
What are the alleles an individual inherits?
Feb 14, 2020 · How alleles are inherited? Although an individual gene may code for a specific physical trait, that gene can exist in different forms, or alleles. One allele for every gene in an organism is inherited from each of that organism's parents. Alleles produce phenotypes (or physical versions of a trait) that are either dominant or recessive.
What is the relationship between genes and alleles?
Dec 20, 2020 · Variations in genes for a trait causes different forms. Each of these variations of a gene is an allele. The two alleles in a pair of genes are inherited, one from each parent. Alleles interact with the other in various ways known as inheritance patterns. These two copies of the gene in your chromosomes affect the way cells function.
Do we inherit genes or alleles from our parents?
An allele is one of two or more versions of a gene. An individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. If the two alleles are the same, the individual is homozygous for that gene. If the alleles are different, the individual is heterozygous.
What is the difference between an allele and a gene?
Feb 06, 2021 · Alleles play a big role in determining our inherited traits, along with DNA and genes. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the hereditary material that humans and other living organisms get from each parent. It's technically a molecule that's responsible for carrying all of the necessary genetic information in the body’s cells.

How are alleles inherited from parents?
Each person inherits at least two alleles for a particular gene—one allele from each parent. They are also called allelomorphs. A good example of how alleles are expressed is eye color; whether we have blue or brown eyes depends on the alleles that are passed down from our parents.Feb 6, 2021
What is an allele and how are alleles inherited?
An allele is one of two or more versions of a gene. An individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. If the two alleles are the same, the individual is homozygous for that gene. If the alleles are different, the individual is heterozygous.
How many alleles are inherited?
two allelesHumans are called diploid organisms because they have two alleles at each genetic locus, with one allele inherited from each parent. Each pair of alleles represents the genotype of a specific gene.
How are alleles formed?
New alleles can be formed as a result of mutations, it is the ultimate source. Mutations are permanent changes taking place in the sequences of DNA. It is the first step in creating a new DNA sequence for a specific gene that creates a new allele.
Is allele and gene same?
So, what it is the difference between a gene and an allele? The short answer is that an allele is a variant form of a gene. Explained in greater detail, each gene resides at a specific locus (location on a chromosome) in two copies, one copy of the gene inherited from each parent.
How many genes are inherited from each parent?
twoAn international research effort called the Human Genome Project, which worked to determine the sequence of the human genome and identify the genes that it contains, estimated that humans have between 20,000 and 25,000 genes. Every person has two copies of each gene, one inherited from each parent.Mar 22, 2021
Why do you only get one allele from each parent?
During meiosis, chromosome pairs are split apart and distributed into cells called gametes. Each gamete contains a single copy of every chromosome, and each chromosome contains one allele for every gene. Therefore, each allele for a given gene is packaged into a separate gamete.Jan 1, 2022
What is gene inheritance?
Inheritance is the process by which genetic information is passed on from parent to child. This is why members of the same family tend to have similar characteristics.Jul 21, 2021
How do alleles determine traits?
An allele is an alternative form of a gene (one member of a pair) that is located at a specific position on a specific chromosome. These DNA codings determine distinct traits that can be passed on from parents to offspring through sexual reproduction....Multiple Alleles.Blood GroupsGenotypeAB(IA,IB)O(IO,IO)2 more rows•Aug 21, 2019
Can two parents have one allele?
Somatic cells contain two alleles for every gene, with one allele provided by each parent of an organism. Often, it is impossible to determine which two alleles of a gene are present within an organism's chromosomes based solely on the outward appearance of that organism.
Why are there 2 alleles for each gene?
Since diploid organisms have two copies of each chromosome, they have two of each gene. Since genes come in more than one version, an organism can have two of the same alleles of a gene, or two different alleles.
Is an allele A chromosome?
allele, also called allelomorph, any one of two or more genes that may occur alternatively at a given site (locus) on a chromosome. Alleles may occur in pairs, or there may be multiple alleles affecting the expression (phenotype) of a particular trait.
What is an allele?
Allele. Allele. =. An allele is one of two or more versions of a gene. An individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. If the two alleles are the same, the individual is homozygous for that gene. If the alleles are different, the individual is heterozygous.
What is an allele in narration?
Narration. "Allele" is the word that we use to describe the alternative form or versions of a gene. People inherit one allele for each autosomal gene from each parent, and we tend to lump the alleles into categories. Typically, we call them either normal or wild-type alleles, or abnormal, or mutant alleles.
What is an allele in genetics?
An allele is an alternative form of a gene (one member of a pair) that is located at a specific position on a specific chromosome. These DNA codings determine distinct traits that can be passed on from parents to offspring through sexual reproduction.
What happens when you inherit only dominant alleles?
Individuals inheriting only dominant alleles will have an extreme expression of the dominant phenotype; individuals inheriting no dominant alleles will have an extreme expression of the recessive phenotype; individuals inheriting different combinations of dominant and recessive alleles will exhibit varying degrees of the intermediate phenotype.
