What are biogenic amines?
Biogenic amines (BA) are organic compounds commonly found in food, plants and animals, as well as microorganisms that are attributed with the production of BAs. They are formed as an effect of a chemical process: the decarboxylation of amino acids.
How do you get rid of biogenic amines?
Even though many methods are available, as described above, for delaying biogenic amine accumulation, few methods are available for degrading biogenic amines. Such methods include the use of oxidizing microorganisms, such as biogenic amine oxidizing bacteria, and enzymes such as DAO.
How are exogenous amines absorbed from food?
The exogenous amines are directly absorbed from food in the intestine. Alcohol can increase the absorption rate. Monoamine oxidase ( MAO) breaks down biogenic amines and prevents excessive resorption.
What is the most effective inhibitor of biogenic amine formation?
Cinnamic aldehyde, a component of cinnamon, and eugenol, a compound of cloves were found to be the most effective inhibitors of biogenic amine formation by specific bacteria, E. aerogenes(Wendakoon and Sakaguchi 1995).

Where are biogenic amines released?
They can be present naturally in many foods such as fruits and vegetables, fish, meat, cheese, milk, and chocolate as well as wines and beers. The most common biogenic amines found in foods are histamine, tyramine, cadaverine, 2-phenylethylemine, spermine, spermidine, putrescine, tryptamine, and agmatine.
How are biogenic amines degraded?
Biogenic amines can be degraded by amine oxidases. Diamines, such as histamine and putrescine, are degraded by diamine oxidase (DAO). The activity of these enzymes is maximum under neutral to alkaline conditions, and oxygen is necessary for their action (Beutling, 1992).
How biogenic amines are inactivated?
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) breaks down biogenic amines and prevents excessive resorption. MAO inhibitors (MAOIs) are also used as medications for the treatment of depression to prevent MAO from breaking down amines important for positive mood.
Are biogenic amines harmful?
Biogenic amines (BAs) in food constitute a potential public health concern due to their physiological and toxicological effects. The consumption of foods containing high concentrations of biogenic amines has been associated with health hazards.
What hormones are responsible for biogenic amines?
There are five established biogenic amine neurotransmitters: the three catecholamines—dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline)—and histamine and serotonin (see Figure 6.3).
How biogenic amines are formed?
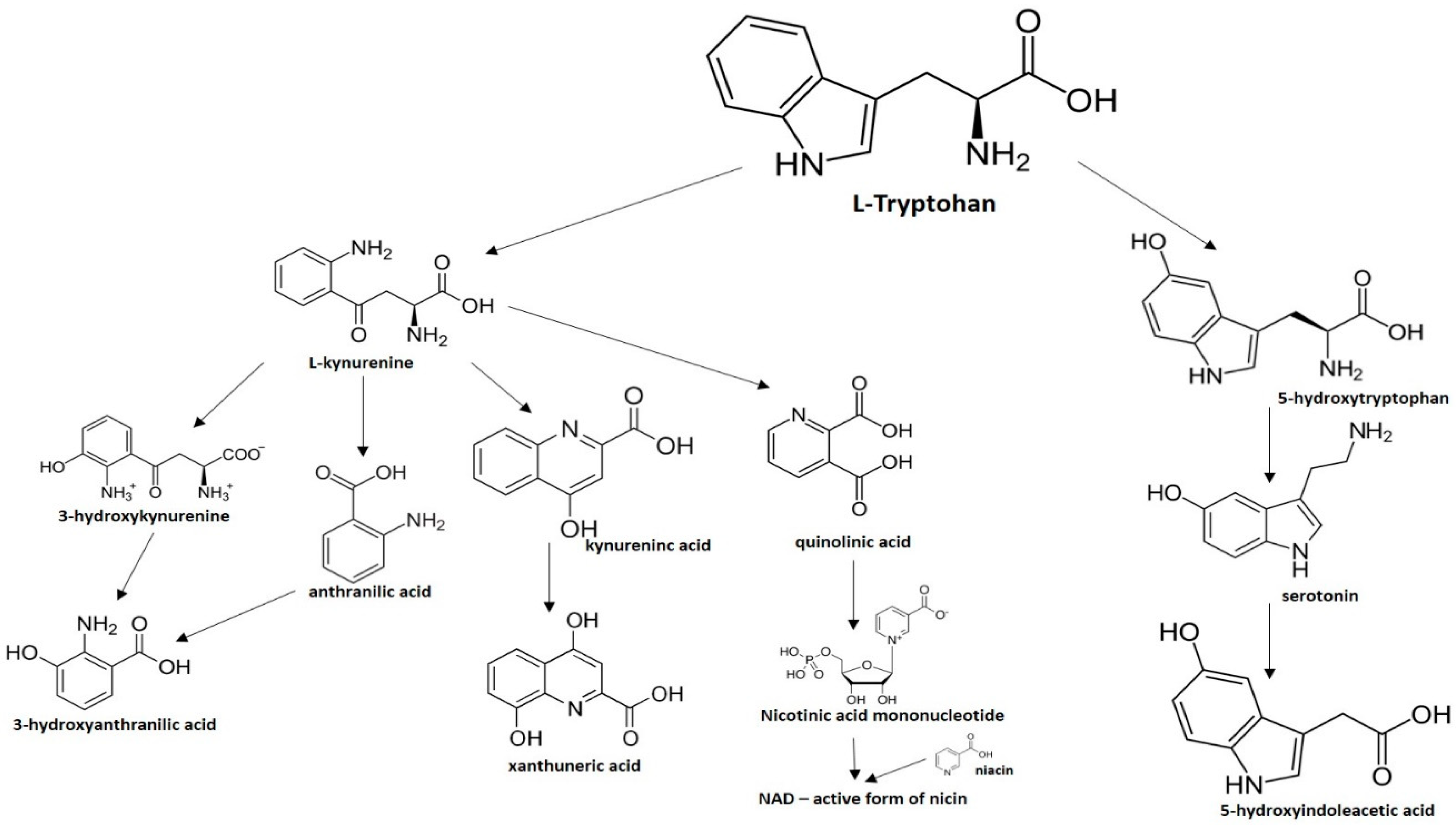
Biogenic amines are produced by the decarboxylation of their respective free precursor amino acids, through the catalytic action of substrate-specific microbial decarboxylases that remove the α-carboxyl group of amino acids to give the corresponding amines.
How are amines broken down in the body?
Histamine and other vasoactive amines are usually broken down and made 'harmless' within our bodies by a digestive enzyme called diamine oxidase.
How amino acids are degraded?
Key steps in amino acid degradation include deamination, catalysed by pyridoxal phosphate-dependent transaminases, oxidoreductases or carbon–oxygen lyases, decarboxylase reactions and carbon skeleton rearrangements catalysed by isomerases.
