What is the process of separating chromosomes called?
When chromatids separate, what are they called?
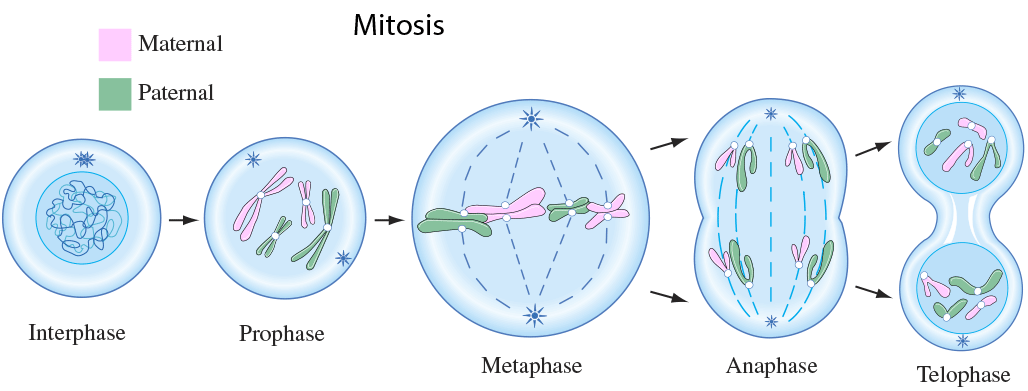
- During interphase, it copies the DNA, so there are two identical strands for each of the 23 pairs in your cells.
- During prophase these DNA strands condense into X-shaped chromosomes. ...
- During anaphase the spindle fibers pull and break the centromere, and the two sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. ...
How do the chromosomes split apart?
How do chromosomes split apart in anaphase? The microtubules get shorter and the spindle poles also move farther apart to split them. Cohesin. protein that holds sister chromatids together to ensure even division and is removed at anaphase. Separase.
What is the third stage of the chromosomes separate?
What type of tumors are cancerous?
- Produce Haploid gametes
- Keep chromosome # constant from generation to generation
- Increases genetic variation
What are the chromosomes in each pair of chromosomes called?
Of the 23 pairs of chromosomes, the first 22 pairs are called "autosomes." The final pair is called the "sex chromosomes." Sex chromosomesdetermine an individual's sex: females have two X chromosomes (XX), and males have an X and a Y chromosome (XY).

How do chromosomes separate during meiosis?
Figure 3: During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are pulled toward opposite poles of the cell. During anaphase I, the microtubules disassemble and contract; this, in turn, separates the homologous chromosomes such that the two chromosomes in each pair are pulled toward opposite ends of the cell (Figure 3).
What part of the cell separates chromosomes?
Finally, during telophase, a nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes to separate the nuclear DNA from the cytoplasm. The chromosomes begin to uncoil, which makes them diffuse and less compact.
Where do chromosomes start separating?
Metaphase: During metaphase, each of the 46 chromosomes line up along the center of the cell at the metaphase plate. Anaphase: During anaphase, the centromere splits, allowing the sister chromatids to separate.
How do chromosomes split apart during anaphase?
During anaphase, the microtubules attached to the kinetochores contract, which pulls the sister chromatids apart and toward opposite poles of the cell (Figure 3c). At this point, each chromatid is considered a separate chromosome.
During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes separate?
anaphaseDuring anaphase, each pair of chromosomes is separated into two identical, independent chromosomes. The chromosomes are separated by a structure called the mitotic spindle.
How does binary fission happen?
binary fission, asexual reproduction by a separation of the body into two new bodies. In the process of binary fission, an organism duplicates its genetic material, or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and then divides into two parts (cytokinesis), with each new organism receiving one copy of DNA.
How is the spindle formed?
At the beginning of nuclear division, two wheel-shaped protein structures called centrioles position themselves at opposite ends of the cell forming cell poles. Long protein fibers called microtubules extend from the centrioles in all possible directions, forming what is called a spindle.
Does the centromere divide?
The centromeres divide, and the sister chromatids of each chromosome are pulled apart - or 'disjoin' - and move to the opposite ends of the cell, pulled by spindle fibres attached to the kinetochore regions. The separated sister chromatids are now referred to as daughter chromosomes.
What is the process of segregation of chromosomes?
