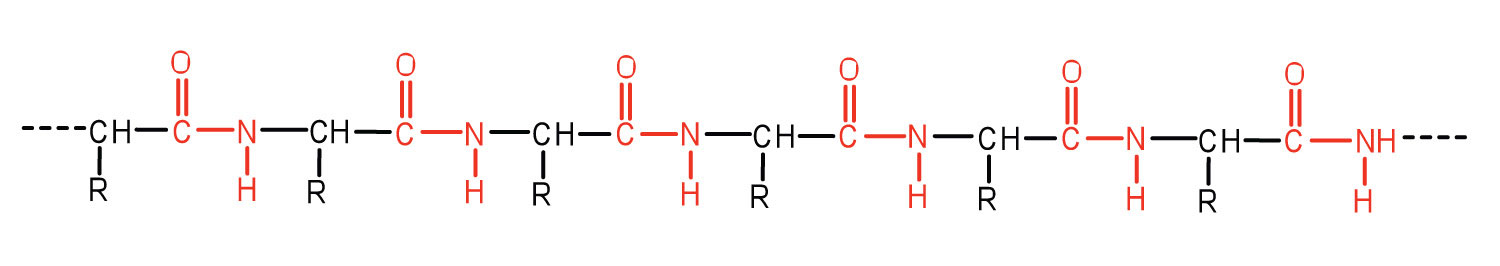
How peptides are formed?
Peptides are formed by the peptide linkage between amino acids. let us understand the peptide formation by taking an example of dipeptide. For the formation of dipeptide, two amino acids approach each other and form a covalent bond between C1 – carbon of carboxylic acid and N2 – nitrogen atom of amino acid group by removal of the water molecule.
How do amino acids form peptide bonds?
In order to form a peptide bond, the molecules of the amino acids in question must be orientated so that the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid is able to react with the amine group of another amino acid.
What is a peptide bond in biology?
A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids when a carboxyl group or C-terminus of one amino acid reacts with the amino group or N-terminus of another amino acid in a condensation reaction (a molecule of water is released during the reaction). The resulting bond is a CO-NH bond and forms a peptide, or amide molecule.
What is meant by peptide sequence?
Peptide Sequence – The peptide sequence is simply the order in which amino acid residues are connected by peptide bonds in the peptide. Peptide Bond – A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids when a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid.
How the peptides are formed?
A peptide bond is formed by a dehydration synthesis or reaction at a molecular level. This reaction is also known as a condensation reaction which usually occurs between amino acids. As depicted in the figure given below, two amino acids bond together to form a peptide bond by the dehydration synthesis.
Are peptides derived from amino acids?
A peptide is a short chain of amino acids (typically 2 to 50) linked by chemical bonds (called peptide bonds). A longer chain of linked amino acids (51 or more) is a polypeptide.
What are amino acids and how is peptide bond formed?
A peptide bond, also referred to as an amide bond, is formed between the α-nitrogen atom of one amino acid and the carbonyl carbon of a second (diagrammed below). So-called isopeptide bonds refer to amide bonds between sidechain amines or carbonyl carbons on the side chain rather than α-amine or α-carbonyl.
What is the difference between peptides and amino acids?
A peptide is a short chain of amino acids. The amino acids in a peptide are connected to one another in a sequence by bonds called peptide bonds. Typically, peptides are distinguished from proteins by their shorter length, although the cut-off number of amino acids for defining a peptide and protein can be arbitrary.
How many amino acids make a polypeptide?
As a general rule, a peptide contains two or more amino acids. And just to make it a little more complicated, you will often hear scientists refer to polypeptides – a chain of 10 or more amino acids.
How do amino acids polymerize to form peptides?
To generate a polypeptide, new amino acids are added sequentially (and exclusively) to the C-terminal end of the polymer. A peptide bond forms between the amino group of the added amino acid and the carboxylic acid group of the polymer; the formation of a peptide bond is associated with the release of a water molecule.
How are peptide bonds formed quizlet?
A peptide bond is formed between two amino acids when the carboxyl group of one amino acids reacts with the amino group of the other amino acid, releasing a molecule of water. This is the dehydration reaction and usually occurs between amino acids.
