How do you count carbons in fatty acids?
The numbers are generally presented in the format (number of carbons in fatty acid chain) : (number of double bonds in fatty acid chain), e.g., 16:0 would be 16 carbons in the fatty acid chain with zero double bonds, or the numeric representation of palmitic acid.
How are fatty acids categorized according to number of carbons in the chain?
Based on the number of carbon atoms in the alkyl chain length, fatty acids can be classified into short-chain (2–4 carbon atoms), medium-chain (6–10 carbon atoms), and long-chain fatty acids (12–26 carbon atoms) (Shete and Patravale, 2013; Trevaskis et al., 2008).
Are carbons in fatty acid chains even numbered?
Though most fatty acids of biological origin have even numbers of carbons, not all of them do. Oxidation of fatty acids with odd numbers of carbons ultimately produces an intermediate with three carbons called propionyl-CoA, which cannot be oxidized further in the beta-oxidation pathway.
Why do fatty acids have even number of carbons?
Most of the natural fatty acids have an even number of carbon atoms, because their biosynthesis involves acetyl-CoA, a coenzyme carrying a two-carbon-atom group.
How is the carbon chain numbered?
If two different substituents are present on the ring, they are listed in alphabetical order, and the first cited substituent is assigned to carbon #1. The numbering of ring carbons then continues in a direction (clockwise or counter-clockwise) that affords the second substituent the lower possible location number.
How fatty acids are numbered?
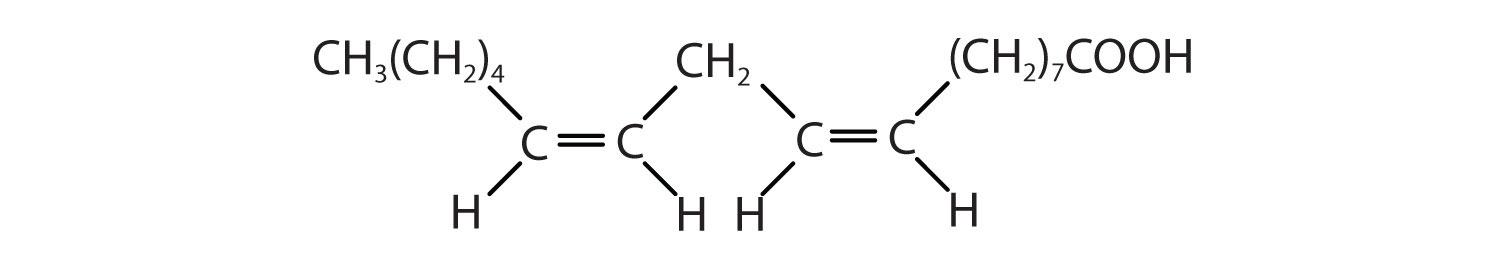
This also illustrates the omega labeling system, with the numbers in blue indicating the number from omega-1, the carbon farthest from the carboxylic acid group, to the first carbon of the double bond. Since the first carbon in a double bond is carbon 9, oleic acid is an omega-9 fatty acid.
How are even-numbered fatty acids formed?
The synthesis of even-chained fatty acid synthesis is done by assembling acetyl-CoA precursors. Because the segments are each two carbons in length the resulting fatty acid has an even number of carbon atoms in it.
Do fatty acids have odd or even numbers of carbons?
Due to the mechanism of synthesis, most fatty acids have an even number of carbons, although odd-numbered carbon chains can also be generated. More variety can be generated by double-bonds between the carbons.
Why all fatty acids are even number?
In short, it's because fatty acids are made from two-carbon blocks. The way that most organisms make fatty acids is by the successive addition of two-carbon units (acetyl-CoA). So we usually get even-numbered fatty acids just because the building blocks are also even.
Why do most fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms quizlet?
-Fatty acids typically have an even number of carbon atoms, because they are built from two-carbon molecules. - Fatty acids differ from one another in the number of carbon atoms that they contain and in their number of carbon-carbon double bonds.
How are odd numbered fatty acids formed?
But in the case of odd chain fatty acids, we generate acetyl CoA as well as a propionyl CoA molecule. The propionyl CoA is ultimately transformed via a three-step process into succinyl CoA, which can then be incorporated into the citric acid cycle.