How do you test for biogenic amines?
Among all methods, liquid chromatography is considered suitable for detection and quantification of biogenic amines in different food matrices.
What are biogenic amines in brain?
Biogenic amines are biogenic substances containing one or more amine groups (10, 11). Five of these amines were found to function as neurotransmitters including dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, histamine, and serotonin.
Is histamine a biogenic amine?
Histamine is a biogenic amine which is a naturally occurring substance in the human body. Histamine is derived from the breakdown (decarboxylation) of the amino acid histidine.
Are bananas high in amines?
Amines are organic compounds that are formed within foods due to the breakdown of proteins. Proteins are naturally broken down in foods as they age and the cooking, processing and maturing processes all increased amine content. Amines also increase in content as fruits ripen such as in avocado and bananas.
What foods contain biogenic amines?
Biogenic amine (BA)s are nitrogenous, and organic compounds and can be found in some fermented foods such as cheese, sausage, fermented vegetable, wine, and fish [1, 2].
Do bananas contain amines?
Dietary amines come from protein breakdown in foods. Levels increase in protein foods (meat, fish, cheese) as they age or mature, and in fruits as they ripen (e.g. bananas, tomatoes).
Is wine high in amines?
You'll find biogenic amines in many foods including processed fish, meat, cheese, and fermented things (such as beer, wine, and kimchi). Higher levels of biogenic amines (especially histamine and tyramine) cause flushing, headaches, nausea, and fatigue.
What does biogenic do to the body?
Biogenic amines in the gastrointestinal tract are important metabolites of dietary protein and amino acids with the help of gut digestive enzymes and microbes, which play a crucial role in the regulation of intestinal functions, including digestion, absorption, and local immunity.
Are biogenic amines good for you?
Biogenic amines, which are responsible for the realization of many physiological conditions of our body, are compounds that can be produced by microorganisms especially in fermented foods with high protein content. They can have harmful effects on human health only when taken in high amounts with food.
Why are biogenic amines important?
Biogenic amines are important nitrogen compounds of biological importance in vegetable, microbial and animal cells. They can be detected in both raw and processed foods. In food microbiology they have sometimes been related to spoilage and fermentation processes.
Are Oats high in amines?
Oats are likely suitable for a low histamine diet. Oats are likely low in histamine and other amines and does not trigger release of the body's natural histamine.
Are hormones biogenic amines?
Biogenic amines are low molecular weight organic bases which consist of one or more amine group, they provide a vital source of nitrogen for the synthesis of nucleic acids, alkaloids, amines, proteins and hormones.
How are amino acids synthesized and degraded?
The amino acids synthesized from TCA cycle intermediates (aspartate, asparagine, glutamate, glutamine, proline, and arginine) are reconverted to these intermediates during degradation. Histidine is converted to glutamate and then to the TCA cycle intermediate α-ketoglutarate.
