactionDehydration reaction - Wikipedia to produce carbon and water. The heat of the reaction vaporizes the water causing the column of carbon to form.
Does sugar react with acid?
Explanation. Concentrated sulfuric acid can perform a dehydration reactiondehydration reactionIn chemistry, a dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes, the reverse of a hydration reaction.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dehydration_reactionDehydration reaction - Wikipedia with table sugar. After mixing, the color changes from white to brownish and eventually to black. The expansion of the mixture is the result of vaporization of water and CO2 inside the container.
Is sucrose polar or nonpolar?
polarLike water, the sucrose molecule has bonds between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. And like water, the area near the oxygen is slightly negative and the area near the hydrogen is slightly positive. This gives sucrose many areas of positive and negative charge and makes sucrose a polar molecule.
What happens to glucose in alkaline medium?
In an alkaline solution, D-glucose and D-fructose are interconverted via their 1,2-enolates. When the enolates are oxidized in situ with oxygen, D-arabinonic and formic acids are mainly formed.
What is glucose control solution?
Glucose control solution is a liquid made up of water, glucose, buffers, and microbicides. These ingredients are vital to creating a solution with the following properties: Has a concentration of glucose that can be used to test the functionality of your meter and test strips.
How does the blue bottle experiment work?
An alkaline solution of glucose acts as a reducing agent and reduces added methylene blue from a blue to a colourless form. Shaking the solution raises the concentration of oxygen in the mixture and this oxidises the methylene blue back to its blue form.
When D-glucose is treated with base it is converted into?
When an aqueous solution of D-glucose is treated with a base, it is converted into D-fructose and D-mannose, this conversion (isomerisation) involves. Get Answer to any question, just click a photo and upload the photo and get the answer completely free, UPLOAD PHOTO AND GET THE ANSWER NOW!
How many carbon sugars are in C6H12O6?
Things get a bit less complicated however, because living things use almost exclusively one of the two mirror image sugars of a certain formula, so only 8 aldehyde six carbon sugars occur in organisms and only 4 of the ketone six carbon sugars. Still that's a lot of variety.
Where are the enzymes that break down sugars?
However, in the body, specific enzymes are used to break down the sugars. The enzyme for sucrose and is sucrase and it’s in your saliva, as well as in your stomach. Some of the other enzymes to break disaccharides into monosaccharides are also in your mouth. Others are in your stomach and small intestines.
What happens when sulphuric acid is concentrated?
However, if concentrated (98%) sulphuric acid is used, the reaction is firstly dehydration of the sucrose to give carbon; -
What is the anhydride of sulfuric acid?
Burning of sulfur produces sulfur dioxide, SO₂, which has to be oxidized further to become sulfur trioxide, SO₃, the anhydride of sulfuric acid.
What happens if an excess of concentrated acid is present?
If an excess of concentrated acid is present though, it can then oxidise the solid carbon to CO2, being reduced itself to sulphur dioxide & water :
What is the reaction of dehydration?
The dehydration reaction is a type of elimination reaction. C12H2O11 (sugar) + H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) → 12 C ( carbon) + 11 H2O (water) + mixture water and acid. Although the sugar is dehydrated, the water isn't 'lost' in the reaction. Some of it remains as a liquid in the acid. Since the reaction is exothermic, ...
How many different sugars have the same formula?
There are 16 different aldehyde sugars with the same formula as glucose, and 8 different ketone sugars with exactly the same formula.
Who discovered that alkali is different from starch?
Taylor & Salzmann (1933) found that the action of alkali on starch was different for unmodified and modified starches and were able to distinguish them by this method and later Taylor et al. (1935) developed a method to determine the alkali- labile value of starch and starch products.
What are two methods of analysis of glucose syrup?
Two methods of analysis of glucose syrup are described, the first concerning the determination of the DE of glucose syrups and the second a theoretical example of the analysis of glucose syrup-sucrose mixtures.
What happens to the water molecule on the fructose ring?
Finally, the water molecule on the fructose loses a proton, restoring the catalyst. As Jan mentioned in the comments, the specific acid used is irrelevant so long as it is strong enough to sufficiently acidify the solution. (Credit to Khan Academy for the image)
Why is a reaction catalyzed by a substance?
The key to why a reaction is catalyzed by a substance has to do with the mechanism, in particular the rate determining step. The answers above do not show that step or discuss it, but rather they show a step which precedes it, namely the protonation of the bridge oxygen.
Does water bind to fructose?
Based on that reference, I do not believe @Tyberius is correct in saying, “Water then binds to the fructose ring, breaking its bond with the acetal linking O”. Rather, water only comes in after the oxocarbonium ion has been formed in the C-O bond cleavage step. The detailed answer to your question is that the presence of an acid makes that C-O bond cleavage step happen quicker.
What happens when chlorobenzene reacts with NaNH2 NH3?
Aniline can be prepared by the reaction of chlorobenzene with NaNH2/Liq. NH3 .
Why chlorobenzene does not react with?
Chlorobenzene is less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction because of the following reasons: … This results in delocalization of the electrons of C – Cl bond and a partial double bond character develops in the bond, which makes it difficult for the Nucleophile to cleave the C – Cl bond.
What happens when chlorobenzene reacts with water?
Under high pressure and at high temperature, chlorobenzene reacts with water or with ammonia, which displace the chlorine atom and form phenol or aniline. …
What happen when chlorobenzene is reduced?
With LiAlH4 or nickel aluminium alloy (Ni-Al), haloarenes undergo reduction to hydrocarbons in the presence of an alkali. The reduction is brought about by nascent hydrogen.
What happens when chlorobenzene is hydrolysis?
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis? Hint:Chlorobenzene is an aromatic compound in which a chlorine atom is present on the benzene ring when it is hydrolyzed, it is reacted with water. Under specific conditions, the chlorine on the benzene ring will be replaced with a hydroxyl group.
What happens when methyl bromide is treated with?
When methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether, ethane is formed. This reaction is known as the Wurtz reaction.
Which reaction is not feasible chlorobenzene?
Note: It is important to know that chlorobenzene can be prepared from various set of reactions like the Gattermann and Sandmeyer reaction. However, these reactions are not feasible on a commercial scale. Thus, Raschig process is preferred for the production of chlorobenzene in bulk quantity.
