How are Boyle's Law and Charles's law alike?
Boyle showed that the volume of a sample of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure (Boyle's law), Charles and Gay-Lussac demonstrated that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature (in kelvins) at constant pressure (Charles's law), and Avogadro postulated that the volume of a gas is ...
What is the difference between Boyle's law and Henry's law?
0:183:25Video 3 - Henry's Law & Boyle's Law - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLess dissolved gases can be dissolved in the fluid. So they will start to come out of the solutionMoreLess dissolved gases can be dissolved in the fluid. So they will start to come out of the solution as we reduce the pressure. And boyle's losses as we reduce.
What are two differences between Lussac's law and Charles's law?
Gay-Lussac's Law is very similar to Charles's Law, with the only difference being the type of container. Whereas the container in a Charles's Law experiment is flexible, it is rigid in a Gay-Lussac's Law experiment.
What two things does Charles law compare?
Explanation: Since pressure is kept constant, the only variable that is manipulated is temperature. This means that we can use Charles's law in order to compare volume and temperature. Since volume and temperature are on opposite sides of the ideal gas law, they are directly proportional to one another.
What are the assumptions of Charles Law?
Charles's law, a statement that the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, if the pressure remains constant. This empirical relation was first suggested by the French physicist J. -A.
What is the other name of Charles Law?
Charles' Law, also sometimes referred to as the law of volumes, gives a detailed account of how gas expands when the temperature is increased. Conversely, when there is a decrease in temperature it will lead to a decrease in volume.
What is the difference between Boyle's law?
In Charles law, temperature and volume of the gas are kept at constant pressure. Whereas in Boyle's law, pressure and volume of the gas are kept at a constant temperature. In Boyle's law, pressure and volume vary inversely whereas, in Charles law, pressure and volume vary directly.
What does Boyle's law state?
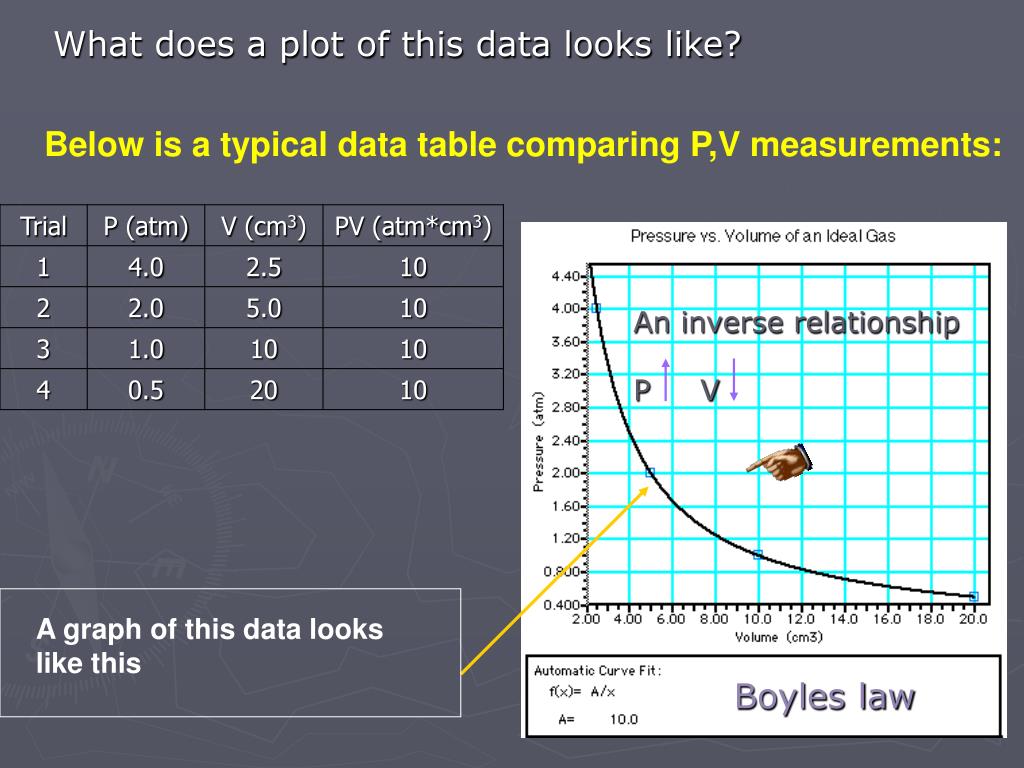
This empirical relation, formulated by the physicist Robert Boyle in 1662, states that the pressure (p) of a given quantity of gas varies inversely with its volume (v) at constant temperature; i.e., in equation form, pv = k, a constant. The relationship was also discovered by the French physicist Edme Mariotte (1676).
What is a good example of Charles Law?
Examples of Charles's Law in Everyday Life Heating the air in the balloon increases the balloon's volume. This decreases its density, so the balloon rises in the air. To come down, chilling the air (not-heating-it) allows the balloon to deflate. The gas becomes more dense and the balloon sinks.
What relationship does Charles Law have and what relationship does Boyle's law have?
Boyle's law states that pressure and volume have an inverse relationship. Charles's law states that volume and absolute temperature have a direct relationship. Gay-Lussac's law states that pressure and absolute temperature have a direct relationship.
What are the formulas of Boyle's Law and Charles Law?
Derivation of the Combined Gas Law The combined gas law is an amalgamation of the three previously known laws which are- Boyle's law PV = K, Charles law V/T = K, and Gay-Lussac's law P/T = K. Therefore, the formula of combined gas law is PV/T = K, Where P = pressure, T = temperature, V = volume, K is constant.
What is a good example of Boyle's Law?
You can observe a real-life application of Boyle's Law when you fill your bike tires with air. When you pump air into a tire, the gas molecules inside the tire get compressed and packed closer together. This increases the pressure of the gas, and it starts to push against the walls of the tire.
What is Henry's law?
Henry's law, statement that the weight of a gas dissolved by a liquid is proportional to the pressure of the gas upon the liquid. The law, which was first formulated in 1803 by the English physician and chemist William Henry, holds only for dilute solutions and low gas pressures.
What is an example of Henry's law?
Examples of Henry's Law The gas above the unopened carbonated drink is usually pure carbon dioxide, kept at a pressure which is slightly above the standard atmospheric pressure. As a consequence of Henry's law, the solubility of carbon dioxide in the unopened drink is also high.
What is the purpose of Henry's law?
The main application of Henry's law in respiratory physiology is to predict how gasses will dissolve in the alveoli and bloodstream during gas exchange. The amount of oxygen that dissolves into the bloodstream is directly proportional to the partial pressure of oxygen in alveolar air.
What is Henry's law and its application?
Henry law explains the solubility of a gas in a liquid solution by partial pressure and mole fraction of the gas in the liquid. Henry's Law states that “the partial pressure applied by any gas on a liquid surface is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in a liquid solvent.”