
How Can Corals Teach Us About Climate?
- Recording Climate with Coral Skeletons. Scientists can study these rings and other characteristics to determine the climate conditions during the seasons in which the coral grew As corals grow, they ...
- Examining Layers of Data and Information. ...
- Investigating the Past to Predict the Future. ...
Full Answer
How can corals be used to predict the future climate?
By using corals to determine the past climate in the tropical oceans, paleoclimatologists can also predict future trends in the climate system By using corals to determine the past climate in the tropical oceans, paleoclimatologists can also predict future trends in the climate system.
Why do scientists use Coral rings to date coral reefs?
Scientists can study these rings and other characteristics to determine the climate conditions during the seasons in which the coral grew. These growth bands also allow scientists to date coral samples to an exact year and season.
Where do scientists take coral samples from?
Scientists take samples from the center of the coral. Clipperton Atoll, 10°N, 109°W. Photo by Maris Kazmers (courtesy of th NOAA Image Gallery).
What can corals tell us about the El Niño Southern Oscillation?
The information corals provide about the tropical oceans can be very useful in examining the El Niño Southern Oscillation. El Niño, which is spawned in the Pacific Ocean, greatly affects weather from Asia and Australia to North and South America.
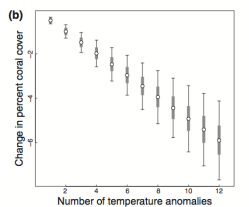
How are corals used to determine past climates?
These seasonal variations in density produce growth rings similar to those in trees. Scientists can study these rings and other characteristics to determine the climate conditions during the seasons in which the coral grew. These growth bands also allow scientists to date coral samples to an exact year and season.
What can coral tell us about past climates and environments?
Fossil coral reefs can be used to accurately reconstruct past sea level variations, climate change and environmental perturbations. According to Camoin, they provide the most precise records of sea-level changes. This is because corals always live within very strict ecological requirements.
What do coral reefs tell us about climate change?
“Think of them as foundation or habitat-building species.” Corals are also the most obvious indicators of any deadly environmental change, particularly as a result of increased seawater temperatures of as much as 2 degrees over the average, over a period of 2 to 4 weeks.
Why are corals important for climate?
Reefs are vital for people too – they protect coastlines by reducing the impact of storms and waves, which can cause destruction and land erosion.
What do coral cores show us?
Coral cores These natural historical archives contain records of coral growth rates, climate and environmental variability that extend over several centuries, pre-dating both observational records of reef environments and human interference in regional and global environments.
How are past sea level changes reconstructed using fossil corals in this investigation?
How are past sea-level changes reconstructed using fossil corals in this investigation? Successive coral reefs, separated by an erosional unconformity, indicates that high sea levels fell then rose again. Corals grow near the sea surface, so their presence in the geologic record reveals sea-level position.
Do corals help climate change?
Shallow and jagged reefs are the most effective barriers, the study shows, making them invaluable natural resources as man-made climate change swells sea levels by up to 3 feet and boosts the number of category 4 and 5 hurricanes over the next century.
How coral reefs can act as both an indicator and adapt to climate change?
The study found that some corals in the normally cool waters of the Cook Islands carry genetic variants that predispose them to heat tolerance. This could help the population adapt more quickly to rising temperatures.
Do coral reefs regulate climate?
Like terrestrial rainforests, corals may be involved in a regulatory cycle that helps regulate local climates. Coral production of DMSP increases in response to stress caused by rising water temperatures, basically acting as anti-oxidants for cellular protection.
How do coral reefs change the environment?
The Impacts Coral reefs provide shelter, spawning grounds, and protection from predators. They also support organisms at the base of ocean food chains. As reef ecosystems collapse, already at-risk species may face extinction.
What are the importance of coral reefs?
Coral reefs provide an important ecosystem for life underwater, protect coastal areas by reducing the power of waves hitting the coast, and provide a crucial source of income for millions of people. Coral reefs teem with diverse life. Thousands of species can be found living on one reef.
Why are the coral reefs important?
Coral reefs protect coastlines from storms and erosion, provide jobs for local communities, and offer opportunities for recreation. They are also are a source of food and new medicines. Over half a billion people depend on reefs for food, income, and protection.
How are pollen grains used to determine past climates?
Because there is a lot of pollen and it doesn't fall apart easily, it is often preserved in layers of sediments and can become fossilized within rocks – even in places where other plants and animals are not likely to be preserved as fossils. This makes pollen a good source of data about past climates.
How does pollen help us understand climate?
Not only can pollen records tell us about the past climate, but they can also tell us how we are impacting our climateBy analyzing pollen from well-dated sediment cores, paleoclimatologists can obtain records of changes in vegetation going back hundreds of thousands, and even millions of years.
How do pollen records show climate change?
