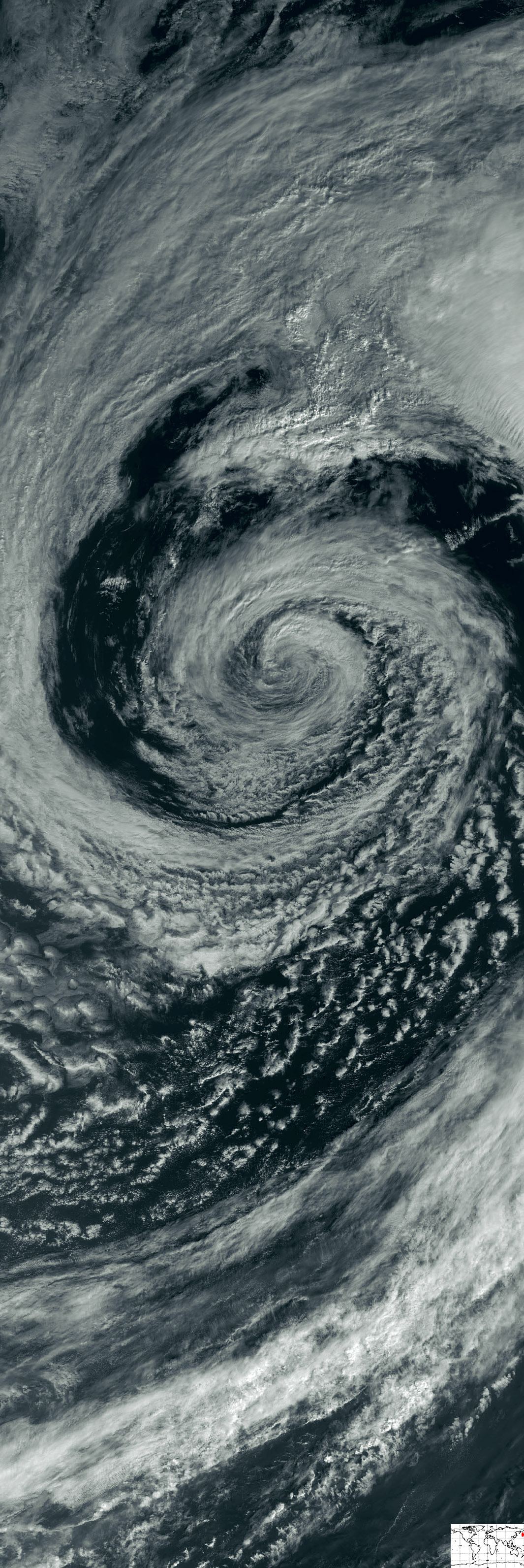
Where does and extratropical cyclone form?
Known by many names, extratropical storms form outside of the tropics, usually at mid-latitudes between 30° and 60° latitude from the equator.
How extratropical cyclones are formed Upsc?
Extratropical cyclones present a contrast to the more violent cyclones or hurricanes of the tropics, which form in regions of relatively uniform temperatures. According to the polar-front theory, extratropical cyclones develop when a wave forms on a frontal surface separating a warm air mass from a cold air mass.
How are the cyclones formed?
A cyclone is formed when the warm, moist air rises upward over the ocean. As this air moves up, there is a formation of a low-pressure area below. Now the low-pressure area is filled with the high-pressure air from the surroundings. Again, the next batch of cool air gets warm and moist over the ocean moving upward.
What is the difference between tropical cyclones and extratropical cyclones?
Extratropical cyclones cover a larger area and can originate over the land and sea. Whereas the tropical cyclones originate only over the seas and on reaching the land they dissipate. The extratropical cyclone affects a much larger area as compared to the tropical cyclone.
What is the definition of extratropical?
extratropical (not comparable) Occurring outside the tropics, usually in temperate latitudes.
Why do Extra-tropical cyclones move from west to east?
Answer: because Air in the tropics generally moves in the direction of the equator. Moving air is deflected by the rotation of the Earth.
What are the main causes of cyclones?
What causes cyclone? Cyclones are centred on areas of low atmospheric pressure, usually over warm ocean waters near the equator. The warm moist air over the ocean rises from the surface in the upward direction, resulting in the formation of the low-pressure zone over the surface.
What are the 5 causes of cyclone?
