How does stress cause inflammation?
Your immune system sends chemical messengers to the site of the infection in order to fend off whatever is attacking you and return your body to health. However, in the case of trauma or chronic stress, it seems that your body's stress response system gets dysregulated, resulting in inflammation becoming chronic.
What is inflammation and why is it important?
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injuries or infections. It is a vital part of the human immune system as it acts as a defence and healing mechanism. There are generally two types of inflammation — acute and chronic inflammation. Acute or short-term inflammation results in pain or swelling that typically lasts for a few days.
Is PTSD a systemic illness linked to trauma?
The more we have inflammation in our body, the more easily we are overwhelmed by stress. Flory and Yehuda (2018) proposed that if inflammation markers are an extension of trauma-related outcomes and lead to medical illnesses, then PTSD should properly be understood as a systemic illness linked to psychological trauma.
What are the factors that can cause acute inflammation?
Some factors and infections that can lead to acute inflammation include: 1 acute bronchitis, appendicitis and other illnesses ending in “-itis” 2 an ingrown toenail 3 a sore throat from a cold or flu 4 physical trauma or wound

Can emotional trauma cause inflammation?
There is considerable evidence that psychological stress can activate the inflammatory response.
How does trauma affect inflammation?
Traumatic stress disorder, mainly PTSD, is related to the immune response, including increases in inflammatory factors and decreases in anti-inflammatory factors. In addition, it has been demonstrated that PTSD and immune diseases have a common genetic basis at the gene expression level.
What injuries cause inflammation?
Some of the most common injuries that can result in inflammation include:Runner's knee.ACL injuries.Meniscal injuries.Achilles tendon injuries.Tennis elbow.Golfer's elbow.UCL injuries.Rotator cuff tears.More items...
Can an injury cause systemic inflammation?
Severe injury is associated with the Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS). This response starts within thirty minutes of a major injury, and is an inflammatory response to blood loss and tissue damage rather than infection.
How trauma affects your immune system?
Following trauma, the immune system is exposed to a large amount of tissue damage and endogenous antigens, including alarmins, and cell debris are likely released from necrotic cells and tissue. There may also be significant exposure to microbial molecules that are part of the microbiome [36].
How do I rid my body of inflammation?
Follow these six tips for reducing inflammation in your body:Load up on anti-inflammatory foods. ... Cut back or eliminate inflammatory foods. ... Control blood sugar. ... Make time to exercise. ... Lose weight. ... Manage stress.
