The Weber test
Weber test
The Weber test is a screening test for hearing performed with a tuning fork. It can detect unilateral conductive hearing loss and unilateral sensorineural hearing loss. The test is named after Ernst Heinrich Weber. Conductive hearing ability is mediated by the middle ear composed of the oss…
How to do Rinne and Weber tuning fork tests for doctors?
For what is Weber's tuning fork used? The Weber test is a screening test for hearing performed with a tuning fork . It can detect unilateral (one-sided) conductive hearing loss (middle ear hearing loss) and unilateral sensorineural hearing loss (inner ear hearing loss).
What is a tuning fork test?
The tuning fork tests provide a reliable clinical method for assessing hearing loss They are most useful in patients with unilateral hearing loss which is purely conductive or purely sensorineural Patients with bilateral loss or mixed losses are better …
What are 512-hz tuning forks used for?
These tuning forks don’t have weights attached to them and they’re commonly used around the body and ears to balance the body’s energy, instead of being placed directly on the body. These tuning forks are usually used for physical, emotional, spiritual, and mental awareness.
What is the Weber test used for?
Weber. The Weber test is used in conjunction with the Rinne test and is most useful in patients with unilateral hearing loss. The aim is to identify the better-hearing cochlea. The 512-Hz tuning fork is struck and placed in the midline on either the forehead or the vertex.
For what is Weber's tuning fork used quizlet?
"It identifies a problem with the normal pathways for sound to travel to your inner ear." Placing the tuning fork on the mastoid bone is one part of the Rinne's test, which assesses the normal pathways for sound to travel to the inner ear.
What is Weber test used for?
The Weber test is a useful, quick, and simple screening test for evaluating hearing loss. The test can detect unilateral conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. The outer and middle ear mediate conductive hearing.Feb 2, 2022
When do you use the Weber and Rinne test?
Rinne and Weber tests are exams that test for hearing loss. They help determine whether you may have conductive or sensorineural hearing loss. This determination allows a doctor to come up with a treatment plan for your hearing changes. A Rinne test evaluates hearing loss by comparing air conduction to bone conduction.
How do you use a Weber tuning fork test?
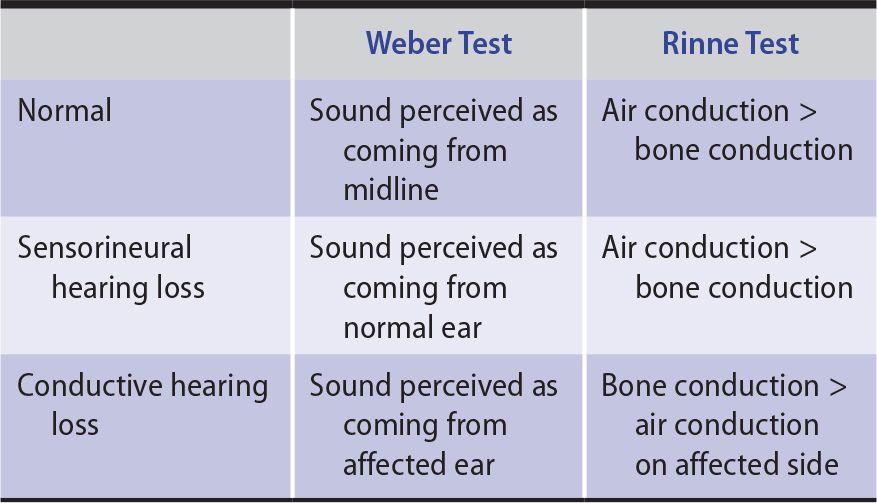
Weber test: Place the base of a struck tuning fork on the bridge of the forehead, nose, or teeth. In a normal test, there is no lateralization of sound. With unilateral conductive loss, sound lateralizes toward affected ear. With unilateral sensorineural loss, sound lateralizes to the normal or better-hearing side.
How do you use a Weber?
How to do Weber's TestTo perform Weber's test strike the fork against your knee or elbow, then place the base of the fork in the midline, high on the patient's forehead. ... Then ask the patient: “Do you hear the sound louder in one ear than the other?”
What is the difference between Rinne and Weber test?