How do amino acids combine to form proteins?
To form polypeptides and proteins, amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds, in which the amino or NH2 of one amino acid bonds to the carboxyl (acid) or COOH group of another amino acid.
What is the difference between a peptide and a polypeptide?
A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds; a polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids; and a protein contains one or more polypeptides. Therefore, proteins are long chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds.
How do you identify amino acids in a peptide?
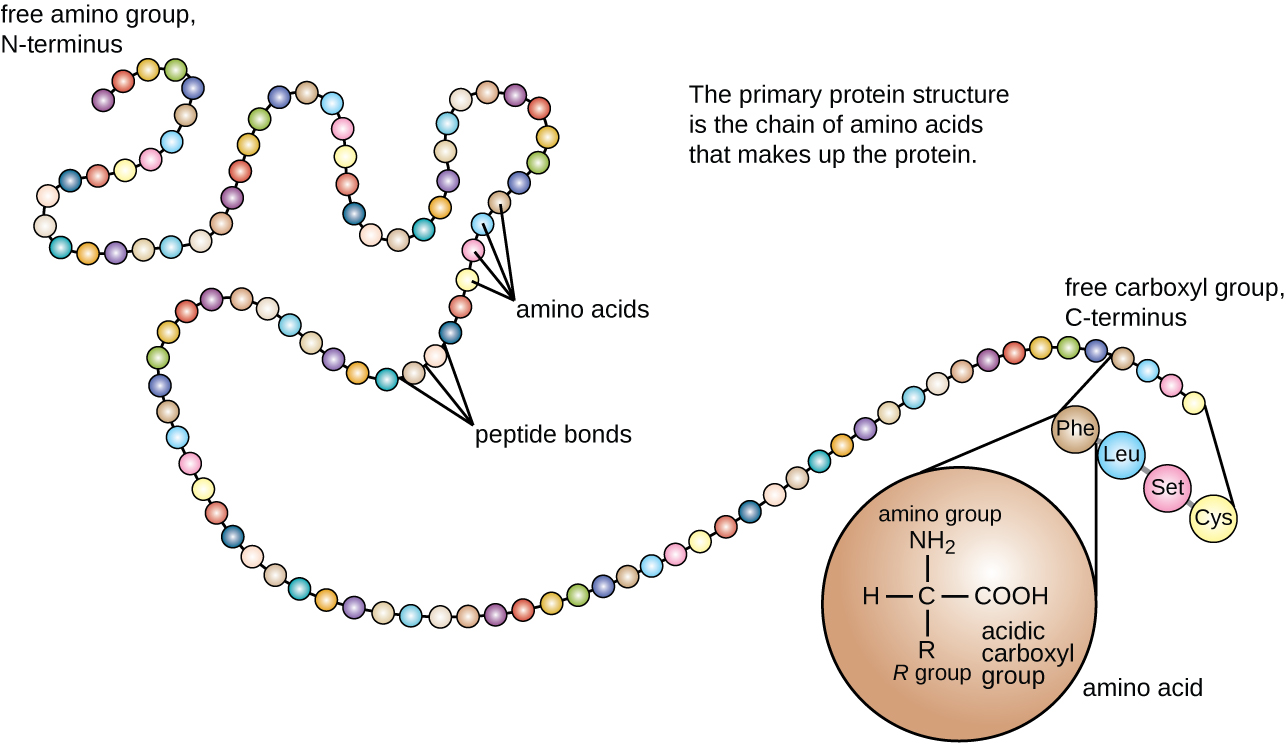
By convention, peptide and protein structures are depicted with the amino acid whose amino group is free (the N-terminal end) on the left and the amino acid with a free carboxyl group (the C-terminal end) to the right.
Can proteins be made without amino acids?
Whether in the body or the factory, the backbone of polypeptide chains is usually formed by the linking of an amino group with the acid group of individual amino acids. Like pearls on a string, the amino acids then line up. However, to get to such a structure, it isn't absolutely necessary to start from amino acids.
Are all polypeptides proteins?
Proteins are therefore also known as polypeptides. Each type of protein has a unique sequence of amino acids, exactly the same from one molecule to the next. Many thousands of different proteins are known, each with its own particular amino acid sequence.
How are peptides grouped?
Peptides are grouped and named according to the number of amino acids the structure possesses.
How do peptide bonds form?
As mentioned earlier, the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids brings about the formation of a molecule of water. As a carboxyl group loses its hydroxyl (OH) and an amine group loses its hydrogen (H) atom, they combine to form one molecule of water for each peptide bond. This process is reversible; peptide bonds can be broken by the addition of a water molecule. The water molecule restores the hydroxyl (OH) to the carboxyl group and a hydrogen atom to the amine group, thus giving rise to two separate individual amino acids per peptide bond and releasing energy. This process is referred to as a hydrolysis reaction.
What is a Polymer of Amino Acids?
As explained earlier, a protein is made of a sequence of amino acids linked together via peptide bonds in a process titled polymerization. The order and sequence of amino acids are specific to each protein, which gives rise to the protein's primary structure.
How do amino acids bind?
Two amino acids bind via a peptide bond. The formation of a peptide bond occurs between a carboxyl group of one amino acid and an amine group of the other.
What are proteins made of?
Proteins, which are vital to the functionality of all living organisms, are made up of multiple amino acid monomers linked together via peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are chemical covalent bonds linking one amino acid to the other, and they form between a carbon atom of one amino acid and a nitrogen atom of the other amino acid. The end of a protein with a free nitrogen atom is referred to as the N-terminus, while the other end of a protein with a free carbon atom is referred to as the C-terminus.
How many amino acids are in a protein?
A protein molecule is generally composed of a multitude of amino acids, or peptides, linked together via peptide bonds. The human body makes use of 20 naturally occurring amino acids. Proteins differ in the number and type of amino acids they possess.
What is the code for protein expression?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) serves as the code that dictates protein expression in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. DNA is made of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sugar and phosphate molecules together form what is called the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA, which anchors to the nitrogenous base and gives it the ability to form hydrogen bonds with nitrogenous bases of the complementary DNA strand. Recent scientific breakthroughs allowed the development of peptide nucleic acids (PNAs). PNAs are man-made DNA look-alike substances, in which the sugar-phosphate backbone is replaced with a peptide polymer. Because of their flexible and uncharged nature, they bind to complementary DNA strands in a very efficient manner. Therefore, PNAs are used in research and diagnostic settings, in which they are employed in hybridization assays.
How do amino acids react in peptide synthesis?
The basic reaction in peptide synthesis relies on a coupling between two amino acids. They react with each other to form the dipeptide, with the separation of water. This does not happen spontaneously, so they have to be activated for the reaction to occur. For this purpose, “coupling reagents” have been developed. They generate more reactive derivatives of the amino acids and remove the water which is formed concomitantly from the system.
What is a peptide?
A peptide is a chain of amino acids, which are used as building blocks. More commonly, peptides are short proteins with varying lengths from 2 amino acids to 100 amino acids. Peptides can be found in nature and can perform biological functions such as acting as messengers in the body. If you are interested in learning more about what a peptide is please go and read our article . Peptides are very interesting molecules for many applications from therapeutics to cosmetics and diagnostics. But how are they made?
What is SPPS in peptides?
SPPS is the core expertise of Bachem for peptides manufacturing for more than 50 years. Most peptides sold by Bachem or manufactured as contract synthesis, are produced by SPPS. Solution synthesis is still chosen for the synthesis of some of our peptide generics, for very short peptides (e.g. dipeptides), and peptides modified at the C-terminus. The essential advantages of the solid-phase synthesis over the solution synthesis are its rapidity and ease of automation.
What are the main protecting groups used for amino acids?
At Bachem, the main protecting groups used for the α-amine (Nα) of amino acids are Fmoc (9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonly), Boc (t-Butoxycarbonyl), and Z (Benzyloxycarbonyl). Each of them will define the overall strategy of peptide synthesis and therefore, the deprotection and cleavage conditions will change accordingly. Fmoc will be deprotected in basic condition with a piperidine washing, whereas Boc will require acidic condition like a trifluoroacetic washing. Z will be deprotected by catalytic hydrogenation on palladium.