How many alleles are there in ABO?
ABO blood types exist as three alleles, which are represented as (IA, IB, IO). These multiple alleles are passed from parent to offspring such that one allele is inherited from each parent. There are four phenotypes (A, B, AB, or O) and six possible genotypes for human ABO blood groups. Blood Groups.
What is the difference between a dominant and recessive allele?
When allele pairs are the same, they are homozygous. When the alleles of a pair are heterozygous, the phenotype of one trait may be dominant and the other recessive. The dominant alle le is expressed and the recessive allele is masked.
What is complete genetic dominance?
This is known as complete genetic dominance. In heterozygous relationships where neither allele is dominant but both are completely expressed, the alleles are considered to be co-dominant. Co-dominance is exemplified in AB blood type inheritance. When one allele is not completely dominant over the other, the alleles are said to express incomplete ...
How are blood types determined?
A common example of this in humans is ABO blood type. Human blood type is determined by the presence or absence of certain identifiers, called antigens, on the surface of red blood cells. Individuals with blood type A have A antigens on blood cell surfaces, ...
What is an allele?
An allele is one of two or more versions of a gene. An individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. Darryl Leja / NHGRI. Science. Biology. Genetics. Basics.
What is an allele in biology?
Alleles. Alleles and Inheritance. Title. Alleles and Inheritance. An Allele is an alternative form of a gene (one member of a pair) that is located at a specific position on a specific chromosome. Alleles are dominant or recessive. Homozygous = two same alleles (purebred)
What is heterozygous for?
They are heterozygous for a certain gene if they two different alleles. The genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual. For example, it is the particular combination of alleles. The phenotype is the characteristics expressed by an individual. For example, it is the actual eye colour.
What is a monohybrid cross?
Monohybrid Cross. In a monohybrid cross two plants or animals, which differ at only one gene and which are bred together. By looking at alleles of the genes that the parents have we can tell how the offspring will turn out. This can be very useful when carrying out selective breeding of plants or animals.
What is the dominance of alleles in genetics?
Allelic dominance in genetic disorders. A number of genetic disorders are caused when an individual inherits two recessive alleles for a single-gene trait. Recessive genetic disorders include albinism, cystic fibrosis, galactosemia, phenylketonuria (PKU), and Tay–Sachs disease.
What is an allele in biology?
An allele is one of two, or more, versions of the same gene at the same place on a chromosome. It can also refer to different sequence variations for several-hundred base-pair or more region of the genome that codes for a protein. Alleles can come in different extremes of size.
What is dominant or recessive interaction?
In many cases, genotypic interactions between the two alleles at a locus can be described as dominant or recessive, according to which of the two homozygous phenotypes the heterozygote most resembles. Where the heterozygote is indistinguishable from one of the homozygotes, the allele expressed is the one that leads to the "dominant" phenotype, and the other allele is said to be "recessive". The degree and pattern of dominance varies among loci. This type of interaction was first formally-described by Gregor Mendel. However, many traits defy this simple categorization and the phenotypes are modeled by co-dominance and polygenic inheritance .
What is an allele?
An allele ( UK: / ˈæliːl /, / əˈliːl /; US: / əˈliːl /; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος állos, "other") is one of two, or more, forms of a given gene variant. For example, the ABO blood grouping is controlled by the ABO gene, which has six common alleles. Nearly every living human's phenotype for the ABO gene is some combination of just these six alleles. An allele is one of two, or more, versions of the same gene at the same place on a chromosome. It can also refer to different sequence variations for several-hundred base-pair or more region of the genome that codes for a protein. Alleles can come in different extremes of size. At the lowest possible size an allele can be a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). At the higher end, it can be up to several thousand base-pairs long. Most alleles result in little or no observable change in the function of the protein the gene codes for.
How many base pairs can an allele be?
At the lowest possible size an allele can be a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). At the higher end, it can be up to several thousand base-pairs long. Most alleles result in little or no observable change in the function of the protein the gene codes for.
What is wild type allele?
The term " wild type " allele is sometimes used to describe an allele that is thought to contribute to the typical phenotypic character as seen in "wild" populations of organisms, such as fruit flies ( Drosophila melanogaster ).
What are heritable traits?
While heritable traits are typically studied in terms of genetic alleles, epigenetic marks such as DNA methylation can be inherited at specific genomic regions in certain species, a process termed transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. The term epiallele is used to distinguish these heritable marks from traditional alleles, which are defined by nucleotide sequence. A specific class of epiallele, the metastable epialleles, has been discovered in mice and in humans which is characterized by stochastic (probabilistic) establishment of epigenetic state that can be mitotically inherited.
