
...
| Physical Properties of Sulfur | |
|---|---|
| Chemical Classification | Native element |
| Streak | Yellow |
| Luster | Crystals are resinous to greasy. Powdered sulfur is dull or earthy. |
What are the healing properties of sulfur?
- Sulphur eradicates harmful substances that are collected in the body.
- For skin sulphur is a great boon. Due to its keratolyitc action, sulphur makes the skin smooth and silky.
- Sulphur also promotes proper circulation in the body.
- Sulphur is also present in the matrix of bone joints as chondroitin sulphate and glucosamine sulphate. ...
What are 5 common uses for sulfur?
sulfur: Uses. Elemental sulfur is used in black gunpowder, matches, and fireworks; in the vulcanization of rubber; as a fungicide, insecticide, and fumigant; in the manufacture of phosphate fertilizers; and in the treatment of certain skin diseases. The principal use of sulfur, however, is in the preparation of its compounds.
Does sulfur have metallic luster?
The Physical Properties of Sulfur are as follows: Color : Pale yellow - Non-metallic. Phase : Solid. Crystalline structure & Forms : Rhombic, Amorphous and Prismatic.
What does sulfur like to bond with?
Sulfur, nonmetallic chemical element, one of the most reactive of the elements. Pure sulfur is a tasteless, odorless, brittle solid that is pale yellow in color, a poor conductor of electricity, and insoluble in water. It reacts with all metals except gold and platinum, forming sulfides.
See more
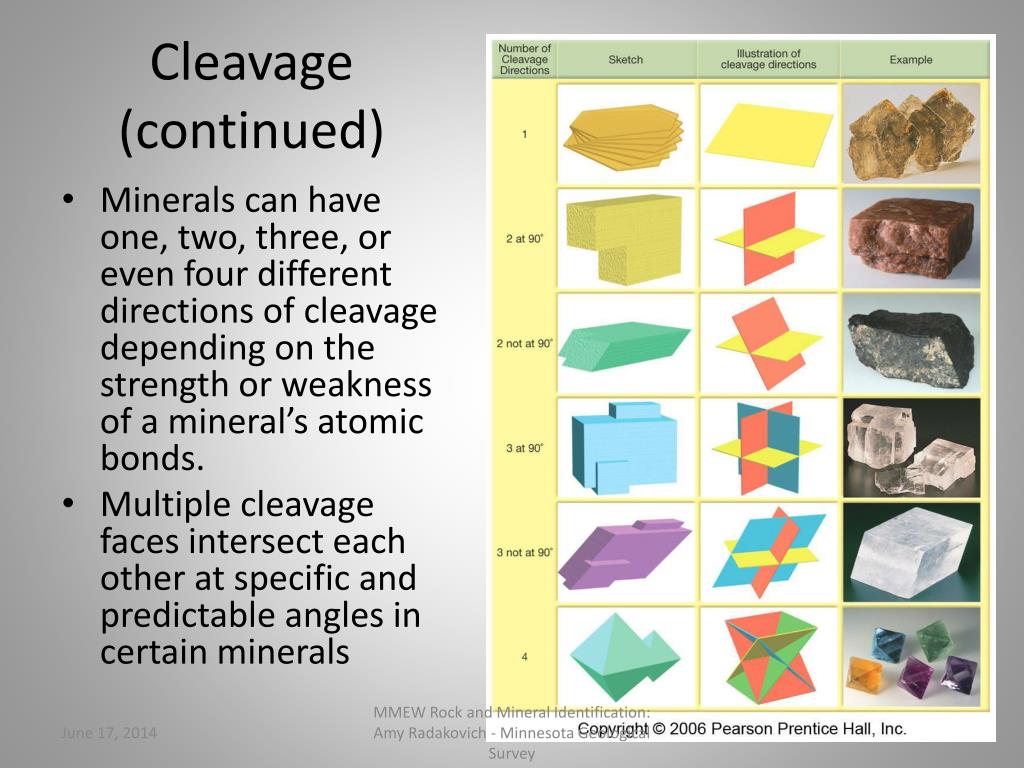
What type of luster does sulfur have?
SulfurPhysical PropertiesFractureConchoidalLusterResinousTransparencyTransparent to translucentStreakWhite14 more rows
Does sulfur have luster metallic?
Luster may also be spelled lustre. Luster has two main categories: Metallic and Non-metallic. Pyrite, for example, has a metallic luster. Sulfur, however, does not.
Is sulfur luster shiny or dull?
ElementLusterConductivityNeonColorlessPoor conductorSiliconDull, metallicConducts heat wellSulfurDullDoes not conduct electricityManganeseShinyConducts electricity
What is the color and luster of sulfur?
