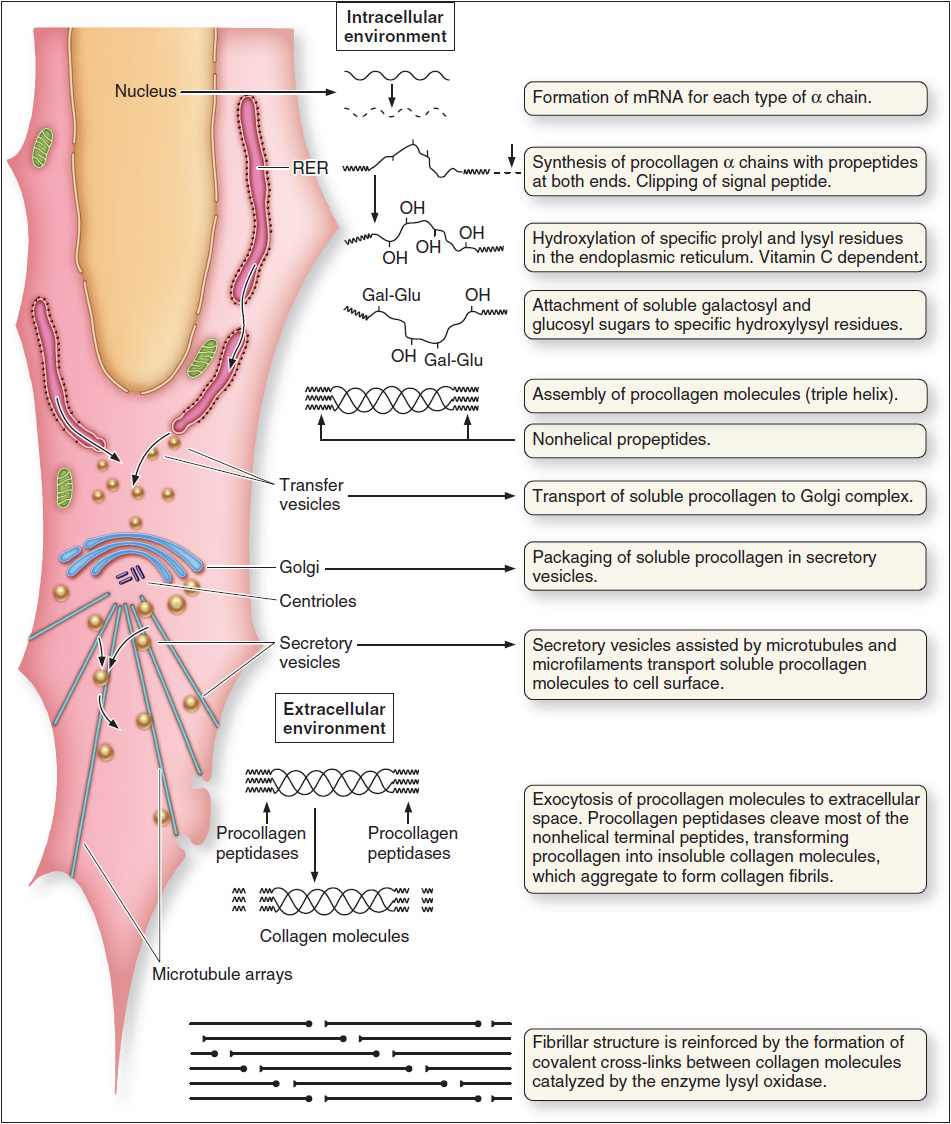
Glycosaminoglycan disaccharides are added to protein cores and form proteoglycans Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through a …Proteoglycan
What are glycosaminoglycans?
Glycosaminoglycans are long unbranched polysaccharides which are composed of repeating disaccharide units and also called as GAGs or mucopolysaccharides due to their viscous and lubricating properties, just like in mucous secretions. They are found in collagen and elastin and water sticks to GAGs which allows resistance to pressure.
What are the repeating regions in glycosaminoglycans composed of?
