
Ketone Bodies and Their Function
- 3 major types of ketones are produced in the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. ...
- Other ketones are synthesized from the metabolism of triglycerides (i.e., β-ketopentanoate, β-hydroxypentanoate).
- Ketone bodies are produced during periods of caloric restriction.
Why ketone bodies is synthesized?
Ketone bodies are produced mainly in the mitochondria of liver cells, and synthesis can occur in response to an unavailability of blood glucose, such as during fasting. The production of ketone bodies is then initiated to make available energy that is stored as fatty acids. Click to see full answer. Moreover, what is ketone synthesis?
Why does liver do not use ketone bodies?
Why can the liver not use ketone bodies? they lack the enzyme Thiophorase which catalyses the reaction from acetoacetate to acetoacetyl CoA occurring in the degradation of ketone bodies. Why is it possible to convert acetyl CoA into ketone bodies for use of energy, even though they are broken down back into 2 Acetyl CoA molecules?
How do I know if I'm in ketosis?
The most accurate way to see if you are in ketosis is by testing your blood with a blood ketone meter (which we will learn a bit more about later in the article). 1. Dry Mouth and Increased Thirst The combination of carb restriction and ketone production will cause your body to lose water at a rapid rate.
Why are ketone bodies produced during starvation?
Why are ketone bodies produced during starvation? Ketone bodies are synthesized from the acetyl CoA generated by the oxidation of fatty acids in the liver. The fact that a significant portion of the fatty acids mobilized from adipose tissue is converted to ketone bodies for brain metabolism during starvation is significant.
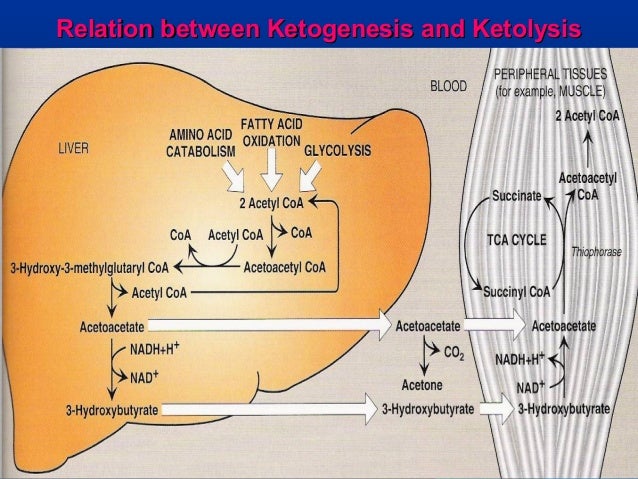
Where does synthesis of ketone bodies occur?
Production. Ketone bodies are produced mainly in the mitochondria of liver cells, and synthesis can occur in response to an unavailability of blood glucose, such as during fasting.
How are ketone bodies synthesized and degraded?
Ketone bodies are water soluble transport form of acetyls. Ketone bodies are produced when excessive acetyl-CoA is present. Acetyl-CoA is produced in hepatic β-oxidation, i.e. the liver pre-arrange fatty acids and provide ketone bodies as an alternative source of energy.
How are ketone bodies formed and used?
Ketone bodies are produced by the liver and used peripherally as an energy source when glucose is not readily available. The two main ketone bodies are acetoacetate (AcAc) and 3-beta-hydroxybutyrate (3HB), while acetone is the third, and least abundant, ketone body.
What regulates ketone body synthesis?
What regulates ketone body synthesis? The primary regulator of ketone body synthesis is fatty acid availability.
What are the three steps that regulate ketone body formation?
This reaction is performed in three steps: (1) cleavage of acetyl-CoA with formation of a covalent bond between the acetyl moiety and the thiol group of catalytic cysteine (acetyl-SH-Enzyme) with the release of free CoA-SH; (2) binding of acetoacetyl-CoA with acetyl-SH-Enzyme and formation of HMG-CoA (Enzyme-S-HMG-CoA ...
Why are ketone bodies produced during starvation?
Fatty acids themselves are not metabolized by the brain, so that ketone bodies (which do cross the blood-brain barrier) are the fuel of choice during starvation.
What happens to ketone bodies after they are synthesized?
E) ATP, carnitine, and coenzyme A. What happens to ketone bodies after they are synthesized? Question options: A) They are oxidized in the mitochondria of the liver.
How are ketones made from fatty acids?
Fatty acids in the blood are converted to ketone bodies when insulin is low, and the fatty acid concentration is high. Fatty acyl CoA is transported into the liver mitochondria by the carnitine shuttle system.
How are ketone bodies metabolized?
Ketone bodies are metabolized through evolutionarily conserved pathways that support bioenergetic homeostasis, particularly in brain, heart, and skeletal muscle when carbohydrates are in short supply.
How are ketones removed from the body?
If food is not eaten to replenish the glucose supply, ketone bodies can begin to build up. While ketone bodies are removed by your kidneys, if they are produced at a high rate they can overwhelm the kidney. When this happens, acetone is formed from the spontaneous breakdown of the other ketone bodies in the blood.
