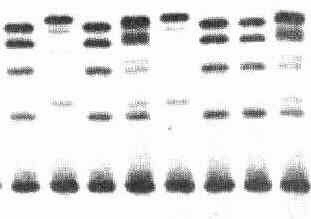
Isoenzymes are multiple molecular forms of an enzyme derived from the same source and having at least one substrate in common. The multiple forms are sometimes tissue specific. They are generally separated by chromatography or electrophoresis.
How do coenzymes separate?
What enzymes catalyze the addition or removal of groups?
What are coenzymes for transfer of H?
What is the role of coenzyme in enzymes?
How many subunits are in lactic acid dehydrogenase?
Which coenzyme is used to make dehydrogenases?
How many atoms of oxygen molecules are incorporated into the substrate?
See 2 more

How are isoenzymes separated in laboratory?
Isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase, separated by electrophoresis on cellulose acetate, were developed by a substrate—gel imprint. The gel was prepared in an alkaline buffer and contained β-naphthyl acid phosphate, which was hydrolyzed to β-naphthyl and phosphorus.
How is isoenzymes are separated by electrophoresis?
Electrophoretic techniques used for separation of LDH isoenzymes. Lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes can be separated using various supporting media such as starch, agarose, cellulose acetate, and polyacrylamide gel.
How can isozymes be differentiated?
Isozymes are usually distinguished by their electrophoretic mobilities. All living systems apparently require multiple molecular forms of certain enzymes in order to maximize biological capacity. Isozymes arise from gene duplications and/or different epigenetic modifications of a gene product(s).
What are the techniques used in the separation of ALP isoenzymes?
The individual ALP isoenzymes normally can be separated by electrophoresis according to charge differences. The separated ALP isoenzymes are visualised using a specific chromogenic substrate.
What is an isozyme pattern?
Isozymes are defined as multiple molecular forms of an enzyme demonstrating similar or identical catalytic properties.
What are isoenzymes explain?
In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. different KM values), or are regulated differently.
What are the different types of isoenzymes?
The five isoenzymes are found in different amounts in tissues throughout the body.LDH-1: found in heart and red blood cells.LDH-2: found in white blood cells. ... LDH-3: found in lung tissue.LDH-4: found in white blood cells, kidney and pancreas cells, and lymph nodes.LDH-5: found in the liver and muscles of skeleton.
Are isozymes encoded by the same gene?
Although, strictly speaking, allozymes represent enzymes from different alleles of the same gene, and isozymes represent enzymes from different genes that process or catalyse the same reaction, the two words are usually used interchangeably.
What are the properties of isoenzymes?
Isoenzymes, or isozymes, are distinct, often readily separable forms of an enzyme elaborated by the same organism. Isozymes catalyze the same chemical reaction, but typically differ with respect to their primary structure, intracellular location, and physiological role.
What are the methods used for acid phosphatase determination?
Acid phosphatase activity is determined by splitting 1-naphthyl phosphate, concurrently diazotizing the released 1-naphthol with Fast Red TR, and measuring the resulting color. The test is performed in the presence and absence of tartrate.
What are the isoenzymes of ALP?
Alkaline phosphatase is divided into four isozymes depending upon the site of tissue expression that are Intestinal ALP, Placental ALP, Germ cell ALP and tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase or liver/bone/kidney (L/B/K) ALP.
What is ALP isoenzyme test?
The ALP isoenzyme test is a lab test that measures the amounts of different types of ALP in the blood. The ALP test is a related test. Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.
What is mechanism of enzyme action?
mechanisms of enzymatic action. An enzyme attracts substrates to its active site, catalyzes the chemical reaction by which products are formed, and then allows the products to dissociate (separate from the enzyme surface). The combination formed by an enzyme and its substrates is called the enzyme–substrate complex.
Are isozymes encoded by the same gene?
Although, strictly speaking, allozymes represent enzymes from different alleles of the same gene, and isozymes represent enzymes from different genes that process or catalyse the same reaction, the two words are usually used interchangeably.
What are the functions of isoenzymes?
Isoenzymes (or isozymes) are a group of enzymes that catalyze the same reaction but have different enzyme forms and catalytic efficiencies.
What are the two models that illustrate the binding of a substrate to an enzyme?
There are two models used to describe the way enzymes interact with substrates: The 'lock and key' model. The 'induced fit' model.
Isozymes: Definition, Function, and Examples I ResearchTweet
Isozymes are most commonly caused by gene duplication, although they can also be caused by polyploidization or hybridization. If the function of the new variation remains the same as the original over time, one or the other will most likely be lost as mutations accumulate, resulting in a pseudogene.
Study Notes on Isoenzymes (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion
ADVERTISEMENTS: The below mentioned article provides study notes on Isoenzymes. Isoenzymes or isozymes are proteins which have different molecular and physicochemical properties, but have identical catalytic activity. They generally occur in branched metabolic pathways in which several end-products are synthesized from a common precursor molecule. A hypothetical branched pathway in which three ...
Isozymes: Definition, Occurrence and Characteristics | Enzymes
ADVERTISEMENTS: Isozymes: Definition, Occurrence and Characteristics! Definition of Isozymes: The enzymes that occur in a number of different forms and differ from each other chemically, immunologically and electrophoretically are called “Isoenzymes” or “isozymes”. ADVERTISEMENTS: Occurrence of Isozymes: Isozymes are present in the serum and tissues of mammals, amphibians, birds ...
How do coenzymes separate?
They combine loosely with the enzyme molecules and so, the coenzyme can be separated easily by dialysis. Coenzymes are considered as group carriers and they can be classified:
What enzymes catalyze the addition or removal of groups?
These enzymes catalyze the addition or removal of groups e.g. H2O, NH3, or CO2, Without hydrolysis, oxidation or reduction. e.g. Dehydratases (or hydratases): they catalyze removal or addition of water to or from the substrate. e.g.
What are coenzymes for transfer of H?
a. Coenzymes for transfer of H. They are called hydrogen carriers. e.g:
What is the role of coenzyme in enzymes?
The coenzyme is essential for the biological activity of the enzyme. A coenzyme is a low molecular weight organic substance, without which the enzyme cannot exhibit any reaction.
How many subunits are in lactic acid dehydrogenase?
Example: Lactic acid dehydrogenase is a tetrameric enzyme, formed of 4 subunits of two types H and M. Only the tetrameric molecule is active. H and M subunits combined to form 5 isoenzymes as follows:
Which coenzyme is used to make dehydrogenases?
b) Dehydrogenases depend on riboflavin coenzymes (FAD and FMN).
How many atoms of oxygen molecules are incorporated into the substrate?
Dioxygenases: Two atoms of oxygen molecules are incorporated into the substrate. As in tryptophan metabolism.
Popular Answers (1)
We have used predominantly electrophoretic method for the separation of LDH isoenzymes, which appeared not so hard even in med lab environment. Due to their different amino acid compositions the LDH isoenzymes can be separated in polyacrylamide used as a matrix.
All Answers (9)
We have used predominantly electrophoretic method for the separation of LDH isoenzymes, which appeared not so hard even in med lab environment. Due to their different amino acid compositions the LDH isoenzymes can be separated in polyacrylamide used as a matrix.
Similar questions and discussions
How to purify two different proteins with very close molecular weights and pI values?
How are isozymes separated?
Isozymes can be separated from each other using a process called gel electrophoresis, a lab process that separates proteins based on charge and size.
How Can You Isolate Isozymes?
If you were interested in isolating a single isozyme of Twinkinase only expressed in the pinky toe, what do you think the first step would be? Well, first you would need a way to separate Twinkinase from other proteins and enzymes floating in the pinky toe. This is simple if you only have one form of Twinkinase. However, imagine this is not the case and there are multiple forms to deal with.
What Is an Isozyme?
Enzymes are proteins that make things happen in cells. For example, enzymes produce energy, restore DNA mutations, move things across the plasma membrane and many other things that make life possible for cells. Think of all the things a cell has to do, enzyme regulation becomes complex quick!
What happens to the proteins in a pinky toe sample?
After the gel has been run, all of the proteins and enzymes in the sample will appear as bands once you color them with a dye that stains proteins.
Why are isozymes important?
However, the main reason for isozymes is that enzymes have limited conditions such as temperature, salinity, and pH, at which they will work.
Why do organs have isozymes?
Organs in the body may have a variety of isozymes because these organs serve diverse functions and have dissimilar internal conditions. An isozyme of Twinkinase that would work in the stomach may not work in the muscles because the stomach and muscles vastly differ in pH.
What is the name of the enzyme that can be made by a single gene?
A single gene can make different variations of the enzyme called allozymes.
Where are the 5 isoenzymes found?
The five isoenzymes are found in different amounts in tissues throughout the body. LDH-1: found in heart and red blood cells. LDH-2: found in white blood cells. It is also found in heart and red blood cells, but in lesser amounts than LDH-1. LDH-3: found in lung tissue. LDH-4: found in white blood cells, kidney and pancreas cells, and lymph nodes.
What does it mean when LDH isoenzymes are not normal?
If your results showed that levels of one or more LDH isoenzymes were not normal, it probably means you have some kind of tissue disease or damage. The type of disease or damage will depend on which LDH isoenzymes had abnormal levels. Disorders that cause abnormal LDH levels include: Anemia. Kidney disease.
What is the name of the enzyme that is released when a tissue is damaged?
This test can help your provider find out the location and cause of your tissue damage. Other names: LD iso enzyme, lactic dehydrogenase iso enzyme.
Why do you need an LDH isoenzyme test?
You may need this test if your health care provider suspects that you have tissue damage based on your symptoms and/or other tests. An LDH isoenzymes test is often done as a follow-up to a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) test. An LDH test also measures LDH levels, but it doesn't provide information on the location or type of tissue damage.
How do coenzymes separate?
They combine loosely with the enzyme molecules and so, the coenzyme can be separated easily by dialysis. Coenzymes are considered as group carriers and they can be classified:
What enzymes catalyze the addition or removal of groups?
These enzymes catalyze the addition or removal of groups e.g. H2O, NH3, or CO2, Without hydrolysis, oxidation or reduction. e.g. Dehydratases (or hydratases): they catalyze removal or addition of water to or from the substrate. e.g.
What are coenzymes for transfer of H?
a. Coenzymes for transfer of H. They are called hydrogen carriers. e.g:
What is the role of coenzyme in enzymes?
The coenzyme is essential for the biological activity of the enzyme. A coenzyme is a low molecular weight organic substance, without which the enzyme cannot exhibit any reaction.
How many subunits are in lactic acid dehydrogenase?
Example: Lactic acid dehydrogenase is a tetrameric enzyme, formed of 4 subunits of two types H and M. Only the tetrameric molecule is active. H and M subunits combined to form 5 isoenzymes as follows:
Which coenzyme is used to make dehydrogenases?
b) Dehydrogenases depend on riboflavin coenzymes (FAD and FMN).
How many atoms of oxygen molecules are incorporated into the substrate?
Dioxygenases: Two atoms of oxygen molecules are incorporated into the substrate. As in tryptophan metabolism.
