Do veins carry oxygenated blood to the heart?
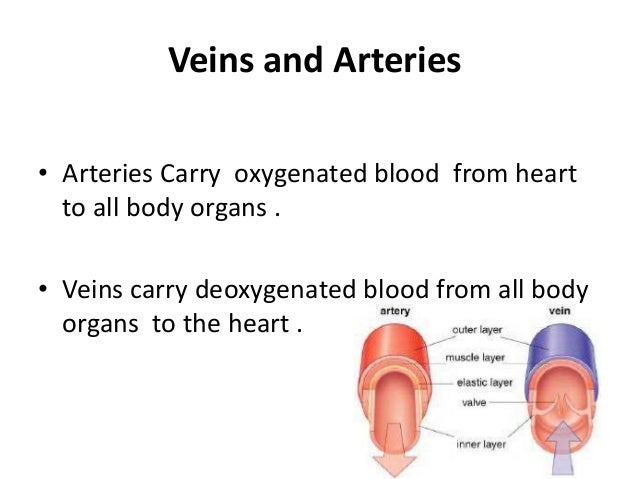
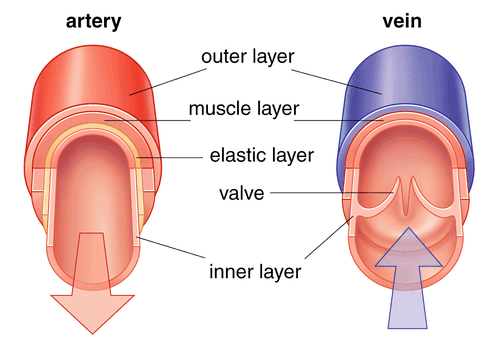
Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart. Your heart has a special electrical system called the cardiac conduction system.
Are veins oxygenated or deoxygenated?
Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart.
Do capillaries carry deoxygenated blood?
Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart. Likewise, do capillaries carry oxygenated blood? Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
What is the function of the great cardiac vein?
The distal portion of the coronary sinus commonly narrows to form the great cardiac vein. In most human hearts we have observed valves of Vieussen covering the ostium of the great cardiac vein. This cardiac vein returns deoxygenated blood (metabolic waste products) from the anterior surfaces of the left ventricle.

Do cardiac veins carry oxygenated blood?
The coronary arteries are responsible for carrying nutrient-rich, oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the myocardium; while the coronary veins take nutrient – poor deoxygenated blood away from the myocardium and to the right atrium.
Where does the great cardiac vein carry blood to?
Coronary sinusThe great cardiac vein, also called the anterior interventricular vein, is a large blood vessel found on the anterior (sternocostal) surface of the heart....Great cardiac vein.Drains fromSmall venules of the apex of heartDrains toCoronary sinusDrainage areaExternal layer of the myocardium of the ventricles and left atrium1 more row•May 11, 2020
What does the great cardiac vein supply?
Function: This cardiac vein returns deoxygenated blood (metabolic waste products) from the anterior surfaces of the left ventricle.
Does the coronary sinus carry oxygenated or deoxygenated blood?
deoxygenated bloodThe coronary sinus is a large vein that that returns deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle to the right side of the heart so that it can be replenished with oxygen.
Which of the following vessels carries oxygenated blood?
Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood.
What is the function of the cardiac vein?
Function: The cardiac veins returns deoxygenated blood (containing metabolic waste products) from the myocardium to the right atrium. This blood then flows back to the lungs for reoxygenation and removal of carbon dioxide.
What are the only arteries that carry oxygen poor blood in the body?
Important Arteries and Veins The pulmonary arteries carry oxygen-poor blood away from the heart to the lungs. These are the only arteries that carry oxygen-poor blood.
What veins drain into the great cardiac vein?
The lateral veins, also known as the left marginal veins or the obtuse marginal veins, course along the left side of the heart and drain the left ventricular myocardium into the great cardiac vein or coronary sinus [7].
Which vein empties deoxygenated blood into the right atrium?
Deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body enters the heart from the inferior vena cava while deoxygenated blood from the upper body is delivered to the heart via the superior vena cava. Both the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava empty blood into the right atrium.
Are coronary veins and cardiac veins the same?
