Cilia and flagella
Flagellum
A flagellum is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals a…
Are flagella more numerous than cilia?
The differences between them are in their number, length, and position. Flagella are less numerous, longer, and usually polar, while cilia are more numerous and shorter, covering much of the cell’s surface.
What are facts about cilia?
Here are the similarities between cilia and flagella:
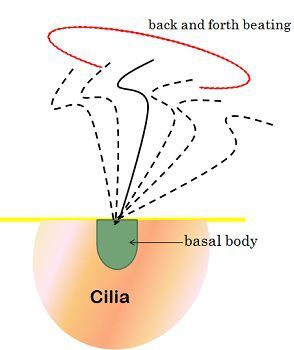
- They both arise from the basal body, a centriole -like structure.
- They both outgrow from the cell’s plasma membrane.
- They both have an axoneme, a central filament. Axoneme has 11 microtubules of which, 9 are in pairs (doublet), and the remaining 2 are located in the center (singlet).
- Their primary function is locomotion.
Does a plant cell have a cilia or a flagella?
The basic plant cell shares a similar construction motif with the typical eukaryote cell, but does not have centrioles, lysosomes, intermediate filaments, cilia, or flagella, as does the animal cell. Beside above, are cilia and flagella the same? Cilia are short and there are usually many (hundreds) cilia per cell.
How does a cilium differ from a flagellum?
The main difference between cilia and flagella is that cilia prevent the accumulation of dust inside the breathing tubes, creating a thin layer of mucous along the tubes whereas flagella are mainly used by sperm cells to propel themselves through the female reproductive organ.

What is the difference between the cilia and flagella and function?
Cilia are short, hair like cell organelle extending from the surface of a living cell. Flagella are long, threadlike cell organelle present on the surface of a living cell. It is found in Eukaryotic cell. It is found in Prokaryotic cell as well as in eukaryotic cells.
What is the difference between cilia and flagella quizlet?
What is the difference between cilia and flagella? Cilia and flagella are both involved in movement, though cilia moves substances across its surface, while flagella moves itself as an entire cell from one point to another.
What are the similarities and differences between cilia and flagella?
Cilia and flagella are alike in that they are made up of microtubules. Cilia are short, hair-like structures that exist in large numbers and usually cover the entire surface of the plasma membrane. Flagella, in contrast, are long, hair-like structures; when flagella are present, a cell has just one or two.
What is the primary difference between cilia and flagella in eukaryotes?
Cilia are short, hair like appendages extending from the surface of a living cell. Flagella are long, threadlike appendages on the surface of a living cell.
What do cilia and flagella have in common?
Eukaryotic flagella and cilia have long been recognized as organelles involved in motility, and their structure and function have both been studied in detail. Almost all motile (secondary) cilia and flagella have the same internal structure and have essentially the same function.
How do cilia and flagella move?
Abstract. Cilia and flagella are cell organelles serving basic roles in cellular motility. Ciliary movement is performed by a sweeping-like repeated bending motion, which gives rise to a self-propagating "ciliary beat". The hallmark structure in cilia is the axoneme, a stable architecture of microtubule doublets.
What's the difference between flagella and flagellum?
flagellum, plural flagella, hairlike structure that acts primarily as an organelle of locomotion in the cells of many living organisms. Flagella, characteristic of the protozoan group Mastigophora, also occur on the gametes of algae, fungi, mosses, slime molds, and animals.
What is the main difference between flagella and pili?
Flagella are helical appendages that protrude through the cell membrane and are long and whip-like. Pili are hollow filamentous extensions that emerge from the cell's surface. 2.
What is the function of cilia?
Overview. The bronchus in the lungs are lined with hair-like projections called cilia that move microbes and debris up and out of the airways. Scattered throughout the cilia are goblet cells that secrete mucus which helps protect the lining of the bronchus and trap microorganisms.
What is the function of cilia when present )? Quizlet?
Cilia: are the hair like projections present on the internal free surfaces of some organs like respiratory tract, intestine etc. these cilia move to and from to produce wave motion. these wave motion helps in the clearance excess mucous and fluids in various tracts and example, respiratory tract.
What is the flagella function?
Flagellum is primarily a motility organelle that enables movement and chemotaxis. Bacteria can have one flagellum or several, and they can be either polar (one or several flagella at one spot) or peritrichous (several flagella all over the bacterium).
