
Precautions
Valproic acid (VPA) is an organic weak acid, while its conjugate base is called valproate. The sodium salt of the acid is called sodium valproate and a coordination complex of the two is known as divalproex sodium (DVP). Pharmacokinetically, VPA is very similar, but not the same as DVP. DVP is also an enteric-coated (coated for stomach protection) ester preparation of VPA.
Is valproate and valproic acid the same?
What medication causes low sodium? Medications that increase your risk of hyponatremia include thiazide diuretics as well as some antidepressants and pain medications. In addition, the recreational drug Ecstasy has been linked to fatal cases of hyponatremia. Conditions that decrease your body's water excretion.
What drugs cause low sodium?
Complications. Acute valproate toxicity results in dose-related and reversible hepatotoxicity. Stopping the drug therapy usually results in normalization of liver function abnormalities, but idiosyncratic fulminant hepatic failure and death have been reported with valproate toxicity.
What are complications of Valproate toxicity?
Sodium valproate is a commonly used anticonvulsant. It is widely recognized that valproate can cause hyperammonemia, particularly in people with underlying liver disease. Patients with urea cycle disorders are genetically predisposed to this adverse event and can develop severe hyperammonemia if given valproate.
Can valproate cause liver disease?
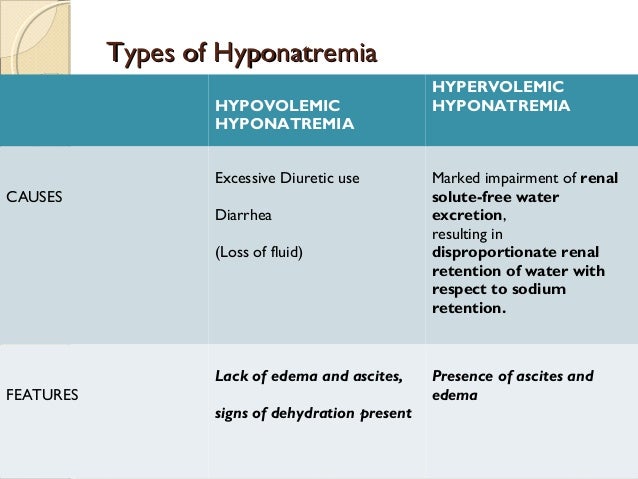
Does sodium valproate cause hyponatremia?
Administration of high doses of the mood stabilizer and antiepileptic drug sodium valproate can cause an SIADH-like syndrome with hyponatremia. We recommend that sodium levels be monitored regularly during administration of high doses of sodium valproate.
Which is major side effect of valproic acid?
Taking too much valproic acid can lead to symptoms such as: feeling or being sick (nausea or vomiting) headaches, or feeling dizzy. muscle weakness.
What medications cause hyponatremia?
Known offenders include acetazolamide, amiloride, amphotericin, aripiprazole, atovaquone, thiazide diuretics, amiodarone, basiliximab, angiotensin II receptor blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, bromocriptine, carbamazepine, carboplatin, carvedilol, celecoxib, cyclophosphamide, clofibrate, desmopressin, ...
Which mood stabilizer causes hyponatremia?
Mood stabilizers such as carbamazepine/ oxcarbazepine, valproate, and lamotrigine have been shown in several studies to cause hyponatremia;16,17 however, reports are limited for lamotrigine-induced hyponatremia and SIADH.
What is the problem with sodium valproate?
Many people can take sodium valproate safely for many months or years. However, there are potential side effects that can happen over a long time. Long-term treatment with sodium valproate can cause osteoporosis and osteopenia (increasing your risk of breaking a bone).
Is valproic acid a high risk medication?
A very small number of people who take valproic acid develop life-threatening disorders. Children younger than 2 years of age and other people who are taking more than one seizure medicine have the greatest risk. See Serious side effects.
What is the most common cause of hyponatremia?
What causes hyponatremia? In general, having too much water in your body is usually the main problem. The excess water dilutes the sodium levels. Much less frequently, hyponatremia is due to significant sodium loss from your body.
What antidepressants can cause hyponatremia?