What are the decomposition products of the urine for ketone bodies?
Ketones bodies are the end product of fatty acid breakdown and consists of : Beta-hydroxybutyric acid. Acetoacetic acid. Acetone....The β- hydroxybutyric acid + acetoacetic acid readily converts to acetone.It shows that the main ketone is acetone to be tested.Some of the kits only measure acetoacetic acid.
In which cellular compartment are ketone bodies synthesized?
They assist in the digestion of lipids. Insulin is produced by liver cells known as hepatocytes. In which cellular compartment are ketone bodies synthesized? A) Mitochondrial intermembrane space.
What is the name of the process that produces two ketones?
Ozonolysis of alkenes. When one or both alkene carbons contain two alkyl groups, ozonolysis generates one or two ketones. The ozonolysis of 1,2‐dimethyl propene produces both 2‐propanone (a ketone) and ethanal (an aldehyde).
How are ketones prepared?
The following sections detail some of the more common preparation methods: the oxidation of secondary alcohols, the hydration of alkynes, the ozonolysis of alkenes, Friedel‐Crafts acylation, the use of lithium dialkylcuprates, and the use of a Grignard reagent.
What is the name of the reagent used to make acetophenone?
Lithium dialkylcuprates. The addition of a lithium dialkylcuprate (Gilman reagent) to an acyl chloride at low temperatures produces a ketone. This method produces a good yield of acetophenone.
What happens when you add water to an alkyne?
The addition of water to an alkyne leads to the formation of an unstable vinyl alcohol. These unstable materials undergo keto‐enol tautomerization to form ketones. The hydration of propyne forms 2‐propanone, as the following figure illustrates.
Where are ketone bodies transported?
Ketone bodies are transported from the liver to other tissues, where acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate can be reconverted to acetyl-CoA to produce reducing equivalents (NADH and FADH 2 ), via the citric acid cycle.
What are ketone bodies?
Ketone bodies. Acetone. Acetoacetic acid. ( R )- beta -Hydroxybutyric acid. Ketone bodies are water-soluble molecules that contain the ketone groups produced from fatty acids by the liver (ketogenesis). They are readily transported into tissues outside the liver, where they are converted into acetyl-CoA ...
Why do fatty acids have mitochondria?
Fatty acids are very high energy fuels and are taken up by all metabolizing cells that have mitochondria. This is because fatty acids can only be metabolized in the mitochondria. Red blood cells do not contain mitochondria and are therefore entirely dependent on anaerobic glycolysis for their energy requirements.
What is the level of ketones in the body?
This induced ketosis is sometimes called nutritional ketosis, but the level of ketone body concentrations are on the order of 0.5–5 mM whereas the pathological ketoacidosis is 15–25 mM .
What does it mean when you smell acetone in your breath?
The overall picture of ketonemia and ketonuria is commonly referred to as ketosis. The smell of acetoacetate and/or acetone in breath is a common feature in ketosis.
What is the concentration of ketone bodies in blood?
The concentration of ketone bodies in blood is maintained around 1 mg/dL. Their excretion in urine is very low and undetectable by routine urine tests (Rothera's test). When the rate of synthesis of ketone bodies exceeds the rate of utilization, their concentration in blood increases; this is known as ketonemia.
How long does it take for a brain to become a fuel?
After about 24 days, ketone bodies become the major fuel of the brain, making up to two-thirds of brain fuel consumption. Many studies suggest that human brain cells can survive with little or no glucose, but proving the point is ethically questionable.

Overview
Fuel utilization across different organs
Ketone bodies can be used as fuel in the heart, brain and muscle, but not the liver. They yield 2 guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and 22 adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules per acetoacetate molecule when oxidized in the mitochondria. Ketone bodies are transported from the liver to other tissues, where acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate can be reconverted to acetyl-CoA to produce reducing equivalents (NADH and FADH2), via the citric acid cycle. Though it is the source of keto…
Production
Fats stored in adipose tissue are released from the fat cells into the blood as free fatty acids and glycerol when insulin levels are low and glucagon and epinephrine levels in the blood are high. This occurs between meals, during fasting, starvation and strenuous exercise, when blood glucose levels are likely to fall. Fatty acids are very high energy fuels and are taken up by all metabolizing cell…
Ketosis and ketoacidosis
In normal individuals, there is a constant production of ketone bodies by the liver and their utilization by extrahepatic tissues. The concentration of ketone bodies in blood is maintained around 1 mg/dL. Their excretion in urine is very low and undetectable by routine urine tests (Rothera's test).
When the rate of synthesis of ketone bodies exceeds the rate of utilization, their concentration i…
See also
• Fatty acid metabolism
External links
• emerg/135 at eMedicine - Diabetic Ketoacidosis
• Fat metabolism at unisanet.unisa.edu.au
• Ketone+Bodies at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
• McGuire, L. C; Cruickshank, A. M; Munro, P. T (2006). "Alcoholic ketoacidosis". Emergency Medicine Journal. 23 (6): 417–420. doi:10.1136/emj.2004.017590. PMC 2564331. PMID 16714496.