There are disaccharides repeating regions in glycosaminoglycans chains which are composed of uronic acid-like D-glucoronic acid or L-iduronic acid and amino sugar like D-galactosamine or D-glucosamine.
What is the function of glycosaminoglycan disaccharides?
Glycosaminoglycan disaccharides are added to protein cores and form proteoglycans. They are essential to life and important components of connective tissues. GAG chains are covalently bonded to other proteins like chemokines, cytokines, morphogens, growth factors, enzymes and adhesion molecules and forming proteoglycans.
Why do glycosaminoglycans have high degrees of heterogeneity?
Glycosaminoglycans have high degrees of heterogeneity with regards to molecular mass, disaccharide construction, and sulfation due to the fact that GAG synthesis, unlike proteins or nucleic acids, is not template driven, and dynamically modulated by processing enzymes.
Where do glycosaminoglycans come from?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), also known as mucopolysaccharides, are negatively-charged polysaccharide compounds. They are composed of repeating disaccharide units that are present in every mammalian tissue. [1] Their functions within the body are widespread and determined by their molecular structure.
Where are glycosaminoglycans found?
Glycosaminoglycans are molecules found throughout the body, including skin, joints, blood plasma, and the mucous membrane of various organs. Various GAGs exist, each with its own function and benefit in the body.
What is the major component of GAGs?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), which consist of repeating disaccharide units in linear arrangement, usually include a uronic acid component (such as glucuronic acid) and a hexosamine component (such as N-acetyl-D-glucosamine).
What are glycosaminoglycans made of?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are linear polysaccharides comprised of disaccharide units, each of which is composed of an acetamido sugar (N-acetyl-d-glucosamine or N-acetyl-d-galactosamine) and a uronic acid (d-glucuronic or l-iduronic acid) or d-galactose units.
What is the function of GAGs?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) participate in many biological processes through the regulation of their various protein partners called proteoglycan. The large structural diversity of GAGs makes them approachable for biochemical, structural biology and molecular modelling and made them useful in the discovery of new drugs.
Is glycosaminoglycan a protein?
Except for HA, all mammalian GAGs are linked to a core protein to form proteoglycans (PGs). The structure of the protein cores, the composition of the glycosaminoglycan chains, and the distribution of the proteoglycan all affect the biological activity of proteoglycans (Lindahl et al., 2015).
What is the most common glycosaminoglycan?
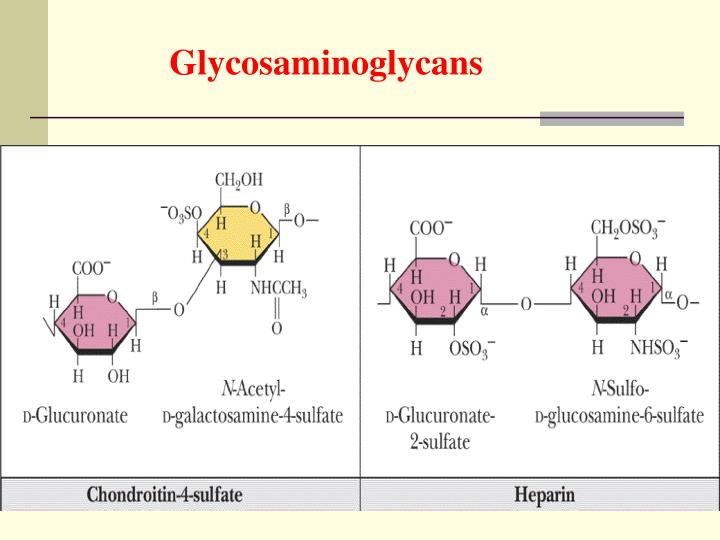
Heparan/heparin sulfate and chondroitin sulfate are the most common GAGs contained by proteoglycans.
How many types of GAGs are there?
There are four classes of glycosaminoglycans: (1) hyaluronan, (2) chondroitin sulfate (CS)/dermatan sulfate (DS), (3) heparan sulfate (HS)/heparin, and (4) keratan sulfate (KS). All four classes of glycosaminoglycan are found in normal lungs and all except hyaluronan are bound to core proteins.
What are glycosaminoglycans in skin?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are the body's natural moisturisers. They are hydrophilic molecules that help to draw water into your skin and keep your skin hydrated. By holding moisture within our skin cells, they help to maintain your skin's structural integrity by providing volume, elasticity and firmness.
What is the most abundant glycosaminoglycan?
Glycosaminoglycan Side Chains All four classes of glycosaminoglycan are found in normal lungs and all except hyaluronan are bound to core proteins. The predominant glycosaminoglycan in normal lungs is HS (40–60%) followed by CS/DS (31%), hyaluronan (14%), and heparin (5%).
What is an example of glycosaminoglycan?
Hyaluronate is an example of glycosaminoglycans. They are found in the synovial fluid, articular cartilage, vitreous humor, etc. They are large polymers and are efficient as the body's shock absorber.
Is glycosaminoglycan a protein?
Except for HA, all mammalian GAGs are linked to a core protein to form proteoglycans (PGs). The structure of the protein cores, the composition of the glycosaminoglycan chains, and the distribution of the proteoglycan all affect the biological activity of proteoglycans (Lindahl et al., 2015).
Where does GAG biosynthesis begin?
The process of GAG biosynthesis begins in the cellular cytoplasm with the synthesis of five uridine diphosphate (UDP) derived activated sugars. These sugars include UDP-glucuronic acid, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine, UDP-xylose, UDP-galactose, and UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine.[4] These UDP-activated sugars are then transported from the cytoplasm to the Golgi apparatus through an antiporter transmembrane transporter for further modification.
What are the two precursor sugars in GAG biosynthesis?
Instead of undergoing modification and sulfation in the Golgi apparatus, the HA precursor sugars UDP-glucuronic acid and UDP-N-acetylglucosamine are transported from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane for further processing without sulfation, which leads to the production of HA. [4]
What are GAGs in biology?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), also known as mucopolysaccharides, are negatively-charged polysaccharide compounds. They are composed of repeating disaccharide units that are present in every mammalian tissue.[1] Their functions within the body are widespread and determined by their molecular structure. Historically, the function of GAGs was thought to be limited to cell hydration and structural scaffolding. However, evidence now suggests that GAGs play a key role in cell signaling, which serves to modulate a vast amount of biochemical processes.[2] Some of these processes include regulation of cell growth and proliferation, promotion of cell adhesion, anticoagulation, and wound repair, among many more. The four primary groups of GAGs are classified based on their core disaccharide units and include heparin/heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, and hyaluronic acid.[3] This activity will provide a summary of the molecular structures and resulting physiologic functions of the four primary groups of GAGs.
Which structure of GAGs does not require additional sulfation?
Hyaluronic acid (HA) has the simplest structure of all GAGs and does not require additional sulfation of functional groups in the Golgi apparatus as do the other GAGs. Instead, the structure consists of sequentially bound glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues.[4] These monosaccharide building blocks are synthesized in the cell cytoplasm and are recruited to the plasma membrane by diffusion for HA synthesis.[3] After synthesis within the plasma membrane, HA gets secreted from the cell into the extracellular space unmodified.
What is a mucopolysaccharidose?
Mucopolysaccharidoses comprise a group of rare genetic diseases characterized by a deficiency of lysosomal enzymes required for the metabolism of GAGs. [8] This deficit results in lysosomal accumulation of GAG intermediates that eventually leads to cellular dysfunction and death. Mucopolysaccharidoses manifest with variable symptoms depending on the dysfunctional enzyme and associated expression of affected GAG metabolism in organ systems.
Is the sea a source of glycosaminoglycans?
ReviewThe Sea as a Rich Source of Structurally Unique Glycosaminoglycans and Mimetics.
What is the molecular weight of glycosaminoglycans?
Generally, glycosaminoglycans are linear, negatively charged polysaccharides which can sulfate or non- sulfate and have molecular weights of roughly 10-100 kilodalton. On the basis of their structure units and linkage between disaccharide units; they can be classified into two types.
What are glycosaminoglycan disaccharides?
Glycosaminoglycan disaccharides are added to protein cores and form proteoglycans. They are essential to life and important components of connective tissues. GAG chains are covalently bonded to other proteins like chemokines, cytokines, morphogens, growth factors, enzymes and adhesion molecules and forming proteoglycans.
How many units of monosaccharides are in oligosaccharides?
Oligosaccharide: Hydrolysis of oligosaccharides gives 2-10 units of monosaccharides. Polysaccharides: They are composed of 10-100 or more than those units of monosaccharides. Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates which consist of multiple monosaccharides with other structures. They are also called as glycans as the monosaccharide units are ...
Which glycosaminoglycan has the highest negative charge?
For example; Heparin is a glycosaminoglycan which contains the highest net negative charge of the disaccharides and acts as a natural anticoagulant substance. It can bond strongly to antithrombin III (a protein involved in terminating the clotting process) and inhibits blood clotting.
How many types of polysaccharides are there?
Polysaccharides can be classified in two types.
Which amino acids are repeating regions in glycosaminoglycans chains?
There are disaccharides repeating regions in glycosaminoglycans chains which are composed of uronic acid-like D-glucoronic acid or L-iduronic acid and amino sugar like D-galactosamine or D-glucosamine.
What are some examples of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are large and branched molecules which are often insoluble in water, amorphous in nature and non-sweet carbohydrates. Starch, cellulose, glycogen and chitin are best examples of polysaccharides. Polysaccharides can be classified in two types. Homopolysaccharides.
Why do glycosaminoglycans vary?
Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide construction, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven like proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes.
What is the HSGAG gene?
With regard to HSGAGs, a multimeric enzyme encoded by EXT1 and EXT2 of the EXT family of genes , transfers both GlcNAc and GlcA for HSGAG chain elongation. While elongating, the HSGAG is dynamically modified, first by N-deacetylase, N-sulfotransferase ( NDST1 ), which is a bifunctional enzyme that cleaves the N-acetyl group from GlcNAc and subsequently sulfates the N-position. Next, C-5 uronyl epimerase coverts d-GlcA to l-IdoA followed by 2- O sulfation of the uronic acid sugar by 2- O sulfotransferase ( Heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase ). Finally, the 6- O and 3- O positions of GlcNAc moities are sulfated by 6- O ( Heparan sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase) and 3-O (3-OST) sulfotransferases.
What enzyme is responsible for elongation of keratan sulfate polymer?
Elongation of the keratan sulfate polymer occurs through the glycosyltransferase addition of Gal and GlcNAc. Galactose addition occurs primarily through the β-1,4-galactosyltransferase enzyme (β4Gal-T1) while the enzymes responsible for β-3-Nacetylglucosamine have not been clearly identified.
What is the main component of synovial tissues?
Hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic acid is a major component of synovial tissues and fluid, as well as the ground substance of other connective tissues. Hyaluronic acid binds cells together, lubricates joints, and helps maintain the shape of the eyeballs.
What is the repeating sugar unit?
The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, with the exception of keratan, where in the place of the uronic sugar it has galactose. Because GAGs are highly polar and attract water, they are used in the body as a lubricant or shock absorber.
Which isoform is responsible for hyaluronic acid polymers?
HAS2 is responsible for very large hyaluronic acid polymers, while smaller sizes of HA are synthesized by HAS1 and HAS3. While each HAS isoform catalyzes the same biosynthetic reaction, each HAS isoform is independently active. HAS isoforms have also been shown to have differing Km values for UDP-GlcA and UDPGlcNAc.
Is hyaluronic acid a polysaccharide?
HA, a linear polysaccharide, is composed of repeating disaccharide units of →4)GlcAβ (1→3)GlcNAcβ (1→ and has a very high molecular mass, ranging from 10 5 to 10 7 Da.
What are glycosaminoglycans?