How long does it take for inflammation to go away?
Acute inflammation should go away within a few days, unless it's left untreated. If you're experiencing any signs of long-term inflammation, make an appointment with your doctor. They can run some tests and review your symptoms to see if you need treatment for any underlying conditions.
What causes high inflammation?
Possible Causes The most common reasons for chronic inflammation include: Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus, where your body attacks healthy tissue. Exposure to toxins, like pollution or industrial chemicals. Untreated acute inflammation, such as from an infection or injury.
How does trauma stimulate inflammation?
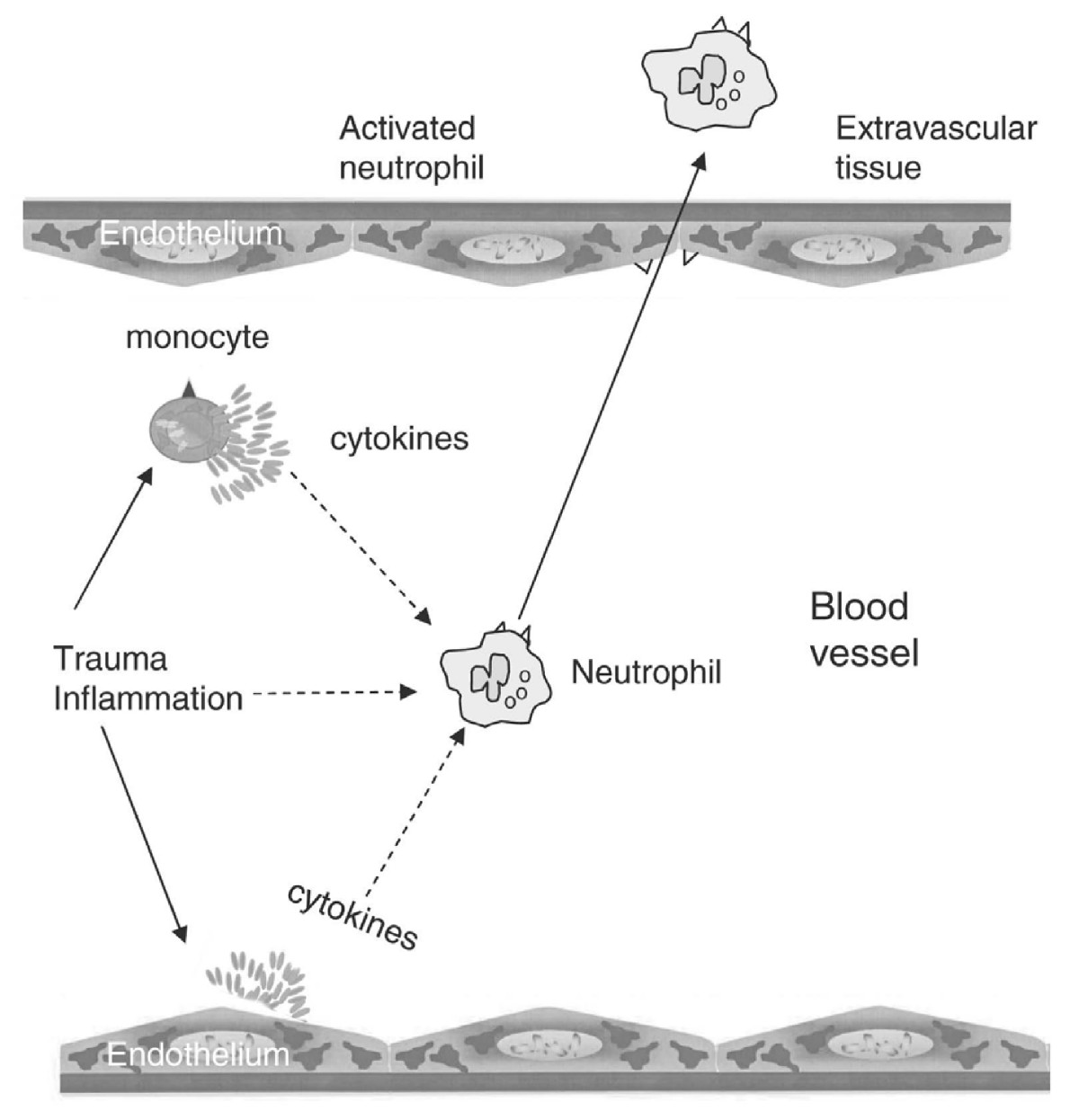
Major trauma induces an inflammatory response initially characterized by increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines and activation of neutrophils. This pathophysiological inflammatory response is determined not only by genetic disposition, physiological states, the type and amount of injury, but also by surgery.
How can trauma cause infection?
Trauma can cause deficits in the immune system by depressing the humoral and cell-mediated systems. After major trauma, the function of lymphocytes is depressed. The neutrophil chemotaxis is decreased and monocyte antigen presenting capacity is impaired. There are also changes in complement components.
Can PTSD cause swelling?
People with post-traumatic stress disorder often have signs of inflammation in the body. But even though psychotherapy reduced their stress level, the inflammation became worse, shows new study. The immune system and mental health disorders are linked.
What causes neuroinflammation?
Neuroinflammation refers to the process whereby the brain's innate immune system is triggered following an inflammatory challenge such as those posed by injury, infection, exposure to a toxin, neurodegenerative disease, or aging.
How does trauma lead to inflammatory response?
How trauma leads to inflammatory response: Mitochondria may be at root of dangerous complications from injury. A new study suggests that mitochondria can be released into the bloodstream following physical injury, resulting in a sepsis-like immune response, and leading to the onset of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
What cells can attack the body?
Hauser, whose laboratory studies focus on neutrophils, circulating white blood cells that can attack the body's organs, wanted to find out how neutrophils might be participating in this dangerous inflammatory cascade.
What are damage-associated cellular patterns?
Some normally intra-cellular molecules can activate PRR, and when they do they are called Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns , or DAMPS. Hauser hypothesized that DAMPs might be triggering inflammatory responses after trauma in the same way that PAMPs triggered inflammation in the face of infection -- and that mitochondria might be ultimately responsible.
