
Will a temporal CT scan show TMJ?
Will a temporal ct scan show tmj? Yes: Ct of temporal area of skull shows mastoids, ear contents, and tempomandibular joint. Gross bony abnormalities, subluxation, and arthritic changes (joint narrowing)in the joint can be detected. Sometimes images are done in open and closed mouth positions.
What is the TMJ concepts CT scanning protocol?
TMJ Concepts CT Scanning Protocol This protocol is to ensure that accurate 3D bone models can be created and used for the design and manufacture of - patient-fitted temporomandibular joint prostheses. does not define the use of It or parameters for cone beam scanners. Consult with TMJ Concepts regarding cone beam scanning parameters.
What is the role of imaging in the evaluation of TMJ?
CONCLUSION. TMJ imaging is an adjunct to the clinical examination and provides useful information about the joint components. When selecting a TMJ imaging technique, the clinician must determine what type of information is needed from the imaging study and whether that information will affect patient management.
How do I perform a TMJ scan?
• Take a scout view and locate the first slice position. Make sure the head is positioned symmetrically so that the first slice is positioned correctly for both the left and right TMJ. • Start the scan so that it includes both the sella and nasion.
How do doctors test for TMJ?
If your doctor or dentist suspects a problem, you may need: Dental X-rays to examine your teeth and jaw. CT scan to provide detailed images of the bones involved in the joint. MRI to reveal problems with the joint's disk or surrounding soft tissue.
Can TMJ be seen on xray?
A panoramic radiograph is considered a “screening” projection and is often used in combination with other hard tissue imaging techniques to image the TMJs. 4 (Fig 1a). It gives an overview of the jaws and teeth, allowing evaluation of mandibular symmetry, the maxillary sinuses and the dentition.
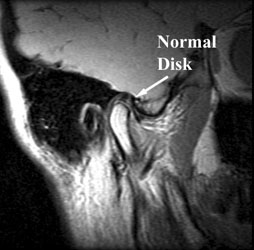
Can you see TMJ on an MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the best diagnostic tools for identification of TMJ pathology, allowing evaluation of TMJ disc position, morphology, mobility, extent of joint degenerative changes, inflammation, and presence of connective tissue/autoimmune diseases.
What is the importance of imaging techniques like CT and MRI in the evaluation of TMJ disorders?
MR imaging and enhanced CT allows for an accurate evaluation of the relationship between the masticatory muscle spaces and the TMJ, as well as the surrounding structures, such as the parotid gland, skull base, and parapharygeal space [149], [150].
What can be mistaken for TMJ?
Conditions That May Be Mistaken for TMJ DisorderTrigeminal Neuralgia. Just as you have two temporomandibular joints on each side of the face, you also have two trigeminal nerves that control your jaw. ... Cluster, Migraine, or Tension Headaches. ... Sinus Issues. ... Other Causes of TMJ Pain.
Where is TMJ pain felt?
TMJ-related jaw pain can be felt at the temples and it may extend all the way down to the sides of the upper jaw and beyond. Sometimes instead of pain, patients experience a feeling of discomfort, often described as feeling as if their jaw is out of alignment.
Should I see a dentist or ENT for TMJ?
One of the first people to notice or diagnose a TMJ disorder is usually your dentist. However, your family physician, an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist, or an oral surgeon can also diagnose and treat your TMJ. Typically, your doctor will check your jaw joints for pain and tenderness.
What is a good muscle relaxer for TMJ?
There are many potential muscle relaxants that can be used for TMJ. Two of the most common are cyclobenzaprine (Amrix and Fexmid) and diazepam (Valium).
Can anxiety cause TMJ pain?
Stress & Anxiety Can Lead to TMJ Disorder Dr. Meyer explains that temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ) can develop over time. This is as a result of restless, stress-induced sleep where you are grinding your teeth and jaw clenching unconsciously.
What is the best imaging modality to assess the TMJ disc?
Cone beam CT provides high-resolution multiplanar reconstruction of the TMJ, with a low radiation dose, without superimposition of the bony structures. MRI is a noninvasive technique, considered to be the gold standard in imaging the soft tissue components of the TMJ.
How do I know if my ear pain is TMJ?