Sulfur Physical PropertiesColorYellow, sulphur-yellow, brownish or greenish yellow, orange, whiteStreakColourlessLusterResinous, GreasyCleavageImperfect/Fair Imperfect on {001}, {110} and {111}.DiaphaneityTransparent, Translucent6 more rows
What are the luster of minerals?
Eleven adjectives are commonly used to describe mineral luster. They are: metallic, submetallic, nonmetallic, vitreous, dull, greasy, pearly, resinous, silky, waxy, and adamantine. These adjectives convey - in a single word - a property that can be important in the identification of a mineral.
What is metallic luster?
Definition of metallic luster : a luster characteristic of metals in a compact state and shown also by other substances (as a mineral or dye)
Which of following element is luster?
So the iodine is most lustrous.
What are the types of luster?
The two main types of luster are metallic and nonmetallic....How many types of nonmetallic luster are there?Vitreous: The luster of glass.Resinous: The luster of resin.Pearly: The luster of pearls.Greasy: Looks like it is covered in a thin layer of oil.Silky: The luster of silk.Adamantine: A hard, brilliant luster.
What is the texture of sulfur?
brittle solidCharacteristics: Sulfur is a soft, pale yellow, odorless, brittle solid.
What are sulfur characteristics?
Pure sulfur is a tasteless, odourless, brittle solid that is pale yellow in colour, a poor conductor of electricity, and insoluble in water. It reacts with all metals except gold and platinum, forming sulfides; it also forms compounds with several nonmetallic elements.
What is the luster of silicon?
Pure silicon is a hard, dark gray solid with a metallic lustre and with a octahedral crystalline structure the same as that of the diamond form of carbon, to which silicon shows many chemical and physical similarities.
Is silver a luster?
Silver (Ag) has a bright, metallic luster, and when untarnished, has a white color. It is rarely found in its native form. Silver can be found combined with a number of different elements such as sulfur, arsenic, antimony or chlorine to form a variety of minerals and ores, such as argentite, chlorargyrite, and galena.
What is metallic luster?
Metallic Luster: A mineral's luster is the general appearance of its surface in reflected light. There are two broad types of luster: metallic and nonmetallic. Metallic luster is that of an untarnished metal surface, such as gold, steel, copper, galena, pyrite, and hematite. Minerals with metallic luster can also be described as having a "shiny", ...
What minerals have a pearly luster?
In some cases, minerals, such as calcite and aragonite may display a pearly luster on cleavage cracks parallel and below the their reflecting surface. Many pearly minerals consist of thin, transparent co-planar sheets. Light reflecting from these layers give them a luster resembling that of a pearl.
What is the luster of adamantine?
Adamantine minerals possess a brilliant , superlative luster which is most notably observed in diamonds. Such minerals are transparent or translucent. Minerals with "true" adamantine luster are uncommon and thus are more valuable.
What is waxy luster?
Waxy Luster: . As the name implies, waxy minerals have a luster resembling the surface of a wax candle or beeswax. Examples include jade, carnelian, chalcedony (left photo), opal and turquoise. Such minerals have a translucent to opaque reflectivity and may come in a variety of colors.
What is resinous luster?
Resinous Luster: Resinous minerals have the appearance of resin, chewing gum or smooth-surfaced plastic. A common mineral that represents a resinous luster, such as the one in the left photo, is amber. Amber is simply a form of fossilized resin that sometimes contains insects, very small lizards, and pollen/spores.
What does azurite look like?
In some cases, earthy minerals look like dirt or dried mud, while others may be rough and porous in texture. Earthy luster may also look like unglazed pottery.
What is tiger eye luster?
This type of luster is best seen on rough specimens of tiger's eye. However, when polished, tiger's eye exhibits a silky-vitreous luster known as "silky sheen" lu ster.
What is the atomic number of sulfur?
What is Sulfur? Sulfur is a chemical element with an atomic number of 16 and an atomic symbol of S. At room temperature it is a yellow crystalline solid. Even though it is insoluble in water, it is one of the most versatile elements at forming compounds. Sulfur reacts and forms compounds with all elements except gold, iodine, iridium, nitrogen, ...
When was sulfur discovered?
The Chinese discovered sulfur in about 2000 BC, used it to make gunpowder in the 7th century, and used gunpowder to launch rockets, shoot projectiles, and make hand grenades in the 10th century. ADVERTISEMENT.
What are the largest minerals in sulfide ore?