What does C18 1 mean?
Octadecenoic acids: The general name for any C18:1 acid including oleic, elaidic, vaccenic, petroselinic and petroselaidic. Octanoic acid: It is an 8-carbon saturated fatty acid (C8:0) also known as caprylic acid. A medium-chain fatty acid occurring in the lauric oils and in Cuphea seed oils.
How are fatty acids categorized?
Fatty acids can be divided into four general categories: saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and trans fats. Saturated fatty acids and trans fats are associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease.
How are fatty acids classified?
Fatty acids are classified according to the presence and number of double bonds in their carbon chain. Saturated fatty acids (SFA) contain no double bonds, monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) contain one, and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) contain more than one double bond.
How do carbon chains in fatty acids differ?
Fatty acids differ from each other in the number of C atoms, from 12-C to 24-C, and in the number of double bonds in the chain, from none to one, two, or three. Seed oils in different species vary widely in the proportion of different fatty acids, although 18-C unsaturated fatty acids generally predominate.
What are the classification of fatty acids?
Fatty acids are classified into three types: saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated.
What is the difference between a medium chain and a long chain?
Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain triglycerides. Long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 13 to 21 carbons. Very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 22 or more carbons.
How are fatty acids classified?
Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by even vs odd carbon content, and by linear vs branched.
How does malonyl-coa work?
Malonyl-CoA is then involved in a repeating series of reactions that lengthens the growing fatty acid chain by two carbons at a time. Almost all natural fatty acids, therefore, have even numbers of carbon atoms. When synthesis is complete the free fatty acids are nearly always combined with glycerol (three fatty acids to one glycerol molecule) to form triglycerides, the main storage form of fatty acids, and thus of energy in animals. However, fatty acids are also important components of the phospholipids that form the phospholipid bilayers out of which all the membranes of the cell are constructed (the cell wall, and the membranes that enclose all the organelles within the cells, such as the nucleus, the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus ).
What is the formula for saturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids have no C=C double bonds. They have the same formula CH 3 (CH 2) n COOH, with variations in "n". An important saturated fatty acid is stearic acid (n = 16), which when neutralized with lye is the most common form of soap .
What is a fatty acid?
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long aliphatic chain , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids ...
How many carbon atoms are in a double bond?
In most naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids, each double bond has three ( n-3 ), six ( n-6 ), or nine ( n-9) carbon atoms after it, and all double bonds have a cis configuration. Most fatty acids in the trans configuration ( trans fats) are not found in nature and are the result of human processing (e.g., hydrogenation ).
Which fatty acids are susceptible to degradation by ozone?
Unsaturated fatty acids are susceptible to degradation by ozone. This reaction is practiced in the production of azelaic acid ( (CH 2) 7 (CO 2 H) 2) from oleic acid.
What is Omega 3 fat?
They are a class of fatty acids found in fish oils that reduce cholesterol and LDL (low-density lipoproteins) levels in the blood, especially in salmon and other cold-water fish. (The "bad" cholesterol is LDL cholesterol.)
What are the most commonly distributed fatty acids?
The 16- and 18-carbon fatty acids, better known as palmitic acid and stearic acid, are among the most commonly distributed fatty acids. In the lipids of most species, both palmitic and stearic acids exist. Palmitic acid makes up as much as 30 percent of body fat in animals. It accounts for between 5 and 50 percent of the lipids in vegetable fats, ...
Why are fatty acids essential?
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that must be consumed by humans and other animals because they are required by the body for good health but can not be synthesized. Fatty acids needed for biological processes are referred to by the term "essential fatty acid" but do not include fats that only serve as fuel.
How are fatty acids classified?
In many ways, fatty acids are classified: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by the content of even vs odd carbon, and by linear vs branched.
What are soaps made of?
Soaps are fatty acid salts of sodium and potassium. Some skincare items contain fatty acids, which can help keep the look and function of the skin healthy. Fatty acids are also commonly marketed as dietary supplements, particularly omega-3 fatty acids.
What are fatty acids used for?
They are used not only in the manufacture of various food products, for instance, but also in soaps, detergents, and cosmetics. Soaps are fatty acid salts of sodium and potassium.