TMJ won't cause discharge from your ears, so that's a definite sign of an infection. Remember: discharge may come from your outer ear or through your eustachian tubes. But TMJ is more likely if: Your doctor says you don't have an ear infection.
How is arthritis of the jaw diagnosed?
Jaw bone and cartilage changes due to arthritis may be seen on imaging tests such as an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI. “Changes that can be visualized on imaging include condylar beaking or flattening [damage to the rounded end part of the bone], and decreased joint space,” Dr. Levi says.
Can you see TMJ on panoramic xray?
A panoramic x-ray, or pan, is an x-ray that shows the dentist your entire jaw, all of your teeth and the structures that surround them. The dentists are able to see the location of major nerves, your sinuses, developing teeth and pathologies. They can look at your jaw joint (TMJ) and the bones of your mouth.
How do you XRAY TMJ?
1:134:01Radiographic Positioning of the TMJs - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipStart with the patient's head lateral to the image receptor Center at a point 1/2 inch anterior toMoreStart with the patient's head lateral to the image receptor Center at a point 1/2 inch anterior to the EAM. And to the ir in other words the TMJ of interest.
How do you fix TMJ disc displacement?
Less frequently, the disk remains displaced and jaw opening is restricted. Diagnosis is based on history and physical examination. Treatment is with analgesics, jaw rest, muscle relaxation, physical therapy, and oral appliance therapy. If these methods fail, surgery may be necessary.
How does TMJ surgery work?
The surgery begins with an incision (above and below the ear) to expose and remove the defective TMJ. The artificial TMJ is then inserted. During the surgery, the surgeon may remove bony growths, excess tissue or some of the diseased bone.
Kalo Well known member
I have not posted in a while. I doubt anyone can give me help. But, I just need some type of response.
AllyC New Member
I have not posted in a while. I doubt anyone can give me help. But, I just need some type of response.
Kalo Well known member
AllyC, Thank you for your reply. Can I ask a question, does your husband have any abdnormalities in his jaw joint. That sad thing is my MD said that it's only going to get worst from here on out...That ass gave me a nocebo...
AllyC New Member
AllyC, Thank you for your reply. Can I ask a question, does your husband have any abdnormalities in his jaw joint. That sad thing is my MD said that it's only going to get worst from here on out...That ass gave me a nocebo...
Andy Bayliss TMS Coach & Beloved Grand Eagle
Why does this problem to mostly happen to women? There is theories that estrogen has a lot to do with it...But I think the TMJ.org is reaching....Because there is no answer....
Kalo Well known member
For me I can handle TMJ if it were muscular in nature. But I hear a crepitus (sand grinding) clicking and popping in that jaw that happened after I chewed gum...When I got the CT scan and saw that the condyle was pulled forward, it's kind of hard not to believe that it isn't structural.
MindBodyPT Beloved Grand Eagle
For me I can handle TMJ if it were muscular in nature. But I hear a crepitus (sand grinding) clicking and popping in that jaw that happened after I chewed gum...When I got the CT scan and saw that the condyle was pulled forward, it's kind of hard not to believe that it isn't structural.
What is CT for TMJ?
CT techniques have a distinct advantage over conventional tomography in that large areas can be imaged in one scan and reformatting can be made in multiple planes chosen by the clinician, providing three-dimensional information about the osseous structures. This is particularly valuable for TMJ imaging, since in addition to the TMJs, the remainder of the jaws as well as the skull base can be evaluated. The scan can be done at various mandibular positions, as with conventional tomography. CBCT is rapidly growing in popularity and is starting to replace conventional tomography for many dental imaging applications. It is currently used for TMJ imaging, pre-surgical implant imaging, orthodontic imaging including localization and orientation of impacted teeth, airway analysis and for a wide range of oral surgery applications. This technique is useful for visualizing osseous detail of the TMJs, including evaluation of osseous ankylosis, neoplasms, heterotopic bone growth and other abnormalities in and around the joints which may not be as well visualized with conventional tomography.2 CBCT is not suitable for patients unable to remain motionless for the duration of the scan. A disadvantage of the technique is volume averaging, which results in artifacts that may simulate erosions on small curved cortical bone surfaces.3
How to image TMJ?
The film and x-ray source are in motion, which blurs structures that are not in a predetermined plane of focus. The joints can be imaged in different orientations, achieving the aim of producing views perpendicular to each other. Tomography may be carried out using conventional tomography or by computed tomography.