Chromosome segregation is the process in eukaryotes by which two sister chromatids formed as a consequence of DNA replication, or paired homologous chromosomes, separate from each other and migrate to opposite poles of the nucleus. This segregation process occurs during both mitosis and meiosis.
What is the process of a chromatid ending up in two nuclei?
These chromatids separate to opposite poles, a process facilitated by a protein complex referred to as cohesin . Upon proper segregation, a complete set of chromatids ends up in each of two nuclei, and when cell division is completed, each DNA copy previously referred to as a chromatid is now called a chromosome.
What type of recombination is most likely to occur during meiotic prophase I?
Most recombination events appear to be the SDSA type. Meiotic chromosomal crossover (CO) recombination facilitates the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes. This is because, at the end of meiotic prophase I, CO recombination provides a physical link that holds homologous chromosome pairs together.
What is the process of alignment of homologous chromosomes?
The process of alignment of paired homologous chromosomes is called synapsis (see Synapsis ). During synapsis, genetic recombination usually occurs.
What stage of meiosis is chromatid segregation?
Meiotic chromosome and chromatid segregation. Chromosome segregation occurs at two separate stages during meiosis called anaphase I and anaphase II (see meiosis diagram). In a diploid cell there are two sets of homologous chromosomes of different parental origin (e.g. a paternal and a maternal set). During the phase of meiosis labeled “interphase ...
Which stage of meiosis is segregated?
The second stage at which segregation occurs during meiosis is prophase II (see meiosis diagram). During this stage, segregation occurs by a process similar to that during mitosis, except that in this case prophase II is not preceded by a round of DNA replication. Thus the two chromatids comprising each chromosome separate into different nuclei, ...
What stage of recombination is chromosome segregation?
Following recombination, chromosome segregation occurs as indicated by the stages metaphase I and anaphase I in the meiosis diagram. Different pairs of chromosomes segregate independently of each other, a process termed “independent assortment of non-homologous chromosomes”.
Why are chromosomes called chromosomes?
Scientists gave this name to chromosomes because they are cell structures, or bodies, that are strongly stained by some colorful dyes used in research.
What is the chromosome made of?
Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Passed from parents to offspring, DNA contains the specific instructions that make each type of living creature unique. The term chromosome comes from the Greek words for color (chroma) and body (soma).
What is the role of chromosomes in DNA?
Chromosomes are a key part of the process that ensures DNA is accurately copied and distributed in the vast majority of cell divisions. Still, mistakes do occur on rare occasions. Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes in new cells may lead to serious problems.
Why do we need centromeres?
Centromeres help to keep chromosomes properly aligned during the complex process of cell division. As chromosomes are copied in preparation for production of a new cell, the centromere serves as an attachment site for the two halves of each replicated chromosome, known as sister chromatids.
How many copies of chromosomes are inherited?
In humans and most other complex organisms, one copy of each chromosome is inherited from the female parent and the other from the male parent . This explains why children inherit some of their traits from their mother and others from their father.
How long would DNA be if it was unwound?
For example, if all of the DNA molecules in a single human cell were unwound from their histones and placed end-to-end, they would stretch 6 feet.
Why do cells divide?
For an organism to grow and function properly, cells must constantly divide to produce new cells to replace old, worn-out cells. During cell division, it is essential that DNA remains intact and evenly distributed among cells.
How many chromosomes are in a cell before it divides?
Before the cell divides, it is actually one large cell, containing 8 chromosomes. 3. A student is watching cell replicate under a microscope, and recording the number of chromosomes present during different phases of the cell cycle. The organism usually has 2 homologous pairs, or 4 chromosomes in adults.
What is the chromosome in the cell cycle?
A chromosome is a string of DNA wrapped around associated proteins that give the connected nucleic acid bases a structure. During interphase of the cell cycle, the chromosome exists in a loose structure, so proteins can be translated from the DNA and the DNA can be replicated. During mitosis and meiosis, the chromosome becomes condensed, ...
What is the name of the DNA and its associated proteins, of which chromosomes are a part?
Related Biology Terms. Chromatin – DNA and its associated proteins, of which chromosomes are a part. Sister Chromatid – The still connected copies of a chromosome, which will be separated into individual chromosomes during anaphase of mitosis or anaphase II of meiosis.