What is the mechanism of sepsis?
The mechanisms that underlie both SIRS and sepsis are rooted in the body's "innate immune" response. Unlike "acquired immunity," which develops over time, innate immunity is present from birth, ready to immediately respond whenever immune cells encounter molecular patterns typical of external pathogens such as bacteria or viruses. These "pathogen-associated molecular patterns," or PAMPS, are in turn, detected by pattern recognition receptor molecules (PRR).
Is inflammation a serious condition?
Share: FULL STORY. Inflammation is at the root of most serious complications occurring after both infection and injury. But while the molecular course of events that leads from microbial infections to the inflammatory condition called sepsis is fairly well understood, it is far less clear how and why physical injury can result in ...
What happens when you have PTSD?
However, if you have PTSD, the intensity of the trauma or your body's reactions to it seems to disrupt the workings of this system. As a result, the parasympathetic nervous system under-reacts and doesn't put the brakes on, leaving you in a hyper-activated, sympathetically dominant state.
What is the reaction of the immune system to a virus?
Inflammation is a normal reaction of your immune system to harmful bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens. Your immune system sends chemical messengers to the site of the infection in order to fend off whatever is attacking you and return your body to health.
What is PTSD in psychology?
Post-traumatic stress disorder ( PTSD) is a complex mental health condition that results from exposure to life-threatening or injurious events. The characteristic symptoms of PTSD include intrusive thoughts, feelings, images, or dreams, avoiding feelings or things that remind you of the trauma, anxiety or anger and bodily signs of tension, and changes in thoughts and/or mood. A subset of people with PTSD experience dissociation —a feeling that they are not present, out of their bodies, or that things are not real.
Does PTSD cause inflammation?
A review of research studies linking inflammation to PTSD found evidence of chronic inflammation in people with PTSD, compared to controls (either people not exposed to trauma or people exposed to trauma but who did not get PTSD). Chronic, low-grade inflammation was measured by immune markers, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and white blood cells (specifically, the cytokines C-Reactive Protein, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ, T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. Elevated inflammatory markers are known risk factors for cardiovascular, metabolic, musculoskeletal, dermatological, and pulmonary diseases. These diseases are also known to be elevated in people with PTSD. Chronic inflammation has also been linked to depression, and people with PTSD have high rates of co-morbid depression as well.
Is PTSD a chronic illness?
As we learn more about this disorder, we are finding out that people with PTSD or who have a lot of exposure to trauma also have more chronic medical conditions that those of us who haven't experienced traumas. Researchers have proposed that there is a common mechanism linking the physical and psychological components of PTSD — chronic, low-grade inflammation.
Is PTSD a reaction to trauma?
Although more work needs to be done, current research supports the idea that PTSD is a reaction to trauma that has long-lasting effects on the way our bodies deal with and recover from stress and on our long-term immunity.
Does PTSD affect the immune system?
PTSD also seems to interfere with the normal feedback loop regulating cortisol. Because cortisol communicates with the immune system, this can create a situation where inflammation gets out of control. Your immune system keeps producing substances called inflammatory cytokines that are designed to attack pathogens. These cytokines seem to stick around, even when there is no pathogen present, putting your immune system in a state of overdrive.
How does inflammation affect the body?
Inflammation is an essential part of your body’s healing process. It occurs when inflammatory cells travel to the place of an injury or foreign body like bacteria. If inflammatory cells stay too long, it may lead to chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a symptom of other health conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Your healthcare provider may recommend medication or at-home management. You can reduce inflammation by eating anti-inflammatory foods and managing stress.
How long does it take for inflammation to heal?
Inflammation does not always require treatment. For acute inflammation, rest, ice and good wound care often relieve the discomfort in a few days.
What happens when your body activates your immune system?
When your body activates your immune system, it sends out inflammatory cells. These cells attack bacteria or heal damaged tissue. If your body sends out inflammatory cells when you are not sick or injured, you may have chronic inflammation. Inflammation is a symptom of many chronic diseases, such as arthritis or Alzheimer’s disease.
What is the first response of the immune system?
Your immune system sends out its first responders: inflammatory cells and cytokines (substances that stimulate more inflammatory cells).
What diet should I follow for inflammation?