What temperature do amines degrade?
Lanning mention that the thermal degradation of amines accelerates above 350°F, so the skin temperature of direct fired reboilers should be kept below 350°F. They recommend a reboiler operation with an amine bulk temperature below 260°F.
What are the two degradation products of tyrosine?
In addition to its proteogenic function, tyrosine can be used either as a precursor for the synthesis of neuromediators, such as dopamine, octopamine, and tyramine, or can be degraded via the tyrosine degradation pathway producing acetoacetate and fumarate (Figure 1E).
How is glycine degraded?
Glycine degradation occurs through three pathways: the glycine cleavage system (GCS), serine hydroxymethyltransferase, and conversion to glyoxylate by peroxisomal D-amino acid oxidase. Among these pathways, GCS is the major enzyme to initiate glycine degradation to form ammonia and CO2 in animals.
How do biogenic amines affect T cells?
By interacting with TAAR1 and TAAR2, biogenic amines also seem to affect the secretion of cytokines by human T cells ( Table 7.3 ). 28 As a part of the adaptive immune system, T cells are activated by specific antigens presented on the surface of professional antigen-presenting cells. Once activated, T helper cells (CD3 + CD4 +) can differentiate mainly into two types of effector cell: Th1 cells and Th2 cells. Whilst differentiation into Th1 cells leads to the secretion of, for example, interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon γ, differentiation into Th2 cells results in the secretion of, for example, interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-5 (IL-5). 48 Stimulation of non-siRNA-transfected T cells with 2-PEA, TYR, and T1AM in a range from 0.01 to 1 nM concentration-dependently increased the secretion of IL-4 up to 300% of the control. 28 In this regard, 2-PEA revealed the highest efficacy of the three biogenic amines tested, whilst the respective EC 50 values were comparable (2-PEA: 0.23 ±0.008 nM, TYR: 0.24 ±0.04 nM, T1AM: 0.1 ±0.05 nM). In contrast, IL-4 secretion of T cells transfected with siRNA specific for TAAR1 and TAAR2 was barely affected by incubation of the cells with the biogenic amines.
What are the biogenic amines in cheese?
Tyramine (aromatic, primary, and monoamine) and histamine (heterocyclic, primary, and monoamine) are the main biogenic amines produced by enterococci in cheeses. They can be formed through the microbial decarboxylation of free amino acids during fermentation such as during cheese ripening.
How are biogenic amines formed?
Biogenic Amines. Biogenic amines (Table 7) are formed from amino acids by decarboxylation, or by amination and transamination of aldehydes and ketones. Because of the structure of their precursor amino acids, they can have either aliphatic, aromatic, or heterocyclic chemical structures. Although some play a role in the physiology ...
How do enterococci cause food intoxication?
Enterococci can cause food intoxication through the production of biogenic amines, which after ingestion can result in a number of symptoms, including headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, flushing, increased blood pressure, and even allergic reactions. The symptoms may occur in conjunction with monoamine oxidase (MAO) and diamine oxidase, which metabolize normal dietary intakes of biogenic amines in the intestinal tracts of mammals. Oxidative deamination catalyzed by MAO is the detoxification mechanism for tyramine and histamine. Under normal circumstances (a low concentration of biogenic amines ingested by a healthy person), the biogenic amines adsorbed from food are detoxified by oxidative deamination, and the end metabolites are readily excreted in the urine. However, the detoxifying mechanisms in humans are not sufficient when the intake in a diet is too high, if individuals are allergic, and if patients are taking drugs that act on MAO inhibitors.
What are the amines that are found in food?
Biogenic amines. Biogenic amines such as histamine, tyramine, phenylethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, and spermidine are found in certain foods and play a role as regulatory agents in human metabolism.
What causes a biogenic amine to form?
Formation of Biogenic Amines by Enterococci. Biogenic amines in foods could be a result of the decarboxylase activity of the fermentative microflora. Favorable conditions for their production may be achieved by the increase in precursor amino acids or the level of biogenic amines may be reduced by the elimination of decarboxylating bacteria.
What is the cause of histamine poisoning?
Histamine fish poisoning (or scombroid poisoning) is a type of food poisoning caused by elevated levels of histamine being present in the fish such as tuna, sardines, mackerel, swordfish, and marlin. Naturally occurring bacteria in fish produce an enzyme, which converts histidine in the fish to histamine.
Highlights
Phosphonic/sulfonic cation exchange groups presented the best removal capacity.
Abstract
The structure and the cation-exchange functional groups of hybrid silica materials were evaluated for the effective detoxification of hydroalcoholic solutions containing eight toxic biogenic amines (BA) usually found in fermented beverages.