1:578:37Weber and Rinne Test - Clinical Examination - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe rené test enables unilateral comparison of bone to air conduction. And takes advantage of theMoreThe rené test enables unilateral comparison of bone to air conduction. And takes advantage of the fact that physiologically. Sound conduction is more efficient via air than via bone.
Why does Weber test localize to affected ear?
The conduction being tested is that through bone to the inner ear. The air medium in the ear, being a less efficient transmitter of sound, results in sound energy loss at the interface of bone and air. The resultant sound energy to the inner ear is therefore less.
How Weber test is done?
In the Weber test, the base of a gently vibrating tuning fork is placed on the midforehead or the vertex. The patient is asked which ear hears the sound better. Normally, the sound is heard equally in both ears. With unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, sound is heard better in the unaffected ear.
How do you remember Rinne and Weber?
2:125:41Weber vs. Rinne Test & Conductive vs. Sensorineural Hearing LossYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBut our mnemonic to remember the rainy test is Rini under the penny.MoreBut our mnemonic to remember the rainy test is Rini under the penny.
How do you read a Weber test?
How do I interpret Weber's? If a patient has a unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, the sound will lateralise – move to the good ear. If a patient has unilateral conductive hearing loss, the tuning fork sound would be heard loudest in the affected ear.Mar 3, 2021
Which action by the nurse is consistent with Weber's test?
Which action by the nurse is consistent with Weber's test? The nurse activates the tuning fork and places it on the midline of the parietal bone in line with both ears.
What is Rinne positive?
Positive or negative in this case means that a certain parameter that was evaluated was present or not. In this case, that parameter is whether air conduction (AC) is better than bone conduction (BC). Thus, a "positive" result indicates the healthy state, in contrast to many other medical tests.
What does Weber's test show?
Weber’s Test Results. In a Normal hearing, a person hears the sound of a tuning fork in both the ear equally. An individual with one-sided conductive deafness (unilateral) will hear the sound of tuning fork louder in the affected ear. As the conduction difficulty covers the surrounding noise of the room.
What is abnormal hearing?
Abnormal Hearing – A person with hearing difficulty will not hear the tuning fork sound after it changed from mastoid to pinna. Therefore, the bone conduction is more than air conduction, up to twice more than air conduction. This is also known as negative Rinne. In both the ears, this test is performed.
What does a positive Rinne test mean?
A normal or positive Rinne test is when sound is still heard when the tuning fork is moved to air near the ear (air conduction or AC), indicating that AC is equal or greater than (bone conduction or BC).
What is the rhine test?
Also called as Rhinne Test by some people, is used in cases of unilateral hearing loss and establishes which ear has the greater bone conduction. It is combined with the patient’s perceived hearing loss. As a result, it can be determined if the cause is sensorineural or conductive.
What is the Rinne and Weber test?
They help in determining the type of unilateral hearing loss such as sensorineural or conductive hearing loss. By determining the type of hearing loss, it helps the doctor to start a treatment plan related to the hearing impairment. These tests require a full examination of the cranial nerves or the ear.
What is tuning fork test?
Overview of Tuning Fork Test is useful in assessing hearing loss. It is used to differentiate between sensorineural or conductive hearing loss. The patient who has over eight years old can go for conductive loss test or#N#asymmetric hearing in the low frequencies. The frequencies range from 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048 Hz.
Why is a hearing test important?
The hearing test is very important in order to identify the relying cause behind your hearing problems. Audiologist performs these tests to satisfy the conditions of hearing loss. Get Overview of Tuning Fork Test.
How to get the best sound from an unweighted tuning fork?
To ensure you get the best sound from an unweighted tuning fork, you should always strike the tuning fork’s prong one-third of the way from the top of the tuning fork. If you have a weighted tuning fork you should hit it on the top of the weighted portion.
How does a tuning fork work?
A tuning fork creates vibrations that interact with the air surrounding it. As the fork’s prongs move away from each other, they push air molecules together, creating small compressions. When the prongs move back together , they pull the air molecules and form low-pressure areas called rarefactions .
Why do audiologists use tuning forks?
Some audiologists still prefer to use tuning forks to diagnose hearing problems, as How Stuff Works reports. They make use of a test known as the Rinne test.
What is tuning fork therapy?