Blood Type Inheritance
What type of inheritance is blood type? Blood type is inherited through an inheritance pattern called codominance. But before getting into the details of codominance, let's explain what blood type is. In humans, red blood cells have proteins with sugars attached to the surface of red blood cells.
How Is Blood Type Inherited?
How is blood type inherited? Our genes control all traits. Humans have two copies of each gene, one from the maternal parent and one from the paternal parent. These different copies are called alleles, and the way alleles interact to produce a trait is called an inheritance pattern.
Blood Type Inheritance: Punnett Squares
How does blood type get passed down? Blood type passes down from the genetics of the parents. Scientists can use a Punnett square tool to determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring for a particular trait. To create a Punnett square, draw a square and divide it into four equal squares.
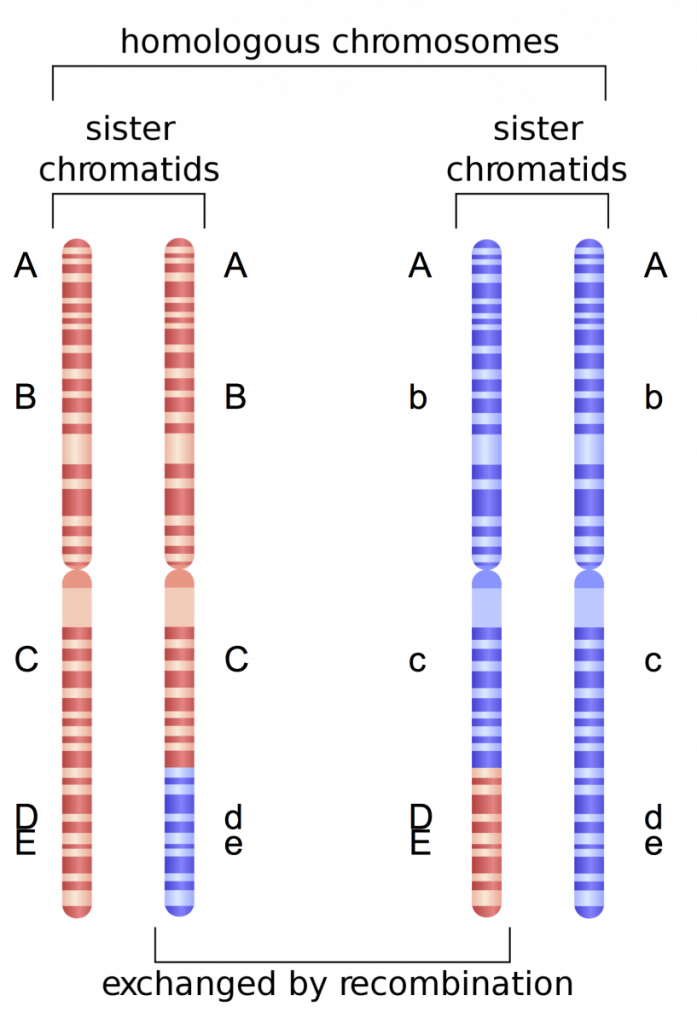
Overview
Epialleles
Etymology
- Polygenictraits are traits that are determined by more than one gene. This type of inheritance pattern involves many possible phenotypes that are determined by interactions among several alleles. Hair color, skin color, eye color, height, and weight are all examples of polygenic traits.The genes contributing to these types of traits have equal infl...
Alleles that lead to dominant or recessive phenotypes
Multiple alleles
While heritable traits are typically studied in terms of genetic alleles, epigenetic marks such as DNA methylation can be inherited at specific genomic regions in certain species, a process termed transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. The term epiallele is used to distinguish these heritable marks from traditional alleles, which are defined by nucleotide sequence. A specific class of epiallele, the metastable epialleles, has been discovered in mice and in humans which is charact…
Genotype frequencies
The word "allele" is a short form of allelomorph ("other form", a word coined by British geneticists William Bateson and Edith Rebecca Saunders), which was used in the early days of genetics to describe variant forms of a gene detected as different phenotypes. It derives from the Greek prefix ἀλληλο-, allelo-, meaning "mutual", "reciprocal", or "each other", which itself is related to the Greek adjective ἄλλος, allos (cognate with Latin alius), meaning "other".
Allelic dominance in genetic disorders
In many cases, genotypic interactions between the two alleles at a locus can be described as dominant or recessive, according to which of the two homozygous phenotypes the heterozygotemost resembles. Where the heterozygote is indistinguishable from one of the homozygotes, the allele expressed is the one that leads to the "dominant" phenotype, and the other allele is said to be "recessive". The degree and pattern of dominance varies among loci. This type of interaction …
See also
A population or species of organisms typically includes multiple alleles at each locus among various individuals. Allelic variation at a locus is measurable as the number of alleles (polymorphism) present, or the proportion of heterozygotes in the population. A null allele is a gene variant that lacks the gene's normal function because it either is not expressed, or the expressed protein is inactive.