Which is the function of a flagellum quizlet?
What are flagella and what is their structure? Responsible for motility and movement. Composed of filament, hook, and basal body.
1. Where are Cilia and Flagella Located?
The motile cilia are located on the epithelial cells of the various internal organs like the trachea, lungs, digestive system, etc. They are also f...
2. From where should students prepare the topic of "Difference Between Cilia and Flagella" for their...
Nowadays, many study materials are available on the internet on the topic of "Difference Between Cilia and Flagella". But students must prefer Veda...
3. Name and describe the four types of flagella.
The four types of flagella are discussed below:Amphitrichous - These are the single flagellum that is present at both the ends of the creature. The...
4. Describe the meaning and the function of non-motile cilia.
Non-motile cilia are one of the types of cilia. In 1898, these primary cilia were discovered. These were also known as vestigial organelles. The fu...
5. In how many parts does the body of flagella is divided?
The structure of the flagella is helical and is made up of flagellin protein. The body of this structure is divided into 3 parts. These parts are m...
What are the characteristics of cilia and flagella?
Both are the outgrowth of the plasma membrane of the cell. Cilia and flagella consist of the central filament called an axoneme. The axoneme contains eleven microtubules. Nine are present in pairs called as the doublet, and two of them present in the center are the singlet. This is called 9+2 microtubular arrangement. The drift in the microtubules of the axoneme causes the movement in the cilia and flagella. The axoneme contains proteins like dynein, tubulin, nexin.
Which is faster, Cilia or Flagella?
Cilia beat coordinately and show rotational motion and are very fast moving also, on the other hand, flagella show whip-like, sinusoidal, undulating, independent movement, but are slow.
What is the molecular structure of the cilia?
Motile cilia consist of ciliary axoneme, which is regarded as the microtubular backbone, they have 9+2 arrangement of the ciliary axoneme and is surrounded by the plasma membrane. In this arrangement, the nine fused pairs of microtubules arranged in a circle, while the two unfused microtubules are present in the center of the circle.
What are some examples of eukaryotic flagella?
Eukaryotic flagella are the complex projections, that beat back and forth. An example is the sperm cell, which propels itself through the female reproductive tract by using its flagellum.
What is a cilia?
Definition of Cilia. Cilia are short, slender, hair-like appendages extending from the surface of the cell. These are present in almost all eukaryotic cells. They play a significant role the cell and overall body development. Cilia are most active during the cell cycle progression and proliferation.
Where are flagella found?
They also take part in capturing food. These both are found in eukaryotic cells, but in prokaryotic cells only flagella. Both of these appendages are found in eukaryotic cells, but in prokaryotic cells only flagella are present. Although these appendages are not found in plants.
How big is a flagella?
They can be about 5-16 µm in length and 12-30 nm in diameter. Flagella are of three types – bacterial flagella, archaeal flagella, eukaryotic flagella. Bacterial flagella are found in Salmonella typhi, E. coli. They can be one, two or many flagella per cell.
Where are flagella and cilia found?
The non-motile cilia are generally found in the dendritic knob of the olfactory neuron. On the other hand, the flagella are usually found on the backside of the cell or the organism, and they help them in smooth movements through the liquids using their whip-like structure. Share this with your friends.
What is the structure of the cilia?
Structure of Cilia. The cilia are made up of microtubules that are coated in the plasma membrane. Each of the cilia consists of nine pairs of microtubules that form the outside ring while the two others make the central microtubules. This structure is known as axoneme. The outer ring microtubules are made up of motor proteins called dynein.
Why is flagella important for eukaryotes?
Flagella helps an organism in the movement, and they act as sensory organs to detect the pH and temperature changes. A few eukaryotes also use flagellum to increase reproduction rates. It has been found recently that the flagella are also used as a secretory organelle.
What is the name of the microscopic hair-like structures that are involved in the locomotion of the cells?
Flagella are the microscopic hair-like structures that are involved in the locomotion of the cells. The word ‘flagellum’ itself means ‘whip.’. Flagella are known to have a whip-like appearance, and they help a cell to propel through the liquid around it.
What are the two types of cilia?