Abstract. Glycosaminoglycans are a group of polysaccharides that play essential physiological functions. Two prominent members in the glycosaminoglycan group are heparan sulfate (HS) and chondroitin sulfate (CS).
How is glycosaminoglycan degraded?
The various GAGs are degraded in highly ordered processes. Hyaluronan is found unattached to protein and is degraded through the action of hyaluronidase, which breaks the long chain into tetrasaccharides and longer fragments, through the cleavage of the β-GlcNAc linkage.
What is the structure of GAGs?
The structure of GAGs can be generically described as that of an alternating copolymer, the repeat unit consisting of a hexosamine (glucosamine or galactosamine) and of another sugar (galactose, glucuronic acid or iduronic acid).
What enzymes degrade GAGs?
There are several naturally occurring enzymes which degrade specific GAGs, the most well-known being hyaluronidase. These enzymes are primarily responsible for the physiological turnover rate of GAGs, which is in the range of 2–14 days. Sign in to download full-size image. FIG.
Which carbons are hydroxyl groups?
Second, the hydroxyl groups on the C3 and C6 carbons of acetylated or deacetylated units.
Is hexosamine a GAG chain?
Individual GAG chains are known to contain occasional substitutions of one uro nic acid for another ; however, the nature of the hexosamine component remains invariant along the chain. There are other deviations from the model of a flawless alternating copolymer, such as variations in sulfate content along the chain.
Is hyaluronic acid a nonsulfated GAG?
Difference in sulfation pattern of GAGs results in their diverse properties. Hyaluronic acid, which is a nonsulfated GAG, is composed of d -glucuronic acid and N -acetyl- d -glucosamine. These disaccharide repeats are connected via alternating β-1,4 and β-1,3 glycosidic linkages. It is naturally synthesized in vertebrates by an integral membrane protein called hyaluronan synthase. Its nontoxicity, biocompatibility, and nonmutagenicity are some of the excellent properties due to which it is being exploited in regeneration applications. 130,131
What are the functions of glycosaminoglycans?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)—also known as mucopolysaccharides—primarily function to support the most important structural proteins of the skin: collagen and elastin. Glycosaminoglycans are water-binding molecules that can hold nearly 1,000 times their own weight, which helps provide moisture to the skin.
What is glycosaminoglycan used for?
In addition to keeping skin youthful-appearing and healthy, glycosaminoglycans are used in the body as a lubricant for joints, for supporting connective tissues such as cartilage and tendons, and may even help assist with weight loss. Common GAG supplements include glucosamine sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, and hyaluronic acid .
What are the components of the dermis?
The dermis layer of skin has three primary components: collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycans . There’s a reason why these are best known as a powerhouse ingredient in skincare products: GAGs offer many health benefits to the skin, helping us keep a youthful glow while also repairing scars and wrinkles.
Does glycosaminoglycan help with wrinkles?
4 So whether you’re looking to reduce the appearance of fine wrinkles and scars or to hydrate your skin, a skin moisturizer with glycosaminoglycans may help.
What is the role of glycosaminoglycans in the cell?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) Glycosaminoglycans' primary role is to maintain and support collagen, elastin and turgidity (bounce) in the cellular spaces and keep protein fibers in balance and proportion. It also promotes the ability of the collagen and elastin fibers to retain moisture, therefore remaining soluble (Source).
What is the role of glycosaminoglycans in the lymphatic system?
Glycosaminoglycans' primary role is to maintain and support collagen, elastin and turgidity (bounce) in the cellular spaces and keep protein fibers in balance and proportion. It also promotes the ability of the collagen and elastin fibers to retain moisture, ...
Where is collagen found?
It is found in connective tissues, such as skin, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, bones, teeth, heart valves, and the cornea. Structurally, collagen is composed of long fibers of protein.
What is the ground substance?
This gel-like fluid is called the ground substance. There are various glycosaminoglycans in the dermis. The most common ones are: hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, keratin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, heparin sulfate, and heparin. The key thing to know about glycosaminoglycans is that they are water-binding substances.
What are the components of the dermis?