All antidepressants except mianserin are associated with hyponatremia. The association is strongest with citalopram and lowest with duloxetine, venlafaxine and mirtazapine.
What is a dangerously low sodium level?
Hyponatremia occurs when your blood sodium level goes below 135 mEq/L. When the sodium level in your blood is too low, extra water goes into your cells and makes them swell. This swelling can be dangerous especially in the brain, since the brain cannot expand past the skull.
Why do antipsychotics cause hyponatremia?
Like other psychotropic medications, it is suspected that atypical antipsychotics can induce hyponatremia by either stimulating antidiuretic hormone release from the brain or enhancing antidiuretic hormone activity in the kidneys [13].
Does gabapentin cause hyponatremia?
Recently, other AEDs, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam and gabapentin have also been reported to cause hyponatremia. Understanding the risk associated with AED-induced hyponatremia and taking effective measures to combat serum sodium imbalance induced by AED therapy are necessary.
Does Seroquel cause hyponatremia?
Quetiapine-associated hyponatremia is extremely uncommon and only a few, relevant reports can be found in the literature. This case underlines the fact that patients on antipsychotic medication and more specifically on quetiapine should be closely monitored and routinely tested for electrolyte disorders.
Which is major side effect of valproic acid Mcq?
More common reactions that have been reported in patients using valproic acid are headache, abdominal pain, somnolence, dizziness, thrombocytopenia, asthenia, nausea & vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, tremor, weight changes, alopecia, constipation, emotional lability, insomnia, petechiae & ecchymosis, depression, rash, ...
What is valproate toxicity?
In patients with a severe overdose of valproate, patients can present with hypotension, tachycardia, respiratory depression, metabolic acidosis, cerebral edema, and valproate-related hyperammonemic encephalopathy which may progress to coma and death, if not treated aggressively.
Is jaundice a side effect of valproic acid?
Valproate hepatotoxicity varies in severity from minimal and asymptomatic ALT elevations to severe liver injury with progressive jaundice, hepatic synthetic dysfunction, coma and death. Monitoring of symptoms and serum aminotransferase levels is recommended for children for the first 6 months of valproate therapy.
Does valproic acid cause tardive dyskinesia?
Sodium valproate, which may increase brain GABA, moderately recuded tardive dyskinesia with doses of 900--3000 mg/day, as measured by a tremorgraph and rating scales. There was no correlation between dosage, blood levels, or clinical response.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not use valproic acid if you are allergic to it, or if you have: 1. liver disease; 2. a urea cycle disorder; or 3. a genetic mitochondri...
How Should I Take Valproic acid?
Follow all directions on your prescription label and read all medication guides or instruction sheets. Your doctor may occasionally change your dos...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Take the medicine as soon as you can, but skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next dose. Do not take two doses at one time.
What Should I Avoid While Taking Valproic acid?
Drinking alcohol may increase certain side effects of valproic acid.Avoid driving or hazardous activity until you know how this medicine will affec...
Valproic Acid Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction (hives, difficult breathing, swelling in your face or throat) or a severe skin...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Valproic acid?
Sometimes it is not safe to use certain medications at the same time. Some drugs can affect your blood levels of other drugs you take, which may in...
How long does it take for valproate to cause hepatotoxicity?
Oral route (Capsule, Delayed Release) Hepatotoxicity (some cases fatal), usually occurring during the first 6 months of treatment, has been reported in patients receiving valproate and its derivatives.
Is Valproate sodium safe for children?