What are the components of fatty acids?
Introduction to Fatty Acid. Fatty acids in plants, animals, and microorganisms make the essential components of lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells). A fatty acid generally consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms along the chain length and at one end of the chain and at the other end ...
What is the point 2 of fatty acids?
Point 2: Odd-numbered fatty acids can be produced by various organisms, and can be linked to dysfunction in humans.
How do we get odd numbered fatty acids?
In plants and in synthetic contexts, we can have some reactions that can produce odd-numbered fatty acids (by building with two-carbon units three times to get six, and then breaking that six in half to get three, for example). Such odd fatty acids are seen in some organisms, but humans are usually thought to get them from other sources (e.g. microbiota, diet).
Why are fatty acids even numbered?
So we usually get even-numbered fatty acids just because the building blocks are also even.
What is the meaning of "back up"?
Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience.
Who has a really good explanation of fatty acid synthesis?
The European Bioinformatics Institute has a really good explanation of fatty acid synthesis. The quote below is from that ( https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/potm/2007_6/Page2.htm ):

Overview
Types of fatty acids
Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by even vs odd carbon content, and by linear vs branched.
• Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of five or fewer carbons (e.g. butyric acid).
• Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain triglycerides.
History
The concept of fatty acid (acide gras) was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: graisse acide and acide huileux ("acid fat" and "oily acid").
Nomenclature
Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of carbon atoms, with a carboxyl group (–COOH) at one end, and a methyl group (–CH3) at the other end.
The position of each carbon atom in the backbone of a fatty acid is usually indicated by counting from 1 at the −COOH end. Carbon number x is often abb…
Production
Fatty acids are usually produced industrially by the hydrolysis of triglycerides, with the removal of glycerol (see oleochemicals). Phospholipids represent another source. Some fatty acids are produced synthetically by hydrocarboxylation of alkenes.
Hyper-oxygenated fatty acids are produced by a specific industrial processes for topical skin creams. The process is based on the introduction or saturation of peroxides into fatty acid ester…
Reactions of fatty acids
Fatty acids exhibit reactions like other carboxylic acids, i.e. they undergo esterification and acid-base reactions.
Fatty acids do not show a great variation in their acidities, as indicated by their respective pKa. Nonanoic acid, for example, has a pKa of 4.96, being only slightly weaker than acetic acid (4.76). As the chain length increases, the solubility of the fatty acids in water decreases, so that the lon…
Circulation
Short- and medium-chain fatty acids are absorbed directly into the blood via intestine capillaries and travel through the portal vein just as other absorbed nutrients do. However, long-chain fatty acids are not directly released into the intestinal capillaries. Instead they are absorbed into the fatty walls of the intestine villi and reassemble again into triglycerides. The triglycerides are coated with cholesterol and protein (protein coat) into a compound called a chylomicron.
Skin
The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis. It is composed of terminally differentiated and enucleated corneocytes that reside within a lipid matrix, like "bricks and mortar." Together with cholesterol and ceramides, free fatty acids form the lipid mortar, a water-impermeable barrier that prevents evaporative water loss. As a general rule of thumb, the epidermal lipid matrix is composed of an equimolar mixture of ceramides (~50% by weight), cho…
Fatty Acids Examples
Essential Fatty Acids
Here Is An Example of Two Essential Fatty Acids
Classification of Fatty Acids
- In many ways, fatty acids are classified: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by the content of even vs odd carbon, and by linear vs branched. 1. Fatty acids with aliphatic tails of five or fewer carbons are short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) (e.g. butyric acid). 2. Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with 6 to 12 carbon aliphatic tai...
List of Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Applications of Fatty Acids
Did You Know?
Table of Contents
Classification of Fatty Acids
- 1. They are classified into three types based on their degree of saturation/unsaturation in the carbon chain: 1. If there is no double bond, the fatty acid is saturated. 2. If there is one double bond, the fatty acid is monounsaturated, 3. If there are two or more double bonds, the fatty acid is polyunsaturated. 2. Furthermore, they can be divided ...
Production of Fatty Acids
Properties of Fatty Acids
Uses of Fatty Acids