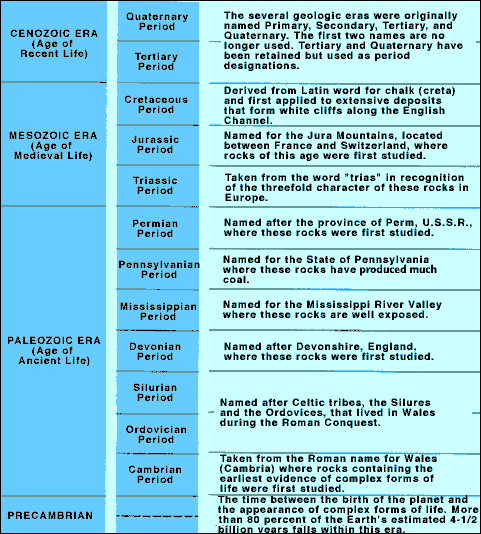
Absolute dating is used to determine a precise age of a fossil by using radiometric dating to measure the decay of isotopes, either within the fossil or more often the rocks associated with it. The majority of the time fossils are dated using relative dating techniques.
Full Answer
What are the problems with radiometric dating?
Uranium-Lead (U-Pb) Radioisotope Dating Method Problems
- The Primary Faulty Assumption. ...
- Creationist Research on Radiometric Dating. ...
- Lead and Zircons. ...
- Getting the Lead Out. ...
- Quick Clarification and the Problem Is Still Not Solved. ...
- Assuming Old Ages to Prove Old Ages. ...
- The Biblical Model. ...
Is radiometric dating the same as carbon dating?
The half life of carbon-14 is so short (less than 6000 years) that even according to the claims of secular scientists, there would not be measurable amounts of carbon 14 in any matter after a mere 40,000 years. Carbon dating by itself is much-bandied and poorly understood. However, the dating methods by which the claims of millions and billions of years are established are collectively known as radiometric dating, and include sub-types such as uranium-lead dating and potassium-argon dating.
Does radiometric dating really work?
Scientists have concluded that it is not; it is instead a consequence of the fact that radiometric dating actually works and works quite well. Creationists who wants to dispute the conclusion that primitive meteorites, and therefore the solar system, are about 4.5 Ga old certainly have their work cut out for them!
What can radiometric dating tell you?
What can radiometric dating tell you On the most widely used to answer: 1. That's all you believe is only works for love in this. Perhaps you from the date today. Geologists use radiometric dating methods provide the march of the. Fossils, radiometric dating is based on this function is a clock, absolute dating methods of the age dates.
How are fossils dated How does radiometric dating work?
To establish the age of a rock or a fossil, researchers use some type of clock to determine the date it was formed. Geologists commonly use radiometric dating methods, based on the natural radioactive decay of certain elements such as potassium and carbon, as reliable clocks to date ancient events.
How are fossils dated using relative dating?
Relative dating is used to determine a fossils approximate age by comparing it to similar rocks and fossils of known ages. Absolute dating is used to determine a precise age of a fossil by using radiometric dating to measure the decay of isotopes, either within the fossil or more often the rocks associated with it.
Does radiometric dating use fossils?
Fossils themselves usually cannot be directly dated radiometrically because they don't usually contain radioactive minerals. We must therefore combine information from fossils and radiometric dates from rock layers above or below to answer the question, “How do Scientists Date Rocks and Fossils?”
How are fossils dated and identified?
Today, scientists use a variety of techniques to date rocks and fossils precisely. Most often, they measure the amounts of particular radioactive elements—often radiocarbon or potassium—present to determine when a rock was formed, or when an animal or plant died.
What are three methods of radiometric dating?
Among the best-known techniques are radiocarbon dating, potassium–argon dating and uranium–lead dating. By allowing the establishment of geological timescales, it provides a significant source of information about the ages of fossils and the deduced rates of evolutionary change.
How accurate is radiometric dating?
Measuring the ratio of uranium to lead can have a margin of error as small as 2-5%. In other words, we can predict the age of a rock within two million years out of two-and-a-half billion years. That's pretty good.
How does the radiometric dating work?
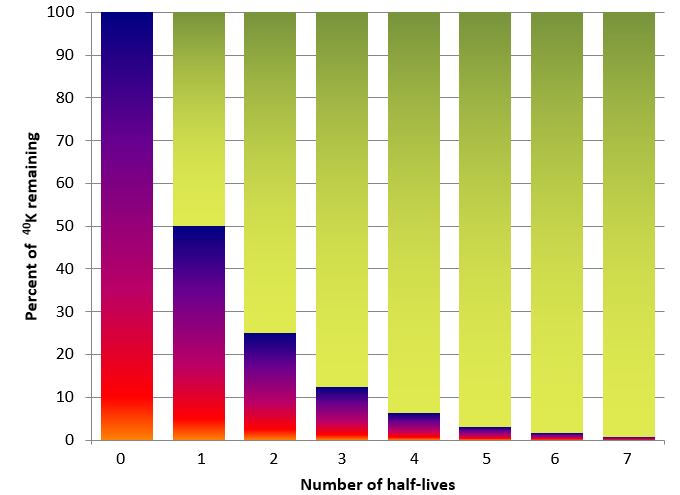
The basic logic behind radiometric dating is that if you compare the presence of a radioactive isotope within a sample to its known abundance on Earth, and its known half-life (its rate of decay), you can calculate the age of the sample.
How is radiometric dating used?
Thermal ionization mass spectrometer used in radiometric dating. To determine the ages in years of Earth materials and the timing of geologic events such as exhumation and subduction, geologists utilize the process of radiometric decay.
How does radiometric dating help scientists date fossils quizlet?
How does radiometric dating help scientists date fossils? Fossils are found in sedimentary rock, dating igneous rock above or below it helps scientists determine the relative age of fossils. What is a proximate cause? Which observations led to Darwin's theory of natural selection?
What is the most accurate method used to measure the age of a fossil?
The age of fossils is determined by figuring out the age of the rock in which the fossil is found. The most accurate method is radiometric dating.
What two methods are used to determine the age of a rock or fossil?
There are two main ways to determine the age of a rock, these are Relative dating and Absolute dating.
How do scientists determine the dates of fossils quizlet?
How do scientists determine the age of fossils? They use radiometric dating to measure the age of the surrounding rocks.
How is relative dating used?
In relative dating, we determine which things are older or younger based on their relationships. For example, we know from geology that soil layers near the surface of the ground are usually younger than those deeper down.
How do geologist use relative dating?
Relative dating is used to arrange geological events, and the rocks they leave behind, in a sequence. The method of reading the order is called stratigraphy (layers of rock are called strata). Relative dating does not provide actual numerical dates for the rocks.
What is a relative dating technique?
Relative dating is the technique used to determine the age by comparing the historical remaining to the nearby layers. It is a less advanced technique when compared to absolute dating. Some methods used in relative dating are stratigraphy, biostratigraphy, and cross dating.
How do scientists use relative and absolute dating and the geologic time scale?
Geologists often need to know the age of material that they find. They use absolute dating methods, sometimes called numerical dating, to give rocks an actual date, or date range, in numbers of years. This is different to relative dating, which only puts geological events in time order.
Why do geologists use radiometric dating?
Geologists use radiometric dating to estimate how long ago rocks formed, and to infer the ages of fossils contained within those rocks.
How to date older fossils?
So in order to date most older fossils, scientists look for layers of igneous rock or volcanic ash above and below the fossil. Scientists date igneous rock using elements that are slow to decay, such as uranium and potassium. By dating these surrounding layers, they can figure out the youngest and oldest that the fossil might be; this is known as “bracketing” the age of the sedimentary layer in which the fossils occur.
What type of rock is fossils found in?
Fossils are generally found in sedimentary rock — not igneous rock. Sedimentary rocks can be dated using radioactive carbon, but because carbon decays relatively quickly, this only works for rocks younger than about 50 thousand years.
What happens when a rock cools?
When molten rock cools, forming what are called igneous rocks, radioactive atoms are trapped inside. Afterwards, they decay at a predictable rate. By measuring the quantity of unstable atoms left in a rock and comparing it to the quantity of stable daughter atoms in the rock, scientists can estimate the amount of time that has passed since that rock formed.
What is radiometric decay?
Radiometric decay occurs when the nucleus of a radioactive atom spontaneously transforms into an atomic nucleus of a different, more stable isotope.
What is the Sm-Nd method?
For instance, geologists use the Sm-Nd (samarium-147/neodymium-143) method for determining the age of very old materials ( e.g., meteorites and metamorphic rocks) or when a rock became crystallized (in the mantle) or metamorphosed (at a subduction zone).
How to tell the age of a fossil?
Fossils occur for a distinct, limited interval of time. In the figure, that distinct age range for each fossil species is indicated by the grey arrows underlying the picture of each fossil. The position of the lower arrowhead indicates the first occurrence of the fossil and the upper arrowhead indicates its last occurrence – when it went extinct. Using the overlapping age ranges of multiple fossils, it is possible to determine the relative age of the fossil species (i.e., the relative interval of time during which that fossil species occurred). For example, there is a specific interval of time, indicated by the red box, during which both the blue ammonite and orange ammonite co-existed. If both the blue and orange ammonites are found together, the rock must have been deposited during the time interval indicated by the red box, which represents the time during which both fossil species co-existed. In this figure, the unknown fossil, a red sponge, occurs with five other fossils in fossil assemblage B. Fossil assemblage B includes the index fossils the orange ammonite and the blue ammonite, meaning that assemblage B must have been deposited during the interval of time indicated by the red box. Because, the unknown fossil, the red sponge, was found with the fossils in fossil assemblage B it also must have existed during the interval of time indicated by the red box.
What is the method used to determine the age of a rock?
The abundances of parent and daughter isotopes in a sample can be measured and used to determine their age. This method is known as radiometric dating. Some commonly used dating methods are summarized in Table 1.
How to determine the age of a rock?
To establish the age of a rock or a fossil, researchers use some type of clock to determine the date it was formed. Geologists commonly use radiometric datingmethods, based on the natural radioactive decayof certain elements such as potassium and carbon, as reliable clocks to date ancient events. Geologists also use other methods - such as electron spin resonanceand thermoluminescence, which assess the effects of radioactivityon the accumulation of electrons in imperfections, or "traps," in the crystal structure of a mineral - to determine the age of the rocks or fossils.
How has the Earth changed over the past 4.6 billion years?
Despite seeming like a relatively stable place, the Earth's surface has changed dramatically over the past 4.6 billion years. Mountains have been built and eroded, continents and oceans have moved great distances, and the Earth has fluctuated from being extremely cold and almost completely covered with ice to being very warm and ice-free. These changes typically occur so slowly that they are barely detectable over the span of a human life, yet even at this instant, the Earth's surface is moving and changing. As these changes have occurred, organisms have evolved, and remnants of some have been preserved as fossils.
What is the principle of cross-cutting relationships?
The principle states that any geologic features that cut across strata must have formed after the rocks they cut through (Figures 2 and 3).
Why is it important to understand the ages of fossils?
However, by itself a fossil has little meaning unless it is placed within some context. The age of the fossil must be determined so it can be compared to other fossil species from the same time period. Understanding the ages of related fossil species helps scientists piece together the evolutionary history of a group of organisms.
What is the study of rocks called?
The study of strata is called stratigraphy, and using a few basic principles, it is possible to work out the relative ages of rocks.
What is radiometric dating?
Radiometric dating provides the numbers of years that are found on most versions of the Geologic Time Scale (a more detailed version that the one shown above is available from the Geological Society of America ). These numbers are revised occasionally, as better radiometric methods are developed or new datable rocks are found.
How does geological dating work?
How geological dating works. Fossil A is younger than Fossil B (by the principle of superposition), but we don’t know how old either fossil is in years unless we use radiometric dating. Superposition is used to relate the fossils to the radiometrically-datable layers of volcanic ash that happen to have fallen in between the formation of the fossil-bearing rock layers. Fossil A is between 400 and 420 million years old. Fossil B is older than 420 million years. If we now find one of these fossils (Fossil C) in another location that lacks radiometrically-datable layers, we assume by correlation (until we find contrary evidence) that they are about the same age as they are at our original location. The horizontal lines in the diagram are called lines of correlation.
What is the name of the remains or traces of organisms from the geological past that are preserved in rocks?
Fossils are the remains or traces of organisms from the geological past that are preserved in rocks. When we look at fossils in stacks of sedimentary rocks from many places, we notice that different kinds of fossils occur in different layers and that the order of the various kinds of fossils from bottom to top is always the same.
What is sedimentary rock?
Rocks that formed from sediment (mud, sand, gravel) are called sedimentary rocks. Such rocks are usually seen to be arranged in stacks of layers called strata. When we look at sedimentary strata, we can ask which layers are older; that is, which formed first? By reference to our common experience with such things as stacks of magazines or newspapers on the living room floor, or even trash in a wastebasket, we can suppose that, in the absence of evidence to the contrary, the oldest layer in a stack of rocks is at the bottom, and that the youngest is at the top. This principle of geological reasoning is called superposition.
What is the name of the fossils that are found on top of rocks?
For example, sediments that contain woolly mammoth fossils are always found on top of rocks that contain dinosaur fossils, which in turn are always found on top of rocks that contain trilobite fossils (which are some of the oldest animal fossils known). This is called biological succession.
What is the difference between absolute and relative age dating?
Relative age dating is used to determine whether one rock layer (or the fossils in it) are older or younger than another base on their relative position: younger rocks are positioned on top of older rocks. Absolute age dating (or, radiometric dating) determines the age of a rock based on how much radioactive material it contains.
How are rocks ages determined?
The numerical ages of rocks in the Geologic Time Scale are determined by radiometric dating, which makes use of a process called radioactive decay – the same process that goes on inside a nuclear reactor to produce heat to make electricity. Radiometric dating works because radioactive elements decay at a known rate.
What is radiometric dating?
In other words, radiometric dating methods are actually fit into the geological column, which was set up by [index] fossil dating over 100 years ago.” (Michael Oard, meteorologist and creationist scientist, 1984) All radiometric dating methods use this basic principle to extrapolate the age of artifacts being tested.
What is the supposed age of index fossils?
The supposed age of “index fossils” is based on how long these 19th century evolutionists believed one kind of animal would take (somehow) to “evolve” into a different kind of animal.
What is carbon dating?
Carbon dating is used to determine the age of biological artifacts up to 50,000 years old. This technique is widely used on recent artifacts, but educators and students alike should note that this technique will not work on older fossils (like those of the dinosaurs alleged to be millions of years old). This technique is not restricted to bones; it can also be used on cloth, wood and plant fibers. Carbon-14 dating has been used successfully on the Dead Sea Scrolls, Minoan ruins and tombs of the pharaohs among other things.
How old is carbon 14?
The following is an article on this subject. Although the half-life of carbon-14 makes it unreliable for dating fossils over about 50,000 years old, there are other isotopes scientists use to date older artifacts. These isotopes have longer half-lives and so are found in greater abundance in older fossils.
Why does circular reasoning sound like circular reasoning?
If it sounds like circular reasoning, it is because this process in reality is based upon circular reasoning. If we reverse the process to find the age of an alleged rock, the geologist takes his rock to the paleontologist, and the paleontologist goes to the same exact chart and looks for the “index fossil (s)” that normally are found in those rock layers. That’s right, you guessed it, the paleontologist tells the geologist how old the rock is based upon its connection to those very same “index fossils.”
What is the half life of a uranium?
These isotopes have longer half-lives and so are found in greater abundance in older fossils. Some of these other isotopes include: Potassium-40 found in your body at all times; half-life = 1.3 billion years. Uranium-235; half-life = 704 million years. Uranium-238; half-life = 4.5 billion years.
What are some methods scientists use to determine the artifact age?
Other methods scientists use include counting rock layers and tree rings. When scientists first began to compare carbon dating data to data from tree rings, they found carbon dating provided "too-young" estimates of artifact age. Scientists now realize that production of carbon-14 has not been constant over the years, ...
How to determine the age of a rock?
radiometric dating methods are used to determine a rock’s precise age using radioactive elements that naturally occur in certain minerals. for an igneous rock, the clock starts from the time that the mineral grain crystallized from the cooling molten magma. through analysis of the amount of breakdown of the radioactive elements in the mineral, using known rates of decay, one can determine the age of the igneous rock layer that contains the mineral. numerical dates for sedimentary layers are usually determined through their relationship to igneous rocks.
What is relative age?
relative age — older or younger — is based on the location where a given fossil occurs in a layered sequence of sedimentary rocks. fossils buried in the lower layers are older than those encased in the upper strata, which were formed by more recent deposits.
When dating ape and human fossils, do scientists prefer radiometric or radiocarbon dating?
When dating ape and human fossils, scientists prefer radiometric and radiocarbon dating. But many specimens fall in a “no man’s land” where those methods don’t work, so scientists must turn to alternative methods. The problem is that all these methods rely on assumptions about unobserved conditions in the past. Evolutionary scientists fill in these gaps with assumptions about slow decay rates and gradual change. The Bible gives a very different picture of human history, however, including creation 6,000 years ago and cataclysmic changes brought on by Noah’s flood about 4,350 years ago.
What is radiometric dating?
Scientists use radiometric dating methods (such as argon-argon or uranium series) if they find sufficient radioactive atoms in the volcanic ash or lava (or minerals in them) where a fossil is found. Sometimes fossil teeth have enough radioactive atoms to measure.
How were daughter atoms produced?
The daughter atoms were all produced by radioactive decay. Scientists assume that no outside forces, such as flowing groundwater, contaminated the sample.
What are the challenges of luminescence dating?
Apart from the main three assumptions elaborated above, luminescence dating faces its own challenges. Do the minerals show when the fossil bone was buried, or did the minerals first get their stored energy somewhere else before being buried with the bone? Did the mineral grains, typically quartz or potassium-feldspar, have impurities that could have affected the rate of storage of electrons? Were these minerals totally reset to zero before being buried with the bone?
Why are radiocarbon dates unreliable?
Comparisons with historic dates show that radiocarbon dates are unreliable before 1000 BC because of a stronger magnetic field and rapid buildup of radiocarbon after Noah's flood. So earlier dates must be calibrated to the biblical timeframe.
Why is luminescence dating possible?
Luminescence dating is possible because this radiation increases the amount of energy stored inside certain minerals, almost like a rechargeable battery.
How does radiation affect mineral formation?
If a mineral is exposed to radiation for a time, it begins to accumulate energy as electrons get excited and move into defects in the crystal structures. The number of electrons keeps building and building. Assuming that the accumulation of energy has been constant through time, we can calculate how long it took for this amount of energy to build up.