Coronary veins are responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the myocardium into the cardiac chambers. Comprised of two venous systems, coronary veins classify into either the greater cardiac venous system or the smaller cardiac venous system.
What chamber of the heart contains deoxygenated blood?
right atriumThe left atrium and right atrium are the two upper chambers of the heart. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood returning from other parts of the body.
Does the superior vena cava carry oxygenated blood?
The superior vena cava collects deoxygenated blood from the venous system associated with the upper limbs, head, neck, and thorax. The superior vena cava terminates in the right atrium providing deoxygenated blood to the pulmonary circulation.
Where does the great cardiac vein start?
apex of the heartThe great cardiac vein (left coronary vein) begins at the apex of the heart and ascends along the anterior longitudinal sulcus to the base of the ventricles. Base and diaphragmatic surface of heart.
Where do the cardiac veins drain?
Venous Supply to the Heart. The great cardiac vein, the middle cardiac vein, and the small cardiac vein all drain into the coronary sinus (which opens into the right atrium). The anterior cardiac veins drain directly into the right atrium.
How many blood vessels carry blood away from the heart?
Secondly, how many blood vessels carry blood away from the heart? There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart the arterioles the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs the venules and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart.
Which organs carry oxygen and nutrients away from the heart?
The arteries carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body’s tissues. The veins take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Arteries begin with the aorta, the large artery leaving the heart. They carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body’s tissues.
How does the heart pump?
With each heartbeat, the heart sends blood throughout our bodies, carrying oxygen to every cell. After delivering the oxygen, the blood returns to the heart. The heart then sends the blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen. This cycle repeats over and over again.
Where does blood go after picking up oxygen?
After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the bodys tissues through the aorta.
What are the functions of blood vessels?
Because the functions of the blood vessels include supplying all organs and tissues of the body with oxygen and nutrients, removal of waste products, fluid balance, and other functions, conditions that affect the vascular system may affect the part of the body supplied by a particular vascular network, such as the coronary arteries of the heart.
How does blood flow in the circulatory system?
The blood moving through the circulatory system puts pressure on the walls of the blood vessels. Blood pressure results from the blood flow force generated by the pumping heart and the resistance of the blood vessel walls. When the heart contracts, it pumps blood out through the arteries. The blood pushes against the vessel walls and flows faster under this high pressure. When the ventricles relax, the vessel walls push back against the decreased force. Blood flow slows down under this low pressure.
Which system is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart?
The circulatory system is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart.
What Are The Effects Of Vascular Disease
Because the functions of the blood vessels include supplying all organs and tissues of the body with oxygen and nutrients, removal of waste products, fluid balance, and other functions, conditions that affect the vascular system may affect the part of the body supplied by a particular vascular network, such as the coronary arteries of the heart.
What Carries Freshly Oxygenated Blood From The Lungs To The Heart
As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The oxygenated blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
Publiez Sans Frais Des Ebooks Et Livres Brochs En Autodition Via Kindle Direct Publishing Et Touchez Des Millions De Lecteurs Sur Amazon
Tout de suite sur le marché. La publication prend moins de 5 minutes et votre livre apparaît dans les boutiques Kindle du monde entier dans les 24 à 48 heures.
What Makes The Heart Pump
Your heart has a special electrical system called the cardiac conduction system. This system controls the rate and rhythm of the heartbeat. With each heartbeat, an electrical signal travels from the top of the heart to the bottom. As the signal travels, it causes the heart to contract and pump blood.
Where Are Your Blood Vessels Located
There are blood vessels throughout your body. The main artery is your aorta, which connects to the left side of your heart. It runs down through your chest, diaphragm and abdomen, branching off in many areas. Near your pelvis, your aorta branches into two arteries that supply blood to your lower body and legs.
When Do Arteries Carry Oxygen Poor Blood
Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from your heart, and veins carry oxygen-poor blood back to your heart. In pulmonary circulation, though, the roles are switched. It is the pulmonary artery that brings oxygen-poor blood into your lungs and the pulmonary vein that brings oxygen-rich blood back to your heart.
Which Conditions Affect The Venous System
Many conditions can affect your venous system. Some of the most common ones include: