Why is gene expression more complex in eukaryotic cells than in prokaryotic cells?
Who is the author of Gene Regulation?
What is an enhancer in biology?
Which type of polymerase is required for transcription to start?
What happens when DNA is transcribed into RNA?
Why are X chromosomes inactivated?
How do histones move?
See 4 more
About this website
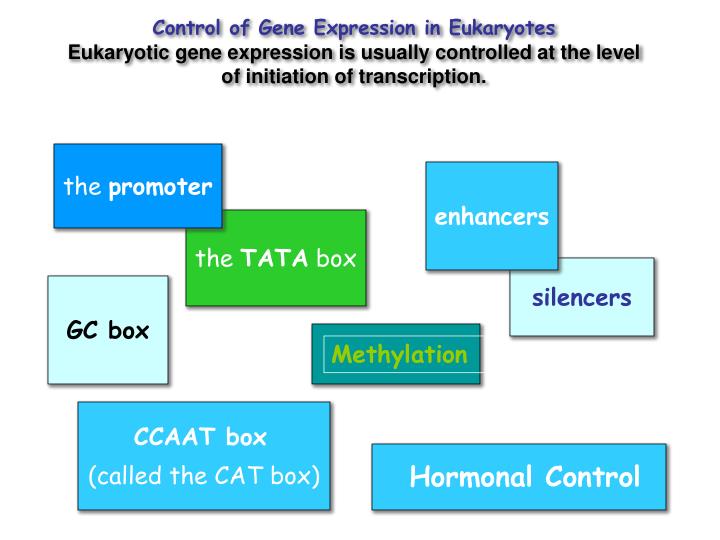
What is the most common control of eukaryotic gene regulation?
Transcription. Transcription is a key regulatory point for many genes. Sets of transcription factor proteins bind to specific DNA sequences in or near a gene and promote or repress its transcription into an RNA.
Are eukaryotic genes individually controlled?
Eukaryotic genes may be clustered (for example, genes for a metabolic pathway may occur on the same region of a chromosome) but are independently controlled.
How can transcription be controlled in eukaryotes?
Transcriptional control in eukaryotes can be accomplished at several levels. Chromatin structure can control transcription. The formation of so‐called hypersensitive sites (sites where the DNA is not bound into nucleosomes) allows protein factors and RNA polymerase to access the DNA.
How can genes be controlled?
Specifically, gene expression is controlled on two levels. First, transcription is controlled by limiting the amount of mRNA that is produced from a particular gene. The second level of control is through post-transcriptional events that regulate the translation of mRNA into proteins.
What is the first level of control of eukaryotic gene transcription?
the epigenetic levelIn eukaryotic cells, the first stage of gene expression control occurs at the epigenetic level. Epigenetic mechanisms control access to the chromosomal region to allow genes to be turned on or off.
What are the four levels of control of gene expression in eukaryotes?
Answer d. Control of gene expression in eukaryotic cells occurs at epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels.
How is transcription directly controlled in eukaryotic cells quizlet?
most eukaryotic genes contain introns. Regulatory proteins control transcription initiation by modulating the ability of DNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. Regulatory proteins function by binding to specific sequences on the DNA called regulatory sequences.
How are genes turned on and off in eukaryotes?
A gene can be turned on or off depending upon the location and modifications to the histone proteins and DNA. If a gene is to be transcribed, the histone proteins and DNA are modified surrounding the chromosomal region encoding that gene.
What is required for eukaryotic gene transcription?
Like prokaryotic cells, the transcription of genes in eukaryotes requires the action of an RNA polymerase to bind to a DNA sequence upstream of a gene in order to initiate transcription.
What are two ways in which eukaryotic cells regulate gene expression?
Gene expression in eukaryotic cells is regulated by repressors as well as by transcriptional activators. Like their prokaryotic counterparts, eukaryotic repressors bind to specific DNA sequences and inhibit transcription.
Do eukaryotes have operons?
Operons are very rare in eukaryotes, but do exist (Box 16.01)). The lactose operon, like many bacterial operons, is controlled at two levels. Specific regulation refers to regulation in response to factors specific for a particular operon, in this case the availability of the sugar lactose.
Which of the following is controlled by genes?
Some of the genes can also act as instructions to transform molecules into proteins. Eye color, Hair color, and Height are those characteristic traits that are controlled by genes. The character or basically the traits that a person possesses are normally controlled by a gene.
What is the main difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic gene regulation?
Prokaryotic gene expression is primarily controlled at the level of transcription. Eukaryotic gene expression is controlled at the levels of epigenetics, transcription, post-transcription, translation, and post-translation.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression?
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression is that the entire prokaryotic gene expression occurs in the cytoplasm whereas a part of the eukaryotic gene expression occurs inside the nucleus while rest occurs in the cytoplasm.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic gene structure?
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene structure is that the prokaryotic gene structure consists of operons and clusters of several functionally-related genes, whereas the eukaryotic gene structure does not contain operons.
Which explains a difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene regulation?
This is Expert Verified Answer Which explains a difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene reguation? A. Prokaryotes do not have mRNA, so they do not have processes to degrade mRNA.
Chapter 13 Gene Regulation Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like When glucose is present in a bacterial cell, it can act to repress the expression of the lac operon because it is preferentially used compared to other sugars. What form of transcriptional regulation is this?, Eukaryotic gene expression can be regulated at which levels?, When _____ binds to CAP, the resulting complex binds to the ...
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes | Gene Regulation
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the Transcriptional and Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes. Transcriptional Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: The variation in the rate of transcription often regulates gene expression. Interactions between RNA polymerase II and basal transcription factors leading to the formation of the ...
How does gene regulation work?
Gene regulation is how a cell controls which genes, out of the many genes in its genome, are "turned on" (expressed). Thanks to gene regulation, each cell type in your body has a different set of active genes – despite the fact that almost all the cells of your body contain the exact same DNA. These different patterns of gene expression cause your various cell types to have different sets of proteins, making each cell type uniquely specialized to do its job.
What is the process of controlling which genes in a cell's DNA are expressed?
Gene regulation is the process of controlling which genes in a cell's DNA are expressed (used to make a functional product such as a protein). Different cells in a multicellular organism may express very different sets of genes, even though they contain the same DNA.
How do cells "decide" which genes to turn on?
Now there's a tricky question! Many factors can affect which genes a cell expresses. Different cell types express different sets of genes, as we saw above. However, two different cells of the same type may also have different gene expression patterns depending on their environment and internal state.
What determines the set of proteins and functional RNAs a cell contains?
The set of genes expressed in a cell determines the set of proteins and functional RNAs it contains, giving it its unique properties.
Why do cells look different?
Your amazing body contains hundreds of different cell types, from immune cells to skin cells to neurons. Almost all of your cells contain the same set of DNA instructions – so why do they look so different, and do such different jobs? The answer: different gene regulation!
How does the cell detect growth factor?
The cell detects the growth factor through physical binding of the growth factor to a receptor protein on the cell surface. Binding of the growth factor causes the receptor to change shape, triggering a series of chemical events in the cell that activate proteins called transcription factors.
How is gene expression determined?
Broadly speaking, we can say that a cell's gene expression pattern is determined by information from both inside and outside the cell. Examples of information from inside the cell: the proteins it inherited from its mother cell, whether its DNA is damaged, and how much ATP it has.
Why are genes turned on and off in eukaryotes?
Like unicellular organisms, the tens of thousands of genes in the cells of multicellular eukaryotes are continually turned on and off in response to signals from their internal and external environments.
What are the two features of the eukaryotic genome?
Two features of eukaryotic genomes present a major information-processing challenge. First, the typical multicellular eukaryotic genome is much larger than that of a prokaryotic cell. Second, cell specialization limits the expression of many genes to specific cells.
Why is the conservation of histone genes important?
The conservation of histone genes during evolution reflects their pivotal role in organizing DNA within cells.
Which histones grip DNA less tightly, providing easier access for transcription proteins in this region?
Acetylated histones grip DNA less tightly, providing easier access for transcription proteins in this region.
Why are there differences between cell types?
The differences between cell types are due to differential gene expression, the expression of different genes by cells with the same genome. The genomes of eukaryotes may contain tens of thousands of genes. For quite a few species, only a small amount of the DNA—1.5% in humans—codes for protein.
Where are interphase chromosomes located?
The chromatin of each chromosome occupies a specific restricted area within the interphase nucleus.
Where are chromatin fibers usually located?
During interphase of the cell cycle, chromatin fibers are usually highly extended within the nucleus.
How does gene expression in eukaryotic cells work?
Not surprisingly, gene expression in eukaryotic cells is controlled by a number of complex processes which are summarized by the following list. After fertilization, the cells in the developing embryo become increasingly specialized, largely by turning on some genes and turning off many others. Some cells in the pancreas, for example, are ...
Which organism has a regulator gene that codes for the synthesis of a repressor molecule hat?
Example of Inducible Transcription: The bacterium E. coli has three genes that encode for enzymes that enable it to split and metabolize lactose (a sugar in milk).
Why are enzymes present in low concentrations?
However, the enzymes are usually present in very low concentrations, because their transcription is inhibited by a repressor protein produced by a regulator gene (see the top portion of the figure below). The repressor protein binds to the operator site and inhibits transcription. However, if lactose is present in the environment, ...
How is protein production regulated?
Regulation of protein production is largely achieved by modulating access of RNA polymerase to the structural gene being transcribed. The promoter gene doesn't encode anything; it is simply a DNA sequence that is initial binding site for RNA polymerase. The operator gene is also non-coding; it is just a DNA sequence that is the binding site for ...
What is gene expression?
By gene expression we mean the transcription of a gene into mRNA and its subsequent translation into protein. Gene expression is primarily controlled at the level of transcription, largely as a result of binding of proteins to specific sites on DNA. In 1965 Francois Jacob, Jacques Monod, and Andre Lwoff shared the Nobel prize in medicine ...
How does differentiation occur in specialized cells?
This differentiation into specialized cells occurs largely as a result of turning off the expression of most genes in the cell; mature cells may only use 3-5% of the genes present in the cell's nucleus. Gene expression in eukaryotes may also be regulated through by alterations in ...
What is the helix of DNA?
The DNA helix is wrapped around special proteins called histones, and this are wrapped into tight helical fibers. These fibers are then looped and folded into increasingly compact structures, which, when fully coiled and condensed, give the chromosomes their characteristic appearance in metaphase.
Why is gene expression more complex in eukaryotic cells than in prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic gene expression is more complex than prokaryotic gene expression because the processes of transcription and translation are physically separated. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells can regulate gene expression at many different levels. Eukaryotic gene expression begins with control of access to the DNA.
Who is the author of Gene Regulation?
Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation. Authored by: Shelli Carter and Lumen Learning. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
What is an enhancer in biology?
Figure 1. An enhancer is a DNA sequence that promotes transcription. Each enhancer is made up of short DNA sequences called distal control elements. Activators bound to the distal control elements interact with mediator proteins and transcription factors. Two different genes may have the same promoter but different distal control elements, enabling differential gene expression.
Which type of polymerase is required for transcription to start?
Answer c. The binding of RNA polymerase is required for transcription to start.
What happens when DNA is transcribed into RNA?
If DNA encoding a specific gene is to be transcribed into RNA, the nucleosomes surrounding that region of DNA can slide down the DNA to open that specific chromosomal region and allow for the transcriptional machinery (RNA polymerase) to initiate transcription (Figure 2).
Why are X chromosomes inactivated?
In females, one of the two X chromosomes is inactivated during embryonic development because of epigenetic changes to the chromatin.
How do histones move?
These signals are tags added to histone proteins and DNA that tell the histones if a chromosomal region should be open or closed (Figure 3 depicts modifications to histone proteins and DNA). These tags are not permanent, but may be added or removed as needed. They are chemical modifications (phosphate, methyl, or acetyl groups) that are attached to specific amino acids in the protein or to the nucleotides of the DNA. The tags do not alter the DNA base sequence, but they do alter how tightly wound the DNA is around the histone proteins. DNA is a negatively charged molecule; therefore, changes in the charge of the histone will change how tightly wound the DNA molecule will be. When unmodified, the histone proteins have a large positive charge; by adding chemical modifications like acetyl groups, the charge becomes less positive.