Tuning fork therapy makes use of vibrational frequency that increases energy flow in the body, which improves circulation and removes blocked energy in the body. This results in many benefits. Contents [ show] 1 Tuning Fork Therapy Benefits. 2 The Types Of Tuning Forks.
How many chakras are there in the body?
All the seven chakras are linked to various glands and organs in the body. To enable chakra healing with the use of tuning forks, it’s good to know what each of the seven chakras requires when it comes to healing sound. The frequencies are measured in hertz (Hz).
What is a tuning fork?
It’s quite amazing to think that initially, the tuning fork was just a small instrument made of steel with two flat prongs. These vibrated and produced a musical note that was of a constant pitch. The fork was used to tune musical instruments, as the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry reports.
What frequency is the 6th chakra?
6 th chakra makes use of 852 Hz and it encourages the intuition to be awakened. 7 th chakra makes use of the previous six frequencies as it connects one to the universe. When your chakras are to be stimulated by tuning forks, you can expect to be asked to lie down on a massage table.
What nerve mediates hearing and balance?
The vestibulocochlear nerve mediates hearing and balance. Hearing can be assessed with a 512-Hz tuning fork. The Rinne and Weber tests are commonly used to assess for sensorineural and conductive deafness.
What happens when the head is turned rapidly?
In the presence of a unilateral vestibular lesion, if the head is turned rapidly towards the affected side, the firing rate does not increase in the vestibular nerve on this side and fails to maintain the position of gaze.
What is the function of semicircular canals?
The semicircular canals detect rotational acceleration of the head. When the head is moved the endolymph stays in place relative to the skull and deflects the cupula within which the hair cells are imbedded. At rest the vestibular nerve from each semicircular canal has a background tonic firing rate.
How is hearing tested?
Hearing is tested by blocking one ear while testing the hearing in the other ear by whispering or varying the intensity of speech. This is followed if necessary by Weber's and Rinne's tests, which are tests of hearing involving the use of a tuning fork.
How to test for lateralization?
The Weber test is a test for lateralization. Tap the tuning fork strongly on your palm and then press the butt of the instrument on the top of the patient’s head in the midline and ask the patient where they hear the sound. Normally, the sound is heard in the center of the head or equally in both ears.
Is air conduction better than bone conduction?
In patients with sensorineural deafness and normal hearing, air conduction is better than bone conduction. With conductive deafness, bone conduction is better than air conduction. Nystagmus noted on eye movement testing may be a sign of vestibular dysfunction.
Which nerve has a tonic firing rate?
At rest the vestibular nerve from each semicircular canal has a background tonic firing rate. When the head is turned in one direction deflection of the hair cells increases the rate of firing from one canal and decreases the rate of firing from the paired contralateral canal (and vice versa).
Why is the sound of a tuning fork faint?
If just held in open air, the sound of a tuning fork is very faint due to the acoustic impedance mismatch between the steel and air.
What is the pitch of a tuning fork?
Currently, the most common tuning fork sounds the note of A = 440 Hz, the standard concert pitch that many orchestras use. That A is the pitch of the violin's second string, the first string of the viola, and an octave above the first string of the cello.
What is radar gun calibration?
Radar gun calibration. A radar gun that measures the speed of cars or a ball in sports is usually calibrated with a tuning fork. Instead of the frequency, these forks are labeled with the calibration speed and radar band (e.g., X-band or K-band) they are calibrated for.
What temperature do tuning forks need to be?
Tuning forks are manufactured to have their correct pitch at a standard temperature. The standard temperature is now 20 °C (68 °F), but 15 °C (59 °F) is an older standard. The pitch of other instruments is also subject to variation with temperature change.
How do tuning forks work?
Forks can be driven electrically by placing electronic oscillator -driven electromagnets close to the prongs.
What is the pitch of A=440?
Alternatives to the common A=440 standard include philosophical or scientific pitch with standard pitch of C=512. According to Rayleigh, physicists and acoustic instrument makers used this pitch. The tuning fork John Shore gave to George Frideric Handel produces C=512.
Why do we use fork shape?
The main reason for using the fork shape is that, unlike many other types of resonators, it produces a very pure tone, with most of the vibrational energy at the fundamental frequency. The reason for this is that the frequency of the first overtone is about 5 2. 1⁄2 octaves above it).