1. Introduction
The application of adsorption processes for the removal of toxic compounds is common in the food and beverage industry. The effectiveness and selectivity requirements of the adsorption will depend on the type of application, so searching for suitable adsorbents can be complex.
2. Experimental section
The eight BA studied in this work were (the size of the molecule is indicated in brackets and expressed as the longer length (nm) (obtained from http://molcalc.org/ )) (purity > 97%): histamine (0.789), putrescine (0.783), cadaverine (0.777), spermidine (0.937), spermine (1.062), 2-phenylethylamine (0.812), tyramine (0.875) and isoamylamine (0.673).
3. Results and discussion
The selection of silica as base material was based on the possibility of easily synthesizing different structures (with different functional groups) and on its chemical stability at acid pH.
4. Conclusions
The results obtained establish the hybrid silica functionalized with phosphonic and/or sulfonic acids as an interesting option to remove the biogenic amines from hydroalcoholic solutions.
Acknowledgements
This study has been financed by the European Union (Horizon 2020) framed in the Marie S. Curie Individual Fellowships program (Reference: 701912).
Abstract
The effectiveness of several functionalized silica materials (cation-exchange materials) for the removal of biogenic amines from wines, and the effects on other wine components and organoleptic characteristics were evaluated.
Introduction
The presence of biogenic amines (BA), such as histamine, putrescine and cadaverine, is very common in fermented foods due mainly to microorganism metabolism 1. In the case of wines, the presence of histamine, in particular, is beginning to generate concern due to its negative effects on health, which are enhanced by the presence of alcohol 2, 3.
Results and discussion
On the basis of the previous results obtained in synthetic wine media 19, a lamellar material functionalized with sulfonic acid groups and macroporous and mesoroporous (SBA-15 type) xerogel structures bi-functionalized with phosphonic and sulfonic acids were selected to evaluate their effectiveness in real wine samples.
Conclusions
The mesoporous silica material bi-functionalized with phosphonic and sulfonic acids allowed the removal of histamine, putrescine, cadaverine, spermine and spermidine from wines, requiring adjustment of the dose according to the removal requirements and the initial levels in wines.
Materials and methods
BA standards of histamine, putrescine, cadaverine, spermidine, spermine, 2-phenylethylamine, tyramine, isoamylamine and n-heptylamine (purity > 97%) were obtained from TCI Europe chemicals (Zwijndrecht, Belgium) and Across chemicals (Geel, Belgium).
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the European Union (Horizon 2020) framed in the Marie S. Curie Individual Fellowships program (Reference: 701912). https://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/200992_en.html.
Author information
Present address: Agrotecnio - Centre for Food and Agriculture Research, Av. Rovira Roure 191, 25198, Lleida, Spain
What are the TAs linked to?
In this article, we focus on the relevance of TAs and their receptors to nervous system-related disorders, namely schizophrenia and depression; however, TAs have also been linked to other diseases such as migraine, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, substance abuse and eating disorders [7,8,36 ].
What is the difference between dopamine and epinephrine?
Epinephrine (adrenaline) – an adrenal stress hormone, as well as a neurotransmitter present at lower levels in the brain. Dopamine – a neuro transmitter involved in motivation, reward, addiction, behavioral reinforcement, and coordination of bodily movement.
What are lactic acid bacteria?
Some lactic acid bacteria isolated from commercial bottled yoghurt have been shown to produce biogenic amines. They play an important role as source of nitrogen and precursor for the synthesis of hormones, alkaloids, nucleic acids, proteins, amines and food aroma components.
How to determine biogenic amines in wine?
The determination of amines in wines is commonly achieved by liquid chromatography, using derivatization reagents in order to promote its separation and detection.
What are some examples of biogenic monoamines?
Monoamines. Some prominent examples of biogenic monoamines include: Histamine – a substance derived from the amino acid histidine that acts as a neurotransmitter mediating arousal and attention, as well as a pro- inflammatory signal released from mast cells in response to allergic reactions or tissue damage.
How are endogenous and exogenous amines produced?
Endogenous amines are produced in many different tissues (for example: adrenaline in adrenal medulla or histamine in mast cells and liver ). The amines are transmitted locally or via the blood system. The exogenous amines are directly absorbed from food in the intestine. Alcohol can increase the absorption rate. Monoamine oxidase ( MAO) breaks down biogenic amines and prevents excessive resorption. MAO inhibitors (MAOIs) are also used as medications for the treatment of depression to prevent MAO from breaking down amines important for positive mood.
What is a biogenic amine?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. A biogenic amine is a biogenic substance with one or more amine groups. They are basic nitrogenous compounds formed mainly by decarboxylation of amino acids or by amination and transamination of aldehydes and ketones. Biogenic amines are organic bases with low molecular ...