What Are the Causes of a Cyclone?Warm temperature at sea surfaces.Coriolis force impact area that forms a low-pressure zone.Atmospheric instability.Increased humidity in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere.Low vertical wind shear.Pre-existing low-level disturbance or focus.
What are the 4 types of cyclones?
There are 4 types of cyclones and they are:Tropical cyclone.Polar cyclone.Mesocyclone.Extratropical cyclone.
What direction do extratropical cyclones travel?
Extratropical cyclones are generally driven, or "steered", by deep westerly winds in a general west to east motion across both the Northern and Southern hemispheres of the Earth.
Do extratropical cyclones have an eye?
Extratropical cyclones The most severe of these can have a clear "eye" at the site of lowest barometric pressure, though it is usually surrounded by lower, non-convective clouds and is found near the back end of the storm.
Why do extratropical cyclones rotate counterclockwise?
In the northern hemisphere, the winds of these cyclonic systems deflect to the right as a result of the Coriolis Effect. The opposite is true in the southern hemisphere. As a result, cyclones have a counterclockwise rotation in the northern hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the southern hemisphere.
What is extratropical cyclone Upsc?
Temperate Cyclone (Extratropical Cyclones) [NCERT Notes For Geography UPSC] Temperate cyclones are also known as Extra-tropical cyclones where the term “Extra-tropical” signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics with a latitude range between 30° and 60°.
Why are there more cyclones in eastern coast of India UPSC?
The temperature of the sea surface and humidity are the most important factors responsible for the formation of cyclones. The average rainfall seen by the Bay of Bengal is very high and hence the probability of the formation of cyclones in this region is also correspondingly very high.
How temperate cyclones are formed?
Temperate cyclones form when two opposing air masses collide, such as light tropical air masses and thick polar air masses. Temperate cyclones are also known as Extra-tropical cyclones.
Why tropical cyclones do not develop during south west Monsoon Upsc?
The southwest monsoon is characterized by the presence of strong westerly winds in the lower troposphere (below 5 km) and very strong easterly winds in the upper troposphere (above 9 km). This results in large vertical wind shear. Strong vertical wind shear inhibits cyclone development.
How do extratropical cyclones form?
According to the polar-fronttheory, extratropical cyclones develop when a wave forms on a frontal surface separating a warm air massfrom a cold air mass. As the amplitude of the wave increases, the pressure at the centre of disturbance falls, eventually intensifying to the point at which a cyclonic circulation begins. The decay of such a system results when the cold air from the north in the Northern Hemisphere, or from the south in the Southern Hemisphere, on the western side of such a cyclone sweeps under all of the warm tropical air of the system so that the entire cyclone is composed of the cold air mass. This action is known as occlusion.
What is the difference between an extratropical cyclone and an anticyclone?
Differences in spatial extent and wind rotation between an extratropical cyclone and an anticyclone in the Northern Hemisphere over the United States. Of the two types of large-scale cyclones, extratropical cyclones are the most abundant and exert influence on the broadest scale; they affect... According to the polar-front theory, extratropical ...
What is a midlatitude cyclone?
Extratropical cyclone, also called wave cyclone or midlatitude cyclone, a type of storm system formed in middle or high latitudes, in regions of large horizontal temperature variations called frontal zones.
What is the weather sequence associated with a cyclone?
Typical weather sequences are associated with extratropical cyclones. Stations ahead of the approaching front side of the wave, called the warm front, normally experience increasingly thickening and lowering clouds, followed by precipitation, which normally persists until the centre of the cyclone passes by the station.
Which type of cyclone is the most abundant?
climate: Extratropical cyclones. Of the two types of large-scale cyclones, extratropical cyclones are the most abundant and exert influence on the broadest scale; they affect... According to the polar-front theory, extratropical cyclones develop when a wave forms on a frontal surface separating a warm air mass from a cold air mass.
Which hemisphere is cyclonic and anticyclonic?
cyclonic and anticyclonic flow in the Northern Hemisphere
Storm and Cloud Dynamics
William R. Cotton, ... Susan C. van den Heever, in International Geophysics, 2011
The Science of Hydrology
Extratropical cyclones are synoptic scale low-pressure systems that occur in the middle latitudes (i.e., pole-ward of about 30° latitude) and have length scales of the order of 500–2500 km (e.g., Hakim, 2003 ).