The dermis layer of skin has three crucial components: collagen , elastin, and glycosaminoglycans (GAG’s). They form the bulk of an important support system called the Extracellular Matrix (ECM). This matrix consists of structural proteins ( collagen and elastin ), glycosaminoglycans, and proteoglycans.
What is the best way to boost collagen synthesis?
Ingredients, such as Vitamin C, boost collagen synthesis by accelerating the reaction. (Vitamin C is an essential coenzyme in collagen synthesis.) You may see ‘hydrolyzed collagen’ on an ingredient list. Collagen in its hydrolyzed form (broken into small pieces) is used to increase skin hydration.
Does collagen stretch easily?
Collagen is tough and does not stretch easily. It provides strength to the skin and holds the skin together. Collagen requires Vitamin C and iron to form healthy protein fibers. In the absence of Vitamin C, collagen forms abnormal fibers. This results in skin lesions, fragile skin, and blood vessels. Because it is a large protein, collagen does not ...
Does collagen increase skin hydration?
Collagen in its hydrolyzed form (broken into small pieces) is used to increase skin hydration. It cannot increase the amount of collagen in skin. Collagen is produced and recycled throughout life. But with age, the rate of collagen production slows down.
What are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates correspond to the bio-polymers that are made up of monomer units. These monomer units are called monosaccharides. Depending on the number of monomers present in the carbohydrate, they are divided into various types-
What are Glycosaminoglycans?
Glycosaminoglycans are defined by long unbranched polysaccharides that consist of repeating disaccharides. In short, they are called GAGs and because of their property of being lubricant and vicious, they are also called mucopolysaccharides. Both glycogen and starch consist of glucose units.
Importance of Glycosaminoglycans
Glycosaminoglycans can be found in collagen and elastin, and also, water sticks to them which allows the resistance to pressure. Consequently, during compression in the aqueous solution of GAGs, the water gets squeezed out. As a result, the GAGs are compelled to cover a smaller volume.
Structure of Glycosaminoglycans
By definition, glycosaminoglycans are negatively charged polysaccharides that are linear in shape and also could be either sulfate or non-sulfate. GAGs weigh around 10 to 100 kilodalton molecular weights. On the basis of the types of linkage between the disaccharide units, and structural units, the glycosaminoglycans can be divided into two parts.
Functions of Glycosaminoglycans
As we all know that GAGs have a lot of functions to perform in the human or animal body. So, they have a pile of work to perform which is very prominent for our body.
Applications of Glycosaminoglycans
In different parts of the world, countries, and scientists have been researching and making discoveries over different applications of glycosaminoglycans. The work is still going on, and there are a lot of new discoveries scientists have been working on.
Health Effects of Glycosaminoglycans
There are a lot of things to discuss upon the health effects of glycosaminoglycans. Being an important part of the body that regulates prominent functions in the body, it has various health effects.
Overview
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invert…
Production
Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes.
GAGs are classified into four groups, based on their core disaccharide structures. Heparin/heparan sulfate (HSGAGs) and chondroitin sulfate/dermata…
Function
CSGAGs Endogenous heparin is localized and stored in secretory granules of mast cells. Histamine that is present within the granules is protonated (H2A ) at pH within granules (5.2–6.0), thus it is believed that heparin, which is highly negatively charged, functions to electrostatically retain and store histamine. In the clinic, heparin is administered as an anticoagulant and is also the first line choice for thromboembolic diseases. Heparan sulfate (HS) has numerous biologica…
Classification
Members of the glycosaminoglycan family vary in the type of hexosamine, hexose or hexuronic acid unit they contain (e.g. glucuronic acid, iduronic acid, galactose, galactosamine, glucosamine).
They also vary in the geometry of the glycosidic linkage.
Examples of GAGs include:
• GlcUA = β-D-glucuronic acid
See also
• Lipopolysaccharide
External links
• King M. 2005. Glycosaminoglycans. Indiana University School of Medicine Accessed December 31, 2006.
• Glycosaminoglycans at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
• MRI evaluation of glycosaminoglycan loss (dGEMRIC evaluation)