What happens to chromatin during cell division?
During cell division, all the proteins are activated and the chromatin becomes densely packed into distinct chromosomes. These dense molecules have a better chance of withstanding the pulling forces that occur when chromosomes are separated into new cells.
Why do we have chromosomes?
Each chromosome carries part of the genetic code necessary to produce an organism. Having the entire genetic code divided into different chromosomes allows the possibility of variation through the different combinations of chromosomes with the different alleles, or genetic variations that they contain.
How many chromosomes are in a prokaryotic cell?
In prokaryotes, there is usually only a single chromosome, which exists in a ring-like or linear shape. The chromatin of most eukaryotic organisms consists of multiple chromosomes, as described later in the article. Each chromosome carries part of the genetic code necessary to produce an organism.
What are the bases of chromosomes?
DNA is made of a two strings of nucleic acid base pairs. The base pairs in DNA are cytosine, adenine, thymine, and guanine.
What is the phase of the cell cycle where chromosomes are evenly divided between two cells?
Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where chromosomes in the nucleus are evenly divided between two cells. When the cell division process is complete, two daughter cells with identical genetic material are produced.
Which phase do the daughter chromosomes migrate?
The daughter chromosomes migrate centromere first and the kinetochore fibers become shorter as the chromosomes near a pole. In preparation for telophase, the two cell poles also move further apart during the course of anaphase. At the end of anaphase, each pole contains a complete compilation of chromosomes.
What happens to the chromosomes in anaphase?
In anaphase, the paired chromosomes ( sister chromatids) separate and begin moving to opposite ends (poles) of the cell. Spindle fibers not connected to chromatids lengthen and elongate the cell. At the end of anaphase, each pole contains a complete compilation of chromosomes.
What are the specialized regions of chromosomes?
Kinetochores, which are specialized regions in the centromeres of chromosomes, attach to a type of microtubule called kinetochore fibers. The kinetochore fibers "interact" with the spindle polar fibers connecting the kinetochores to the polar fibers. The chromosomes begin to migrate toward the cell center.
When do diploid cells begin to form?
It begins prior to the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophase/mitosis. At the end of cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are produced. These are diploid cells, with each cell containing a full complement of chromosomes.
What is the second gap phase of a cell?
The cell synthesizes proteins and continues to increase in size. The G2 phase is the second gap phase. In the latter part of interphase, the cell still has nucleoli present. The nucleus is bounded by a nuclear envelope and the cell's chromosomes have duplicated but are in the form of chromatin.
Why do centrioles move away from each other?
The two pairs of centrioles (formed from the replication of one pair in Interphase) move away from one another toward opposite ends of the cell due to the lengthening of the microtubules that form between them.
Overview
Chromosome segregation is the process in eukaryotes by which two sister chromatids formed as a consequence of DNA replication, or paired homologous chromosomes, separate from each other and migrate to opposite poles of the nucleus. This segregation process occurs during both mitosis and meiosis. Chromosome segregation also occurs in prokaryotes. However, in contrast to eukaryotic chromosome segregation, replication and segregation are not temporally separated. I…
Mitotic chromatid segregation
During mitosis chromosome segregation occurs routinely as a step in cell division (see mitosis diagram). As indicated in the mitosis diagram, mitosis is preceded by a round of DNA replication, so that each chromosome forms two copies called chromatids. These chromatids separate to opposite poles, a process facilitated by a protein complex referred to as cohesin. Upon proper se…
Meiotic chromosome and chromatid segregation
Chromosome segregation occurs at two separate stages during meiosis called anaphase I and anaphase II (see meiosis diagram). In a diploid cell there are two sets of homologous chromosomes of different parental origin (e.g. a paternal and a maternal set). During the phase of meiosis labeled “interphase s” in the meiosis diagram there is a round of DNA replication, so that each of the chromosomes initially present is now composed of two copies called chromatids. Th…
Crossovers facilitate segregation, but are not essential
Meiotic chromosomal crossover (CO) recombination facilitates the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes. This is because, at the end of meiotic prophase I, CO recombination provides a physical link that holds homologous chromosome pairs together. These linkages are established by chiasmata, which are the cytological manifestations of CO recombination. Tog…
See also
• Cell cycle
• Non-random segregation of chromosomes