Cilia Could be of Two Types: Motile and Non-motile. The motile cilia are present in a huge number on the surface of the cells, and they are usually found in the respiratory epithelium in humans. On the other hand, the non-motile cilia act as the sensory cellular antenna that coordinates with a number of cellular signaling pathways.
What is the function of cilia?
Function of Cilia. Cilia help in the locomotion and the sensory functions, and it plays a vital role in the cell cycle and the replication and thus in the development of humans and animals. Multiple cilia wave in a rhythmic motion that helps in keeping the internal passageways free from any foreign agent and mucus.
Where are motile cilia located?
Answer: The motile cilia are located on the epithelial cells of the various internal organs like the trachea, lungs, digestive system, etc. They are also found on the protozoans like the paramecium, and they assist these organisms in the locomotion. The non-motile cilia are generally found in the dendritic knob of the olfactory neuron.
How are flagella and cilia similar?
Cilia and flagella are cell organelles that are structurally similar but are differentiated based on their function and/or length. Cilia are short and there are usually many (hundreds) cilia per cell. On the other hand, flagella are longer and there are fewer flagella per cell (usually one to eight). Though eukaryotic flagella and motile cilia are structurally identical, the beating pattern of the two organelles can be different. The motion of flagella is often undulating and wave-like, whereas the motile cilia often perform a more complicated 3D motion with a power and recovery stroke.
What is the difference between flagella and motile cilia?
The motion of flagella is often undulating and wave-like, whereas the motile cilia often perform a more complicated 3D motion with a power and recovery stroke.
What happens if the cilia in the fallopian tubes are not functioning properly?
If the cilia in the fallopian tubes are not functioning properly then the fertilized ovum will not reach the uterus and thus result in ectopic pregnancy. A defect of the primary cilium in the renal tube cells can lead to polycystic kidney disease (PKD).
What are the three types of flagella?
There are three types of flagella - bacterial, archaeal and eukaryotic. Bacterial flagella are helical filaments that rotate like screws. They are found in E. coli, Salmonella typhimurium.
How many microtubules are in the central bundle of a prokaryotic cell?
In non-motile or primary cilia the two central single microtubules are absent. So the central bundle consists of 9 + 0 microtubules. In prokaryotes cells the flagella are filamentous protein structures composed of flagellin. Prokaryotic flagella are much thinner than eukaryotic flagella, and they lack the typical 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules.
What is the function of eukaryotic flagella?
Eukaryotic flagella are complex cellular projections that lash back and forth. (e.g., the sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract.
Why is flagellum dysfunction important for male infertility?
Flagellum dysfunction can also be responsible for male infertility because the sperm is not motile and cannot swim to the ovum.
What is the difference between flagella and cilia?
Cilia are short, hair like appendages extending from the surface of a living cell. Flagella are long, threadlike appendages on the surface of a living cell. Occurs throughout the cell surface.
What is the flagella?
Flagella are the complex filamentous cytoplasmic structure protruding through cell wall. These are unbranched, long, thread like structures, mostly composed of the protein flagellin, intricately embedded in the cell envelope.
What are the functions of a flagella?
Energy Production. Cilia use ‘kinesin’ which has an ATPase activity that produces energy to perform the movement. Flagella are powered by the proton-motive force by the plasma membrane. 11. Functions. Helps in locomotion, feeding circulation, aeration, etc.
What Are Cilia and Flagella?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain structures known as cilia and flagella. These extensions from the cell surface aid in cell movement. They also help to move substances around cells and direct the flow of substances along tracts. Cilia and flagella are formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies. If the protrusions are short and numerous they are termed cilia. If they are longer and less numerous (usually only one or two) they are termed flagella.
Where Can Cilia and Flagella Be Found?
Both cilia and flagella are found in numerous types of cells. For instance, the sperm of many animals, algae, and even ferns have flagella. Prokaryotic organisms may also possess a single flagellum or more. A bacterium, for example, may have: one flagellum located at one end of the cell (montrichous), one or more flagella located at both ends of the cell (amphitrichous), several flagella at one end of the cell (lophotrichous), or flagella distributed all around the cell (peritrichous). Cilia can be found in areas such as the respiratory tract and female reproductive tract. In the respiratory tract, cilia helps to sweep mucus containing dust, germs, pollen, and other debris away from the lungs. In the female reproductive tract, cilia helps to sweep sperm in the direction of the uterus.