What are the two methods of peptide synthesis?
There are two standard methods of peptide synthesis: solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) and solution (or solution-phase) synthesis. The table below summarizes the similarities and differences between the two methods.
How to obtain dipeptide H-Ala-Phe-OH?
To obtain the desired dipeptide H-Ala-Phe-OH and not a mixture, two protecting groups are needed. They must not be split off under the conditions of the coupling reaction, but be readily cleaved in a separate step after coupling has taken place.
Which group must be protected throughout the entire synthesis?
In contrast to the α-amino group, the terminal acid group must be protected throughout the entire synthesis. The most commonly used protecting groups and their deprotection conditions are shown in the table below:
Which amino group does not form amides?
They have an additional amino group without forming amides (diamino monocarboxylic), e.g., arginine, lysine.
What amino acids cannot be synthesised by animals?
The amino acids which cannot be synthesised by animals through transformation or transamination are called essential amino acids. These amino acids must be present in their diet, viz-, leucine, isoleucine, valine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, lysine and methionine. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What are rare amino acids?
A protein may also possess non-coded amino acids. The latter are called rare amino acids. Rare amino acids are derived from the coded ones through modifications, e.g., hydroxyproline from proline, hydroxylysine from lysine (both in collagen). Amino acid names are abbreviated with the help of first three letters of the name.
What is the difference between a-carbon and amino acids?
They are organic acids (with carboxylic group —COOH) having amino group (—NH 2) generally attached to a-carbon or carbon next to the carboxylic group. Carboxylic group provides an acidic property to the amino acid while amino group gives it a basic reaction. The a-carbon also bears a variable hydrocarbon or alkyl group R and hydrogen.
How many amino acids are in a tripep tide?
There are three amino acids in a tripep- tide, a few in oligopeptide and numerous in a polypeptide. The term peptide is more commonly used instead of oligopeptide. Like an amino acid a peptide has carboxylic group at one end and amino group at the other end.
What happens when an amino acid condenses?
Amino acids condense to produce peptides. Generally condensation reaction occurs between a primer amino acid or peptide and another amino acid. Molecule of water is eliminated. The bond thus formed —NHCO— is actually amide bond which is popularly known as peptide bond or linkage.
What is the name of the group that replaces proline?
In proline and hydroxyproline, amino group (—NH 2) is replaced by imino group (>NH) which also represents the tail of R-group. Proline and hydroxyproline are called heterocyclic amino acids.
What is a peptide?
Peptides. A peptide is a molecule composed of two or more amino acids. The bond that holds together the two amino acids is a peptide bond, or a covalent chemical bond between two compounds (in this case, two amino acids). It occurs when the carboxylic group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, ...
How are proteins formed?
Large proteins are formed by linking amino acids with peptide bonds. The amide bond is formed through a condensation reaction, whereby the carbonyl and the amine group link together with the release of water.
What type of bonds are amide and peptide?
The Amide Bond: Peptide bonds are amide bonds, characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group attached to an amine.
What are higher order structures such as peptide chains and proteins?
Higher-ordered structures such as peptide chains and proteins are formed when amino acids bond to each other. The Peptide Bond: The peptide bond (circled) links two amino acids together. The blue balls represent the nitrogen that connect from the amine terminus of one amino acid to the carboxylate of another. ...
How are long chain polypeptides formed?
Long chain polypeptides can be formed by linking many amino acids to each other via peptide bonds. The amide bond can only be broken by amide hydrolysis, where the bonds are cleaved with the addition of a water molecule. The peptide bonds of proteins are metastable, and will break spontaneously in a slow process.
What is the chemical compound that bonds to an amine group?
Amino acids are chemical compounds consisting of a carbon atom bonded to an amine group, a hydrogen atom, a carboxylic group, and a varying side-chain (R group); it is this side chain that distinguishes each amino acid from another. Higher-ordered structures such as peptide chains and proteins are formed when amino acids bond to each other.
