Are catabolic and anabolic reactions linked?
Conversely, anabolic reactions use the energy produced by catabolic reactions to synthesize larger molecules from smaller ones, such as when the body forms proteins by stringing together amino acids. Both sets of reactions are critical to maintaining life.
Are anabolic and catabolic pathways coupled?
Catabolic and anabolic pathways are often coupled in cell because.
How and why are anabolic and catabolic reactions coupled in the cell?
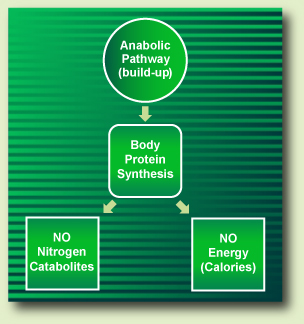
Coupling of anabolic and catabolic pathways Anabolism utilises energy to make macromolecules and biomolecular polymers. Catabolism releases energy when these are broken down into simpler molecules. Metabolism consists of a series of reactions that occur within cells of living organisms to sustain life.
When we say that catabolic and anabolic reactions are coupled What does that really mean?
When we say that catabolic and anabolic reactions are coupled, what does that really mean? Catabolic reactions provide energy and smaller molecules required by anabolic reactions.
Which metabolic pathway is both anabolic and catabolic?
The TCA cycle is amphibolic; i.e., it serves as a catabolic and an anabolic pathway. Reactions that utilize intermediates of the cycle as precursors for the biosynthesis of other molecules are as follows. Some of these reactions occur outside the mitochondria.
What are the 2 types of metabolic pathway?
Metabolic pathways can be broadly divided into two categories based on their effects. Photosynthesis, which builds sugars out of smaller molecules, is a "building up," or anabolic, pathway. In contrast, cellular respiration breaks sugar down into smaller molecules and is a "breaking down," or catabolic, pathway.
Why do metabolic pathways need to be linked?
Such a reaciton pathway can create a new molecule (biosynthesis), or it can break down a molecule (degradation). Sometimes, the enzymes involved in a particular metabolic pathway are physically connected, allowing the products of one reaction to be efficiently channeled to the next enzyme in the pathway.
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between catabolism and anabolism reactions?
Which of the following best describes the relationship between catabolism and anabolism? Catabolic reactions provide the energy for anabolic reactions.
What are some examples of anabolic reactions?
An example of an anabolic reaction is photosynthesis, where plants make glucose molecules from different raw materials. An example of a catabolic reaction is the process of food digestion, where different enzymes break down food particles so they can be absorbed by the small intestine.
Which type of pathway requires energy and is used to build up large molecules from smaller ones?
Anabolic – this type of pathway requires energy and is used to build up large molecules from smaller ones (biosynthesis).
Why do enzymes change substrates?
The enzymes change the substrate at each step in the metabolic pathway in order to get the final product at the end. There are different types of metabolic pathways – some are anabolic and some are catabolic.
Where are enzymes found in the cell?
Enzymes are vital proteins involved in metabolic pathways. Some enzymes can be found embedded within the cell membrane. Other proteins found embedded within the membrane act as: pumps - for example the sodium potassium pump that pumps sodium out ...
Is a metabolic pathway irreversible?
Metabolic pathways can be reversible or irreversible. Almost all pathways are reversible.
What happens when you are in anabolic or catabolic?
Remember: When you’re in an anabolic state, you’re building and maintaining your muscle mass. When you’re in a catabolic state, you’re breaking down or losing overall mass, both fat and muscle. You may be able to manipulate your body weight by understanding these processes and your overall metabolism.
How does catabolism work?
Catabolism uses energy to break down. These metabolic processes work together in all living organisms to do things like produce energy and repair cells. Understanding the difference between anabolic and catabolic processes may help you reach your goals in the gym and on the scale.
How to prevent catabolism?
Preventing catabolism is all about keeping good balance between your nutrition, training, and recovery. Muscle can be maintained by training three or four days a week. The following sample exercise program may help you stay in a building or anabolic state. Try focusing on one area per day, resting in between.
How does catabolic exercise help you lose weight?