Many of these are in fractures and cavities associated with sulfide ore mineralization. The largest are associated with evaporite minerals, where gypsum and anhydrite yield native sulfur as a product of bacterial action.
Where are the blue flames from?
Related: Blue Flames caused by burning sulfur, in this night scene from Kawah Ijen Volcano, located on the island of Java, Indonesia. The best way to learn about minerals is to study with a collection of small specimens that you can handle, examine, and observe their properties.
When did sulfur become the preferred spelling?
In 1990 the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry designated "sulfur" as the preferred spelling. How the word is spelled can often reveal the age and origin of publications and authors. ADVERTISEMENT. Information Sources.
Where does a sulfate ion occur?
It occurs in the dissolved ions of many waters. It is an important constituent of many atmospheric, subsurface, and dissolved gases. It is an essential element in all living things and is in the organic molecules of all fossil fuels.
Where is sulfur fumarole?
This fumarole on the island of Kunashir (in the Kuril Islands, northeast of the Japanese island of Hokkaido) has a significant accumulation of bright yellow sulfur.
Where are the fine sulfur crystals found?
A few drill cores from mining operations deep into the earth have in Texas and Louisiana have been found with fine Sulfur crystals on them, indicating that indeed excellent crystals within the earth are all but destroyed by the mining operations. COMMON MINERAL ASSOCIATIONS.
Where is sulfur found?
The fine specimens from Agrigento and Cattolico in Sicily, Italy, are highly sought by mineral collectors and command very high prices. Sulfur has many industrial uses.
What happens when sulfur is mined?
In mining, underground Sulfur deposits are flooded with hot water, causing the Sulfur to melt into a brine. The brine is pumped to the surface, where the water is evaporated and the sulfur recovered. Such mining operations destroy all specimens. Sulfur crystallizes in the orthorhombic system, but an uncommon monoclinic form of sulfur also exists. ...
Why is sulfur red?
The color may be altered if impurities are present. Clay and selenium impurities, as well as volcanic mixtures in sulfur can cause it to be slightly red, green, brown, or gray. Sulfur often occurs in petroleum deposit s, where it is found coated with greasy black petroleum. Sulfur is soft, light in weight, and very brittle.
What is a sulfate based substance used for?
It is used in the manufacture of black powder, matches and explosives. It is also used to create rubber, in dyes, and as an insecticide and fungicide. It is also used in the manufacturing of sulfuric acid. NOTEWORTHY LOCALITIES.
Is sulfur a polymorph?
This spelling variant is used in Great Britian and other English-speaking locations outside the United States. - Uncommon polymorph of Sulfur. Rosikyite crystallize s in the monoclinic system, whereas Sulfur crystallizes in the orthorhombic system. Other than that, they share the same properties.
Can sulfur be stored in water?
To prevent this, Sulfur should not be stored under humid conditions. It is best not to wash Sulfur specimens, as warm water can dissolve them. Sulfur also has the tendency to crack when exposed to mild heat, including body heat. It should be handled as little as possible, and kept out of light to avoid cracking.
What is submetallic luster?
Submetallic Luster. Some specimens exhibit a luster that falls short of being called "metallic" or makes the observer doubtful about using that adjective. The word submetallic might be used for these specimens. These specimens are usually opaque, and they are often black in color.
What crystals have silky luster?
Tiger's-eye, chrysotile ( serpentine ), tremolite, and ulexite can also exhibit a silky luster. The tourmaline crystals in the first image at the top of this page have a silky luster produced by parallel striations on prismatic crystals.
What is dull luster?
Specimens with a dull luster, sometimes described as an "earthy" luster, are non-reflective. They have a rough, porous, or granular surface that scatters light instead of reflecting light. Kaolinite, limonite, and some specimens of hematite have a dull or earthy luster.
What are the adjectives for luster?
These adjectives convey - in a single word - a property that can be important in the identification of a mineral. The luster of a material can also determine how it will be used in industry.
Why is a specimen not reflective?
Just because a specimen is highly reflective does not give it a metallic luster. It must also be opaque and exhibit the color of a metal. Opacity is an important part of a metallic luster. Light enters specimens that are transparent or translucent.
How to observe luster?
Luster is best observed under direct illumination. That allows the light that strikes the specimen to reflect to the eye of the observer. Proper examination includes moving the specimen (or the light source, or the head of the observer) through a range of angles to observe the full character of the luster.
What is the meaning of luster?
Luster is a word used to describe the light-reflecting characteristics of a mineral specimen. The luster of a specimen is usually communicated in a single word. This word describes the general appearance of the specimen's surface in reflected light. Eleven adjectives are commonly used to describe mineral luster.
