What is the role of lipids in the cell cycle?
At least 11 lipids are involved in cell cycle activity. Sphingolipids play a role in cytokinesis during interphase. Because cell division results in plasma membrane tension, lipids appear to help with mechanical aspects of division such as membrane stiffness. Lipids provide protective barriers for specialized tissues such as nerves.
How are the hydrophilic components of lipids arranged to face each other?
on either side of a single layer of protein between two layers of protein so that the nonpolar parts of two lipids point toward each other so that the hydrophilic components are arranged to face each other
What is an example of a lipid?
Another example of a lipid is cholesterol. Cholesterols arrange into rigid ring structures of five or six carbon atoms, with hydrogens attached and a flexible hydrocarbon tail. The first ring contains a hydroxyl group that extends into water environments of animal cell membranes. The rest of the molecule, however, is water insoluble.
What is the liquid nature of cell membranes?
The liquid nature of cell membranes aids in their function. Lipids make up not only plasma membranes, but also cellular compartments such as the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus and vesicles. Lipids also participate in cell division.

How many lipids are involved in cell division?
Lipids also participate in cell division. Dividing cells regulate lipid content depending on the cell cycle. At least 11 lipids are involved in cell cycle activity. Sphingolipids play a role in cytokinesis during interphase. Because cell division results in plasma membrane tension, lipids appear to help with mechanical aspects of division such as membrane stiffness.
What are lipids in living organisms?
By J. Dianne Dotson. Lipids comprise a group of compounds such as fats, oils, steroids and waxes found in living organisms. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes possess lipids, which play many important roles biologically, such as membrane formation, protection, insulation, energy storage, cell division and more.
What are phospholipids made of?
Phospholipids are made of a triglyceride with a phosphate group substituted in for a fatty acid. They can be described as having a charged head and hydrocarbon tail. Their heads are hydrophilic, or water-loving, whereas their tails are hydrophobic or repellant to water. Another example of a lipid is cholesterol.
What is the role of phospholipids in the cell membrane?
Phospholipids form the foundation for lipid bilayers, with their amphipathic nature, that make up cell membranes. The outer layer interacts with water while the inner layer exists as a flexible oily substance. The liquid nature of cell membranes aids in their function.
What are some examples of lipids?
Examples of Lipids. Fatty acids are one type of lipid and serve as building blocks for other lipids as well. Fatty acids contain carboxyl (-COOH) groups bound to a carbon chain with attached hydrogens. This chain is water-insoluble. Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated.
What are some examples of lipid storage diseases?
Some examples of lipid storage diseases include Fabry disease, Gaucher disease, Niemann-Pick disease, Sandhoff disease and Tay-Sachs. Unfortunately, many of these lipid storage diseases result in illness and death at a young age.
How many carbon atoms are in cholesterol?
Cholesterols arrange into rigid ring structures of five or six carbon atoms, with hydrogens attached and a flexible hydrocarbon tail. The first ring contains a hydroxyl group that extends into water environments of animal cell membranes. The rest of the molecule, however, is water insoluble.
Which particles want to enter the membrane?
the particles the want to enter the membrane are the solutes
Why does cholesterol hinder solidification of the membrane?
At low temperatures, cholesterol hinders solidification of the membrane because it prevents the close packing of phospholipids.
What is the concentration of solutes in a red blood cell?
The concentration of solutes in a red blood cell is about 2%. Sucrose cannot pass through the membrane, but water and urea can. Osmosis would cause red blood cells to shrink the most when immersed in which of the following solutions?
Why do phospholipid bilayers exist?
A phospholipid bilayer can exist as a stable boundary between two aqueous compartments because the molecular arrangement shelters the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids from water while exposing the hydrophilic heads to water.
Where does water move in osmosis?
Water moves by osmosis from the hypotonic environment, the cell interior, to the hypertonic environment.
Which membrane forms a pocket that pinches inward?
The plasma membrane forms a pocket that pinches inward, forming a vesicle that contains material from outside the cell. This describes the process of
How does a molecule move down its concentration gradient?
A molecule moves down its concentration gradient using a transport protein in the plasma membrane. This is an example of
Which lipid keeps the membrane fluid and flexible?
Cholesterol - a steroid lipid that keeps the membrane fluid and flexible.
What makes up the cell membrane?
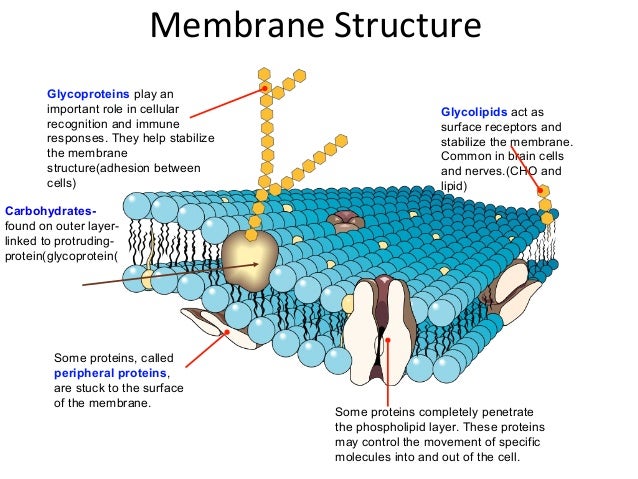
What makes up the cell membrane? The basic structure of the cell membrane includes a two layers of phospholipids, called the phospholipid bilayer. The phospholipid bilayer also has additional macromolecules that help the membrane do its job. What is the structure of the cell membrane? The structure of the cell membrane can be described by the fluid mosaic model. The fluid mosaic model explains that the components of the cell membrane are fluid and can drift laterally in the bilayer. It also explains how the membrane is flexible and able to move with the cell. The fluid mosaic model also describes how the cell membrane is a mosaic, made of many different macromolecules including:
What is a Cell Membrane?
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that separates the cell from its environment and regulates what enters and leaves the cell, called selective permeability. The cell membrane is important for creating a flexible, semi-permeable barrier around the cell. This allows the cell to create stable, internal conditions that are different from a changing environment. The cell membrane is made of two layers of phospholipids and also includes proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol. Forming a barrier is the main function of the cell membrane, but it also has additional functions including:
What is the role of carbohydrates in the cell membrane?
Carbohydrates also play an important role in helping cells attach to the extracellular matrix in cellular adhesion. The collection of carbohydrates on the outside of the cell is called the glycocalyx. In addition to cell adhesion and cell recognition the glycocalyx also helps to cushion the plasma membrane.
What are the two types of proteins in the cell membrane?
There are two types of proteins in the cell membrane: integral and peripheral proteins. Integral proteins span the cell membrane and exist both outside and in it. These proteins have a hydrophobic core that allows them to interact with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids. Peripheral proteins are located on the outside of the cell membrane. These proteins are hydrophilic and attach to the phospholipid heads.
What is the amphipathic structure of a phospholipid?
Phospholipids are a type of amphipathic lipid that make up the cell membrane. Phospholipids have a hydrophobic tail made of two fatty acid chains and a hydrophilic head made of a phosphate group. The head and tail are connected with a glycerol molecule. Because phospholipids have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts, they are called amphipathic. The amphipathic nature of phospholipids contributes to their arrangement in a bilayer in the membrane.
Why is the cell membrane important?
The cell membrane is also important for cell movement and adhesion to the extracellular matrix and other cells. Integral proteins are embedded in the membrane that bind to both internal components of the cell, such as the cytoskeleton, and to external components like the extracellular matrix. These connections can be remodeled as cells need to grow, divide and move throughout the body.