Catabolic workouts, on the other hand, may help you shed pounds by working off both fat and muscle. You’ll weigh less, but you’ll also have far less critical muscle mass.
What is catabolic exercise?
Catabolic exercises are aerobic, or cardio, exercises. They may include moves — like running, swimming, and biking — where you’re in a steady active state for a relatively long period of time. According to the American College of Sports Medicine, aim to get at least the following amounts of aerobic exercise each week:
What happens when you digest food and the molecules break down in the body for use as energy?
Catabolism is what happens when you digest food and the molecules break down in the body for use as energy. Large, complex molecules in the body are broken down into smaller, simple ones. An example of catabolism is glycolysis. This process is almost the reverse of gluconeogenesis.
What are some examples of anabolism?
In this process, small, simple molecules are built up into larger, more complex ones. An example of anabolism is gluconeogenesis.
What is the role of anabolism and catabolism in the body?
Anabolism and catabolism may sound like superheroes from your kid’s favorite TV show, but these terms actually come from the health world. Doctors, dietitians, health coaches, and bodybuilders use their understanding of these two functions to create diet and exercise plans that can influence your metabolism (how your body uses energy) and ultimately, your overall health.
How does food affect anabolism and catabolism?
Catabolism functions no matter what you give your body, states DiMarino. It breaks down food, whether it’s junky or nutritious. Whatever it doesn’t use for energy now, it stores for later (hello, extra pounds).
What is catabolism?
When you think catabolism, think digestion, says DiMarino. This process takes larger structures like proteins, fats or tissues and breaks them down into smaller units such as cells or fatty acids.
Which mechanism takes smaller units like nutrients, cells, or amino acids and bonds them together to create bigger structures?
Anabolism is the opposite of catabolism: It’s the mechanism that takes smaller units like nutrients, cells, or amino acids and bonds them together to create bigger structures.
Is exercise considered anabolic or catabolic?
Different types of exercise are considered anabolic or catabolic, depending on whether they use energy to build or break down something.
Is Cleveland Clinic a non profit?
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cle veland Clinic products or services. Policy
Can I control my metabolism?
A lot of uncontrollable factors, including age, gender and genetics, direct your metabolism. But, says DiMarino, you can positively influence hormones that play a role in anabolism and catabolism with these healthy habits:
Which enzyme facilitates fatty acetyl Co A to come across mitochondria for cleavage?
II. Carnutune facilitates fatty acetyl Co A to come across mitochondria for cleavage.
Where is ATP generated from glucose?
Oxidative Phosphorylation: 90% of ATP generated from glucose results from oxidative phosphorylation via electron transport chain (which is located in the inner membrane of mitochondria). OP releases energy and is accomplished by reactions linking oxidation of NADH +H+ and FADH2 to the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP.
Which cycle produces 6NADH+H+ 2FADH2 and 2 ATPs per 2 molecules?
3. Citric Acid Cycle: Oxaloacetate is the last product and citrate substrate. Generates 6NADH+H+ 2FADH2 and 2 ATPs per 2 molecules acetyl coA. Amphibolic pathway: intermediate products of the citric acid cycle can enter anabolic pathway. ATP not made directly in the cycle but generates from GTP via substrate Phosphorylation.
What is the process that breaks down glycogen into glucose-6-P?
1. Glycogenolysis: Breaks down glycogen to glucose-6-P or glucose. Happens in liver (released into blood) and muscle (G6P can only be used locally)
Which ions are pumped to intermembrane space, generating a force?
II. H ions pumped to intermembrane space, generating a force
What are the two types of metabolic pathways?
There are two types of metabolic pathways: catabolic, involving the breakdown of biochemicals into simpler compounds, and anabolic, involving the synthesis of biochemicals from simpler molecules.
How many metabolic pathways are there?
There are two types of metabolic pathways: catabolic, involving the breakdown of biochemicals into simpler compounds, and anabolic, involving the synthesis of biochemicals from simpler molecules. Each living cell has thousands of distinct metabolic reactions. Each reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme and is linked to other reactions through a pathway. How can you keep them all straight? It is nearly impossible to memorize them. The purpose of this chapter is to provide an organizational framework to metabolism that allows you to view it as something other than a collection of disjointed pathways.