What are the protrusions of cilia and flagella called?
Cilia and flagella are formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies. If the protrusions are short and numerous they are termed cilia. If they are longer and less numerous (usually only one or two) they are termed flagella.
What are cilia used for?
In higher organisms, cilia is often used to propel substances in a desired direction. Some cilia, however, do not function in movement but in sensing.
What are the sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules?
Lysosomes: Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules.
Where are flagella located?
A bacterium, for example, may have: one flagellum located at one end of the cell (montrichous), one or more flagella located at both ends of the cell (amphitrichous), several flagella at one end of the cell (lophotrichous), or flagella distributed all around the cell (peritrichous). Cilia can be found in areas such as the respiratory tract ...
Which structure controls cell growth and reproduction?
Nucleus: Cell growth and reproduction are controlled by the nucleus. Ribosomes: Ribosomes are RNA and protein complexes that are responsible for protein production via translation.
What are the functions of the flagella and cilia?
The Flagella and Cilia are microscopic, contractile and filamentous processes of the cytoplasm which are capable of producing a current in the fluid medium for locomotion and passage of substances. Also, they act as sensory organs and perform many mechanical functions of the cell.
What are the two types of flagella?
Ans: There are two main types of flagella in eukaryotes: 1. Whiplash flagellum is one that does not have hairy flimmers on the surface. 2. The tinsel flagellum is one that has lateral hair-like projections or flimmers, or mastigonemes on the surface.
What are the different types of bacteria?
Based on the number and arrangement of flagella, there are the following types of bacteria: 1 Monotrichous – Vibrio cholerae has a single flagellum only at one end of the cell. 2 Amphitrichous – Nitrosomonas has a single flagellum at each pole. 3 Lophotrichous – Spirillum volutans has a cluster of flagella at one or both ends. 4 Peritrichous – Flagella are spread fairly evenly over the whole surface. Like E. coli. 5 Cephalotrichous – Pseudomonas fluorescens has a cluster of flagella only at one end. 6 Atrichous –Lactobacillus, Pasteurella have no flagella.
What is the name of the hair-like structure that moves cells or substances along the outer surface of the cell?
Cilla. Cilia (singular = cilium) are short, hair-like structures that are used to move entire cells or substances along the outer surface of the cell. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic flagella are different in chemical composition and structure.
What are the parts of a prokaryotic flagella?
The bacterial flagella have the following features: The bacterial flagellum is made up of the flagellin protein. Each flagellum has three parts, hook, shaft, and the basal body.
What is the structure that extends from the plasma membrane?
Flagella (singular = flagellum) are long, hair-like structures that extend from the plasma membrane and are used in the movement of an entire cell.
What are the three parts of the flagellum?
Each flagellum has three parts, hook, shaft, and the basal body. This has a helical structure and very sharp bending outside the outermost membrane. This is called the hook. The hook is made up of different types of proteins. A long shaft runs between the hook and the basal body.

Video Explaining The Difference
Differences in Structure
- Eukaryotic motile cilium and flagellum are structurally identical. Each is a bundle of nine fused pairs of microtubule doublets surrounding two central single microtubules. The movement of both cilia and flagella is caused by the interactions of these microtubules. In non-motile or primary cilia the two central single microtubules are absent. So th...
Types of Cilia and Flagella
- There two types of cilia - motileand non-motile or primary cilia. 1. Non-motile or primary ciliaare found in nearly every cell in all mammals and as the name suggests these do not beat. They can be found in human sensory organs such as the eye and the nose. 1. Motile ciliaare found on the surface of cells and they beat in a rhythmic manner. They can be found in the lining of the trache…
Diseases
- Lack of proper functioning of cilia and flagella can cause several problems in human beings. For example, 1. If the cilia in the fallopian tubes are not functioning properly then the fertilized ovum will not reach the uterus and thus result in ectopic pregnancy. 2. A defect of the primary cilium in the renal tube cells can lead to polycystic kidney disease (PKD). 3. Flagellum dysfunction can al…
References
- wikipedia:Cilium
- wikipedia:Flagellum
- Assembly and Motility of Eukaryotic Cilia and Flagella. Lessons from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii - University of Minnesota(PDF)