What is TMD in dentistry?
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD) can affect a significant portion of the population.1 Clinical symptoms may include one or more of the following: pain in the region of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), headaches, earaches, muscle tenderness, joint noises such as clicking, popping or grating, limited opening or deviation of the mandible on opening/closing, locking, and occlusal changes due to alteration in mandibular positioning. Evaluation of TMD begins with a thorough patient history and clinical examination. In some cases, the clinical examination findings are sufficient to allow the dentist to arrive at a preliminary diagnosis and begin conservative treatment. However, other patients will require diagnostic imaging of the TMJs in order to provide information, which is not available from the clinical examination.
What is hard tissue imaging?
Interpretation of the hard tissue imaging study includes evaluation of condylar and temporal component morphology and integrity of bony articulating surfaces. The TMJs are assessed for signs of remodeling, degenerative joint disease or morphological variations affecting the TMJs, jaws or skull. Condylar position in intercuspation and at maximum opening is evaluated and structures further removed from the TMJs are evaluated if they are included in the study.
What is CBCT scan?
An exciting advance in CT technology is cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), which is particularly suited to imaging hard tissues of the skull and jaws. The patient is exposed to a round or rectangular cone-shaped x-ray beam, which scans the patient’s head in one 360-degree rotation.8 The transmission data is captured by a two-dimensional sensor. During the scan, which may take from 17 seconds to over a minute to perform, 360 exposures or projections are made, one for each degree of rotation. The raw data is then reconstructed and reformatting of this reconstruction allows for two-dimensional or three-dimensional images in any selected plane to be made (Fig. 4). A major advantage of this technique is that one CBCT scan only delivers between 3-20 percent of the radiation dose of a conventional CT scan.9 Furthermore, the dose from a single CBCT scan may be the equivalent of as few as four film-based panoramic radiographs and may be less than the effective dose of a 19-film full mouth intraoral film series.10
Why do we use soft tissue imaging?
Soft tissue imaging is indicated when information about disk position or morphology is needed or to image abnormalities in the surrounding muscles or soft tissues.
What is computed tomography?
Computed tomography (CT) is a more sophisticated digital tomographic technique where the patient is exposed to a fan-shaped x-ray beam directed to a series of detectors. The detectors and/or the x-ray beam move around the patient, usually in the axial plane, to acquire numerous projections at various angles. The transmission data from these projections is used to reconstruct the image, which is viewed on a computer monitor. Further manipulation can be done to reformat images in various orientations for viewing (Fig. 3). CT has several advantages over conventional tomography: there is no superimposition of structures outside the area of interest, contrast resolution is improved so that tissues with small differences in density can be distinguished, data from one imaging study can be viewed in various planes and three-dimensional images can be constructed. If the scan inc#N#ludes the rest of the skull, the need for additional cephalometric plain film views may be eliminated.
Why not see TMJ?
Yes why not see TMJ is a synovial joint of the condylar variety. So mainly the head of the Mandible, meniscotemporal compartment ie part of the temporalis bone with in posterior supported by tympanic plate. All the hard tissues components of the TMJ is clearly visible on X ray it depends how you read it.
What is the TMJ?
The TMJ is a single plane rotational joint until you are open more than around one finger’s width at the incisors, then the condyles translate and slide up the eminences allowing much wider opening. If you posture to the left or right then the process occurs asymmetrically, one joint can have condyle in fossa, the other can be translated up the eminence.
Where is the TMJ innervation?
Sensory innervation of the TMJ is delivered primarily through Auriculotemporal branch of the 3rd Dvision of the Trigeminal nerve.
Does TMJ show up on x-rays?
Yes the temporomandibular joint TMJ as a bony joint does show up on x-ray.
What molars did they remove without pain?
You had a Upper Right 3rd molar extractions. And they did it without you feeling any pain.
Is TMJ visble on MRI?
Not only that TMJ is also quite visble in the MRI scans which are being done in many cases of road accidents and TMJ fracture for better view of point
Can you spot diagnose TMJ?
You are somewhat open in the radiograph, so there is already some slide of the condyles up the eminence. It isn’t possible to do a spot diagnosis based on an x-ray.