Hepatotoxicity (some cases fatal), usually occurring during the first 6 months of treatment, has been reported in patients receiving valproate and its derivatives. Children younger than 2 years and patients with hereditary mitochondrial disease are at a considerably increased risk of developing fatal hepatotoxicity . For these patients under 2 years, valproate sodium should be used with extreme caution as a sole agent. Use is contraindicated in patients with known mitochondrial disorders caused by mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma (POLG) mutations and in children younger than 2 years in which mitochondrial disorder is clinically suspected. Failure of other anticonvulsants is the only indication for divalproex sodium in patients older than 2 years with hereditary mitochondrial disease. Perform POLG mutation screening as clinically indicated. Monitor patients closely and perform liver function tests prior to therapy and at frequent intervals thereafter, especially during the first 6 months. Valproate can impair cognitive development with prenatal exposure and produce major congenital malformations, particularly neural tube defects (eg, spina bifida). Valproate is contraindicated for prophylaxis of migraine headaches in pregnant women and women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraception. Valproate should not be administered to a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed or are otherwise unacceptable. Effective contraception should be used in such situations. Life-threatening pancreatitis has been reported in both children and adults receiving valproate. Cases have occurred shortly after initiation as well as several years after use. If pancreatitis is diagnosed, valproate should ordinarily be discontinued.
What are the side effects of a syringe?
The most commonly reported side effects at the start of therapy include nausea, vomiting, and indigestion; these effects are usually transient. Sedative effects occur most often in patients receiving combination therapy. [ Ref]
What are the symptoms of a swollen stomach?
multiple swollen and inflamed skin lesions. muscle pain or stiffness. muscle tension or tightness. normal menstrual bleeding occurring earlier, possibly lasting longer than expected. numbness of the feet, hands and around mouth. pains in the stomach, side, or abdomen, possibly radiating to the back.
Is valproate contraindicated for migraines?
Valproate is contraindicated for prophylaxis of migraine headaches in pregnant women and women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraception. Valproate should not be administered to a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed or are otherwise unacceptable.
Is POLG contraindicated?
Use is contraindicated in patients with known mitochondrial disorders caused by mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma (POLG) mutations and in children younger than 2 years in which mitochondrial disorder is clinically suspected.
Can you give a woman valproate?
Valproate should not be administered to a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable. In such situations, effective contraception should be used.
Is valproic acid an antiepileptic?
Valproic acid is an antiepileptic drug which has been approved for the treatment of the primary form of generalized epilepsy and for the treatment of the secondary form of generalized epilepsy and partial epilepsy if other antiepileptics do not have a positive effect [1].
Does valproic acid cause SIADH?
The mechanism of hyponatremia and SIADH due to valproic acid is not clear. One hypothesis postulates that valproic acid has a direct effect on tubular cell function, because a few cases of tubular dysfunction (Fanconi syndrome) in association with valproic acid with a positive dechallenge have been described [4].
What is valproic acid?
Valproic acid is used to treat various types of seizure disorders. Valproic acid is sometimes used together with other seizure medications.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
What is the name of the disease that causes a child to die?
a urea cycle disorder; or. a genetic mitochondrial (MYE-toe-KON-dree-al) disorder such as Alpers' disease or Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome, especially in a child younger than 2 years old. Valproic acid can cause liver failure that may be fatal, especially in children under age 2 and in people with liver problems caused by a genetic mitochondrial ...
What to do if you notice a capsule shell in your stool?
Tell your doctor if you notice a capsule shell in your stool that was not absorbed or melted in the body. Your blood levels of valproic acid may need to be checked. You may need frequent blood tests. If you need surgery, tell the surgeon ahead of time that you are using valproic acid.
What are the symptoms of a drug reaction?
Symptoms may include: skin rash, fever, swollen glands, muscle aches, severe weakness, unusual bruising, or yellowing of your skin or eyes.
What causes liver problems?
liver problems caused by a genetic mitochondrial disorder; depression, mental illness, or suicidal thoughts or actions; a family history of a urea cycle disorder or infant deaths with unknown cause; or. HIV or CMV (cytomegalovirus) infection. Some young people have thoughts about suicide when first taking valproic acid.
What are the side effects of a syringe?
Call your doctor at once if you have any of these other side effects: confusion, tiredness, cold feeling, vomiting, change in your mental state; easy bruising, unusual bleeding (nose, mouth, or gums), purple or red pinpoint spots under your skin; severe drowsiness; or. worsening seizures.
How long does hyponatremia last after taking carbamazepine?