Changes in the type of pollen found in different layers of sediment (which can be dated using the principle of stratigraphy or radio carbon dated) in lakes, bogs, or river deltas indicate changes in plant communities. These changes are often a sign of a changing climate.
How do tree rings show climate change?
Because trees are sensitive to local climate conditions, such as rain and temperature, they give scientists some information about that area's local climate in the past. For example, tree rings usually grow wider in warm, wet years and they are thinner in years when it is cold and dry.
Why do scientists use coral reefs?
Related Science. USGS scientists use coral reefs as archives for reconstructing climate change during the Holocene (past 10,000 years). Coral reefs provide proxy information about rates of sea level change in the past, and individual coral colonies can be used to reconstruct the annual cycle of temperature and salinity variations ...
What is the skeleton of coral?
As corals grow, they deposit a hard skeleton made up of the mineral aragonite, a form of calcium carbonate (CaCO 3 ), which supports the softer tissues that comprise the coral polyp. X-rays of coral skeleton slabs show alternating light and dark layers (bands) that are the result of seasonal changes in growth. A couplet of light and dark layers (bands) represents 1 year of growth and can be used to determine the age of the coral by counting back and down the coral from the known year it was sampled.
Why are sediment traps used?
A sediment trap time series in the northern Gulf of Mexico is used to better assess the control of environmental variables (e.g., temperature and salinity) on the flux of both microfossils and molecular fossils to the sediments. The information gained from sediment trap studies is used to develop better proxy-based estimates of past oceanographic conditions from analyses of microfossils and ...
How can we reconstruct past climate?
Past climate can be reconstructed using a combination of different types of proxy records. These records can then be integrated with observations of Earth's modern climate and placed into a computer model to infer past as well as predict future climate.
Why is Paleoclimatology Important?
The science of paleoclimatology is important for past, contemporary, and future issues. Understanding past climate helps us to explain how current ecosystems came to be. For example, climate typically controls what types of vegetation grow in a particular area. Furthermore, paleoclimatology provides data that we can use to model and predict both current and future climate change scenarios. Computer models can be used to study the potential effect of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide on climate.
What Causes Climate Change?
The causes of climate change are complex. There are several major factors that can effect the climate system, including:
How does the Milankovich theory affect climate?
The Milankovich Theory states that variations in Earth's orbit causes climate to change through time. According to this theory, changes in the shape of Earth's orbit around the sun (eccentricity), variations in Earth's axial tilt (obliquity), and the tendency for Earth to 'wobble' with respect to the direction of its rotational axis (precession) affect climate. This wobble can lead to fluctuations in the amount and distribution of incoming solar radiation, resulting in dramatic changes in climate over long time scales. Wobble may cause ice ages.
What does coal mean in sediment?
Charcoal trapped in sediments can indicate past fire events. Remains of organisms such as diatoms, foraminifera, microbiota, and pollen within sediment can indicate changes in past climate, since each species has a limited range of habitable conditions.
What are ice core records?
Ice core records - deep ice cores, such as those from Lake Vostok, Antarctica, the Greenland Ice Sheet Project, and North Greenland Ice Sheet Project can be analyzed for trapped gas, stable isotope ratios, and pollen trapped within the layers to infer past climate.
What is Paleoclimatology?
Scientists take samples from the center of the coral. Clipperton Atoll, 10°N, 109°W. Photo by Maris Kazmers (courtesy of th NOAA Image Gallery).
How Do We Study Past Climates?
Paleoclimatology is the study of climate records from hundreds to millions of years ago. Information for paleoclimate studies come from natural records rather than instruments: these indirect records of climatic conditions are called proxy records.
What Can I Do with Paleoclimate Data? What is it Good For?
Records of past climate provide context for present climate. For instance, one might ask, “How does the drought in the western United States this year compare with droughts of the past?” By analyzing tree rings and sediments from lakes and dunes, scientists can reconstruct the history of drought in the region, and compare the severity and extent of present conditions to droughts of the past. These sorts of comparisons are very valuable for water and other resource managers when they plan for the future.
How are paleoclimate records valuable?
Paleoclimate records, collected by independent science teams worldwide, become even more valuable when plotted and compared with one another. As the following graphs of past temperatures indicated by various methods show, common patterns of temperature trends are broadly consistent across a variety of data collection methods. By comparing multiple sets of proxy records, scientists have been able to reconstruct a fairly consistent story of Earth’s climate for the past few thousand years. While the methods of calculating global average temperature from different proxies vary from team to team, the outcomes are broadly consistent over time, and they converge with the instrumental record. The broad agreement of several datasets increases our confidence that proxies reveal valid temperature records. The set of charts below shows the general agreement among results from multiple science teams using different methods to understand how temperatures have changed over time.
Where do paleoclimates come from?
Paleoclimate records come from all around the world – from the tops of mountains, to the bottom of the ocean, from the tropics to the poles.