You may choose to follow an anti-inflammatory diet. Some research shows that people who follow a Mediterranean diet have lower levels of inflammation in their bodies.
What supplements can help with inflammation?
Supplements: Certain vitamins (vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin D) and supplements (zinc) may reduce inflammation and enhance repair. For example, your healthcare provider may prescribe a fish oil supplement or vitamin (s). Or you may use spices with anti-inflammatory properties, such as turmeric, ginger or garlic.
What is the response to sudden body damage such as cutting your finger?
Acute inflammation: The response to sudden body damage, such as cutting your finger. To heal the cut, your body sends inflammatory cells to the injury. These cells start the healing process.
Why is inflammation important?
Inflammation is a defense mechanism triggered in the body when it recognizes an attack and gathers special resources in response. It’s a requirement for survival. For example, the red soreness that appears around an infected wound is an inflammatory response essential to isolating invaders and ensuring their destruction before they spread. The body responds with inflammation to a wide variety of threats, including not only infections, but also irritants, stress and physical trauma.
How does inflammation affect emotions?
There is growing evidence on many fronts that inflammation affects how we feel. This influence is exerted through many systems, including the immune system, metabolism, sleep, stress responses, cognitive thinking, memory, expression, impulse control, mood, clarity, and more. Much remains to be learned about the mechanisms and effects of inflammation, but the existence of a linkage between inflammation and these many systems, each a key element of emotional functioning, is now indisputable.
How to reduce PTSD symptoms?
Interventions should include things like physical activity, acupuncture, meditation, yoga, anti-inflammatory diet, which may mitigate PTSD symptoms by reducing inflammation. Causes of Inflammation. Many variables can trigger inflammation and initiate mental and physical symptoms: Short and long term exposure to stress.
How does stress affect the immune system?
The mechanism seems to be that stress hormones affect the organisms living in the gut and their balance with each other. Gut imbalance can lead to damage in the lining of the gut (known as “leaky gut”). As a result toxins and bacteria “leak" through the intestines and enter the bloodstream. This triggers a reaction of the immune system: inflammation.
How does the gut affect the brain?
According to Gershon, our gut and its environment play an important role in how we feel. When the gut is not functioning well , communication between the gut and the brain in our head suffers. Our physical and emotional health suffer as a result.
Does stress affect the gut?
The mechanisms for these effects are complex and much remains to be learned. Werbner et al (2019) suggested that stress causes changes in the activity of the gut. These changes trigger immune responses from the body that can include an inflammation “attack” of the body against itself.
Is there research on inflammation?
There’s a lot of research on inflammation now underway. Here are a few areas of research that I find particularly interesting for people with mental health symptoms and their clinicians:
What happens when inflammation is present in the body?
When inflammation is present in the body, there will be higher levels of substances known as biomarkers.
What is the role of inflammation in the body?
Inflammation is part of the body’s defense mechanism and plays a role in the healing process. When the body detects an intruder, it launches a biological response to try to remove it. The attacker could be a foreign body, such as a thorn, an irritant, or a pathogen. Pathogens include bacteria, viruses, and other organisms, which cause infections.
How long does it take for inflammation to show?
Signs of acute inflammation can appear within hours or days, depending on the cause. In some cases, they can rapidly become severe. How they develop and how long they last will depend on the cause, which part of the body they affect, and individual factors.
How to tell if you have acute inflammation?
Acute inflammation. An injury or illness can involve acute, or short-term, inflammation. There are five key signs of acute inflammation: Pain: This may occur continuously or only when a person touches the affected area. Redness: This happens because of an increase in the blood supply to the capillaries in the area.
What causes pain in the body?
Pain results when the buildup of fluid leads to swelling, and the swollen tissues push against sensitive nerve endings.
What is the genetic factor that affects the immune system?
Autoinflammatory diseases: A genetic factor affects the way the immune system works, as in Behçet’s disease. Persistent acute inflammation: In some cases, a person may not fully recover from acute inflammation. Sometimes, this can lead to chronic inflammation.
Can inflammation cause diabetes?
Sometimes, the body mistakenly perceives its own cells or tissues as harmful. This reaction can lead to autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes. Experts believe inflammation may contribute to a wide range of chronic diseases. Examples of these are metabolic syndrome, which includes type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.