What are the key points of an amide bond?
Key Points. An amide bond has various resonance forms which allow for extra stabilization and extra versatility in various environments. Amino acids is the basic building block of proteins; they are composed of a carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, a carbonyl group, an amine group, and an R group. Large proteins are formed by linking amino acids ...
How are peptides formed?
Peptides are formed both naturally within the body and synthetically in the laboratory. The body manufactures some peptides organically, such as ribosomal and non-ribosomal peptides. In the laboratory, modern peptide synthesis processes can create a virtually boundless number of peptides using peptide synthesis techniques like liquid phase peptide synthesis or solid phase peptide synthesis. While liquid phase peptide synthesis has some advantages, solid phase peptide synthesis is the standard peptide synthesis process used today. Read more about peptide synthesis.
What are peptides made of?
There are some basic peptide-related terms that are key to a general understanding of peptides, peptide synthesis, and the use of peptides for research and experimentation: Amino Acids – Peptides are composed of amino acids. An amino acid is any molecule that contains both amine and carboxyl functional groups.
What is the sequence of amino acids?
Peptide Sequence – The peptide sequence is simply the order in which amino acid residues are connected by peptide bonds in the peptide. Peptide Bond – A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids when a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid.
What is an amino acid?
An amino acid is any molecule that contains both amine and carboxyl functional groups. Alpha-amino acids are the building blocks from which peptides are constructed. Cyclic Peptides – A cyclic peptide is a peptide in which the amino acid sequence forms a ring structure instead of a straight chain.
How are ribosomal peptides produced?
Ribosomal peptides often go through the process of proteolysis (the breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides or amino acids) to reach the mature form. Conversely, nonribosomal peptides are produced by peptide-specific enzymes, not by the ribosome (as in ribosomal peptides).
What is a peptide?
A peptide is a biologically occurring chemical compound containing two or more amino acids connected to one another by peptide bonds. A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids when a carboxyl group or C-terminus of one amino acid reacts with the amino group or N-terminus of another amino acid in a condensation ...
What is the process of mapping peptides?
Peptide Mapping – Peptide mapping is a process that can be used to validate or discover the amino acid sequence of specific peptides or proteins.
How many amino acids are in a peptide?
Further, any number of amino acids can be joined together in chains to form new peptides: as a general guideline, 50 or less amino acids are referred to as peptides, 50 – 100 are termed polypeptides, and peptides with over 100 amino acids are generally referred to as proteins.
How do peptide bonds form?
Peptide Bond Formation. In order to form a peptide bond, the molecules of the amino acids in question must be orientated so that the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid is able to react with the amine group of another amino acid. At its most basic, this can be illustrated by two lone amino acids combining through the formation ...
What is a Peptide Bond?
A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids. To form a peptide bond, a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid. As a result, a molecule of water is also released. This is referred to as a condensation reaction. The resulting bond is a CO-NH bond and is henceforth referred to as a peptide bond. Additionally, the resulting molecule is termed an amide.
What wavelength of absorbance is a peptide bond?
The wavelength of absorbance for a peptide bond is 190-230 nm. In the biological realm, enzymes inside living organisms can both form and break down peptide bonds. A number of hormones, antibiotics, antitumor agents and neurotransmitters are peptides, most of which are referred to as proteins (due to the number of amino acids contained).
Why do scientists conduct x-ray diffraction studies of peptides?
Scientists have conducted x-ray diffraction studies of several small peptides in order to ascertain the physical characteristics of peptide bonds. Such studies have indicated that peptide bonds are rigid and planer.
What breaks down peptide bonds?
Hydrolysis (a chemical breakdown of a compound resulting from a reaction with water) can break down a peptide bond. Though the reaction itself is quite slow, the peptide bonds formed within peptides, polypeptides, and proteins are susceptible to breakage when they come into contact with water (metastable bonds).
What is the bond that releases water?
As a result, a molecule of water is also released. This is referred to as a condensation reaction. The resulting bond is a CO-NH bond and is henceforth referred to as a peptide bond. Additionally, the resulting molecule is termed an amide.