In prior studies, hyponatremia has been observed up to 90 days following initiation of carbamazepine. 37 Similar information is not available for valproic acid, phenytoin, and topiramate. Although it is possible that we missed some hyponatremia events occurring after 30 days, we decided to focus on 30-day outcomes to avoid crossover in drug therapy. As well, we did not consider extending the risk window, as the median duration of carbamazepine use in routine care was only 45 (interquartile range [IQR] 30–135) days, precluding meaningful long-term analysis.
What is absolute risk increase?
The likelihood a patient will experience an outcome, referred to as the absolute risk or absolute risk increase, is more useful for patient care than a relative association. Several results in our study used a diagnosis code to assess the presence of hyponatremia, which can underestimate the true incidence of hyponatremia by up to a factor of eight. When we defined the outcome using a sodium value ≤132 mmol/L, carbamazepine use compared to nonuse was associated with a 1% increase in the 30-day absolute risk of hospitalization with hyponatremia. Despite the small increase in absolute risk, the frequency of carbamazepine use means this is hundreds of additional hospitalizations with hyponatremia each year. Mild (chronic) hyponatremia may result in impaired gait, attention deficits, and falls, whereas severe hyponatremia may result in confusion, seizures, coma, or even death. 36
What are the other antiepileptics that cause hyponatremia?
The risk of hyponatremia with three other antiepileptic drugs—valproic acid, phenytoin, and topiramate— is less well understood. Use of any of these three drugs compared to no antiepileptic use was associated with a 2.6‐fold higher RR of hospitalization with hyponatremia within 30 days of drug initiation. Although this risk between antiepileptic ...
Why is propensity score matching important?
Given that treatment allocation was decided based on routine care, propensity score matching was used to ensure that user and nonuser groups were balanced on a wide range of characteristics. The matching ratios were selected to maximize precision while minimizing the loss of antiepileptic drug users in the respective cohorts.
How long does it take to get hospitalized for phenytoin?
Valproic acid, phenytoin, and topiramate users were 2.6 times more likely to be hospitalized with hyponatremia within 30 days compared to nonusers. If patients present to a hospital with symptomatic hyponatremia, these drugs should be considered as potential causes.
What is the highest incidence of epilepsy in older adults?
The incidence of epilepsy is highest in old age (>60 years of age), with an estimated 60–135 new cases per 100,000 older adults each year. 1 - 3 Carbamazepine, valproic acid, phenytoin, and topiramate are frequently used antiepileptic drugs for the control of focal and generalized seizures, and can be initiated as monotherapy. 4 - 6 These drugs are also often used in treatment of nonepileptic conditions such as pain and psychiatric disorders.
What is the ICD-10 code for hyponatremia?
The primary outcome was hospitalization with hyponatremia in the 30 days following the index date, defined by evidence of International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) code E87.1 (hypoosmolality or hyponatremia) in any one of 25 diagnostic fields during a given hospitalization. In our previous validation study, we found that the code had a sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value of 11%, 99%, and 82%, respectively. The presence of the code for hyponatremia identified older patients with a median sodium value of 125 mmol/L at hospital admission (interquartile range [IQR] 120–130 mmol/L); when the code was absent, the median value was 137 (IQR 135–139) mmol/L. 28

Summary
This medication is used to treat seizure disorders, mental/mood conditions (such as manic phase of bipolar disorder), and to prevent migraine headaches.
May Treat: Epilepsy · Absence epilepsy · Bipolar disorder · Complex-partial epilepsy · Mania associated with bipolar disorder and more
Brand Names: Depakene · Stavzor · Dalpro · Deproic
Drug Class: Anticonvulsant - Carboxylic Acid Derivatives · Bipolar Therapy Agents - Anticonvulsant Type
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Do not use. This medication may be harmful to an unborn child.
May Treat: Epilepsy · Absence epilepsy · Bipolar disorder · Complex-partial epilepsy · Mania associated with bipolar disorder and more
Brand Names: Depakene · Stavzor · Dalpro · Deproic
Drug Class: Anticonvulsant - Carboxylic Acid Derivatives · Bipolar Therapy Agents - Anticonvulsant Type
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Do not use. This medication may be harmful to an unborn child.
Lactation: Consult a doctor before using
Driving: May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Use caution
For The Consumer
For Healthcare Professionals
Further Information