Significant Water Vapor Imagery Features Associated With Synoptic Thermodynamic Structures
Christo G. Georgiev, ... Karine Maynard, in Weather Analysis and Forecasting (Second Edition), 2016
Mesoscale Meteorological Modeling
In extratropical cyclones, along synoptic-scale fronts and associated with tropical weather systems, precipitation is often not uniformly distributed, but occurs in well-organized mesoscale-sized bands of heavier snow or rain (e.g., Akiyama 1978 ).
CYCLONES EXTRA TROPICAL
A. Joly, ... S. Malardel, in Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences, 2003
High Frequency Trends in the Isotopic Composition of Superstorm Sandy
Stephen P. Good, ... Gabriel J. Bowen, in Learning from the Impacts of Superstorm Sandy, 2015
Mesoscale Meteorological Modeling
Throughout the troposphere, an extratropical cyclone is characterized by the following during its development stage:
Cyclogenesis and Life Cycle
This figure below shows a portion of the polar front as a stationary front, with cold air to the north and warmer air to the south flowing parallel to the front in opposite directions. These winds moving in opposite directions set up rotation, similar to how a pen will turn if you place it between your hands and move them in opposite directions.
Storm Tracks
The development of a mid-latitude cyclone is a process called cyclogenesis. Certain regions in North America are more favorable for cyclogenesis, including the eastern slopes of mountain ranges like the Rockies and Sierra Nevada, the Atlantic Ocean off the Carolina Coast, and the Gulf of Mexico.
Mid-latitude Cyclone in Three Dimensions
Developing surface lows are usually more intense with height and appear on upper-level charts as a trough or a closed low. However, the low in the upper-levels usually exists to the west of the surface low (again, in the Northern Hemisphere). This is a necessary condition for a low pressure system to continue to develop and intensify.
Redistribution of Heat
Mid-latitude frontal cyclones are both a vital part of global circulation and a result of global circulation. They’re also an important pattern in the climatology of regions in the mid-latitudes.
Where do extratropical cyclones form?
Extratropical cyclones form a bit differently and have different overall structures. As their name implies, extratropical cyclones form away from the tropical zones where tropical cyclones originate. They tend to form: 1 Along the U.S. Eastern seaboard, north of Florida 2 From the southern half of Chile down in South America 3 In the waters near England and continental Europe 4 Southeastern tip of Australia
Why do extratropical cyclones look like commas?
Extratropical cyclones are the result of cold and warm fronts meeting, and the differences in temperatures and air pressures create the cyclonic motions. Given their structure, extratropical cyclones look like commas when the two different fronts are both well-developed, a difference from the spiral shape of tropical cyclones and hurricanes.
How many milibars did the 2012 cyclone reach?
The 2012 cyclone reached 963 to 966 milibars. "Preliminarily, this storm could rank in the Top 10 for Arctic Cyclones in June as well as for the summer (June through August) in strength," Steven Cavallo, a meteorologist at the University of Oklahoma, explained to Earther .
How long did the Great Arctic Cyclone last?
It lasted for 13 days, an incredibly long time for an Arctic cyclone, which typically only lasts for around 40 hours or so.
Why are winter storms stronger than summer storms?
The recent uptick in summer storms is difficult to pin down, however. Climate change may be one reason since it changes sea ice levels and ocean temperatures.
How far away from the equator do tropical cyclones form?
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML), tropical cyclones require several specific conditions to form, including: Ocean waters of around 80 degrees Fahrenheit, often within 300 miles from the equator.
When did cyclones increase?
According to a 2014 study published in the Journal of Climate, Arctic cyclones have increased since 1948, even while other cyclone activity decreased between 1960 and the early 1990s. Such cyclones are more common in the winter than the summer, but that study also noted an uptick in summer cyclones.
Which type of circulation leads to a well-developed extratropical cyclone, with a warm front and?
The cyclonic circulation leads to a well-developed extratropical cyclone, with a warm front and a cold front.
What are the cyclones in the tropics called?
The systems developing in the mid and high latitude ( 35° latitude and 65° latitude in both hemispheres ), beyond the tropics are called the Temperate Cyclones or Extra-Tropical Cyclones or Mid-Latitude Cyclones or Frontal Cyclones or Wave Cyclones.
How long do temperate cyclones last?
(Occluded front explained in detail in previous posts). Normally, individual frontal cyclones exist for about 3 to 10 days moving in a generally west to east direction.
What are temperate cyclones associated with?
They are generally associated with rainstorms and cloudy weather. During summer, all the paths of temperate cyclones shift northwards and there are only few temperate cyclone over sub-tropics and the warm temperate zone, although a high concentration of storms occurs over Bering Strait, USA and Russian Arctic and sub-Arctic zone.
What is the approach of a temperate cyclone?
The approach of a temperate cyclone is marked by fall in temperature, fall in the mercury level, wind shifts and a halo around the sun and the moon, and a thin veil of cirrus clouds.
Why is there a void in the atmosphere?
The cold air pushes the warm air upwards from underneath. Thus a void is created because of lessening of pressure. The surrounding air rushed in to occupy this void and coupled with the earth’s rotation, a cyclone is formed which advances with the westerlies (Jet Streams).
How long does it take for a storm front to move eastward?
If the storm front is directed northwards, the center moves towards the north, but after two or three days, the pressure difference declines and the cyclone dissipates.
How cyclone is formed?
Storm force winds, torrential rain, massive pressure falls, and storm surges are all produced simultaneously by the most deadly weather. Around the Indian Ocean and southeast Pacific, these massive storms are known as cyclones. Cyclones tend to affect countries like Madagascar, India, and parts of Australia. In the Northwest Pacific, tropical storms are known as typhoons.
What are the causes of cyclones?
Scientific explanation: What are the causes of cyclones? Everything is in place, converging trade winds meet the warm air with water vapor rising. In the cooling, the air-water vapor condenses into droplets. This state change from water vapor to liquid releases latent heat, further warming the atmosphere and becoming more buoyant. The air rises even more rapidly and produces more and more violent thunder clouds. But that’s only the beginning.
What is a mid-latitude cyclone?
These enormous weather systems span 1000 kilometers or more. A mid-latitude cyclone is a relatively huge circular weather system. It is a relatively smaller, extremely windy tropical storm.
How does a cold front affect the weather?
As it rises, the warm air cools rapidly. This configuration called a cold front gives rise to cumulonimbus clouds often associated with heavy precipitation and storms. As air masses move pushed by winds, they directly influence the weather in the regions they pass in this way. They help to circulate heat and humidity in the atmosphere.
Why do we get rain in mid-latitudes?
A lot of the storms and precipitation come from because when different air masses come together. If the displaced warm air is unstable and has lots of moisture, we’ll get heavy rain from thunderstorms and an advancing wall of cumulonimbus clouds. But when a cold air mass backs off, the warm air mass sees its chance and creeps in, forming a warm front. The warm air can’t displace the denser, colder air near the ground.
How does rising air affect the troposphere?
The rising air contains vast amounts of moisture evaporated from the ocean’s surface. It cools, condensing to form huge clouds about ten kilometers up in the troposphere as it rises. More warm air rushes in and rises drawn by the draft above. The rising drafts of air carry moisture high into the atmosphere so that these clouds eventually become very thick and heavy.
Why do trade winds move?
Trade winds drawn in at the Earth’s surface arrive on a curved path due to the Earth’s rotation. As the storm grows larger, more moist warm air is drawn in at the surface. More water vapor condenses into cloud droplets, and more latent heat is released. This is how energy is driven into the storm, and the speed of rotation increases. This system is now a tropical storm.
Cyclogenesis and Life Cycle
- This figure below shows a portion of the polar front as a stationary front, with cold air to the north and warmer air to the south flowing parallel to the front in opposite directions. These winds moving in opposite directions set up rotation, similar to how a pen will turn if you place it between your hands and move them in opposite directions. Under the right conditions, a frontal wavewill …
Storm Tracks
- The development of a mid-latitude cyclone is a process called cyclogenesis. Certain regions in North America are more favorable for cyclogenesis, including the eastern slopes of mountain ranges like the Rockies and Sierra Nevada, the Atlantic Ocean off the Carolina Coast, and the Gulf of Mexico. When air flows westward across a north-south extending mountain range, the air on t…
mid-latitude Cyclone in Three Dimensions
- Developing surface lows are usually more intense with height and appear on upper-level charts as a trough or a closed low. However, the low in the upper-levels usually exists to the west of the surface low (again, in the Northern Hemisphere). This is a necessary condition for a low pressure system to continue to develop and intensify. If the upper-level low were directly over the surface …
Redistribution of Heat
- Mid-latitude frontal cyclones are both a vital part of global circulation and a result of global circulation. They’re also an important pattern in the climatology of regions in the mid-latitudes. The temperature gradients that cause frontal cyclones form as a result of the colliding surface air from the polar and Ferrel cells. The strong temperatur...