
Functions of Polysaccharides
- Structural Functions- Common sources of energy are nutrition polysaccharides and most of the organisms can easily break down starch into glucose. However, some complex polysaccharides are not very digestible that are known as dietary fibre and these provide important elements in the diet for humans. ...
- Storage Functions- Storage polysaccharides are starch, glycogen and insulin. ...
What are NSPs made of?
Where are amylopectin and amylose deposited?
Where are arabinoxylans found?
What are the main storage carbs in plants?
What is pectin used for?
What are the three main types of pectic polysaccharides?
What are mixed-linked glucans?
See 4 more
About this website

Are polysaccharides an energy source?
Nutrition polysaccharides are common sources of energy. Many organisms can easily break down starches into glucose; however, most organisms cannot metabolize cellulose or other polysaccharides like cellulose, chitin and arabinoxylans.
What polysaccharide is stored as an energy source?
glycogenAnswer and Explanation: The polysaccharide that is stored as an energy source in the body of animals is glycogen.
Are polysaccharides used for energy storage?
Polysaccharides generally perform one of two functions: energy storage or structural support. Starch and glycogen are highly compact polymers that are used for energy storage. Cellulose and chitin are linear polymers that are used for structural support in plants and animals, respectively.
Why are polysaccharides good energy stores?
Because they are composed of many types of monosaccharides joined by many types of bonds, especially condensation reactions. Once they are broken down, it releases energy which is needed for cell processes.
What are the four examples of polysaccharides?
The four main examples of polysaccharides are cellulose, starch, glycogen and chitin. Starch and glycogen are storage polysaccharides, while cellul...
What are polysaccharides made of?
The linear or branched chains formed by the joining of monosaccharide units with glycosidic linkages are called polysaccharides.
What are the functions of polysaccharides?
a. They serve as storage of reserve food material in plants and animals. b. They form the structural components of the bodies of living organisms.
What are the food sources of polysaccharides?
a. Tubers- Potato, sweet potato, tapioca contain starch b. Seeds grains- such as rice, wheat, corn etc. contain starch c. Fruits- Pectin d. Gums an...
Are polysaccharides good or bad?
Polysaccharides are natural polymers found in plants, animals and microbes. They have high nutritive values and are essential for the good immune s...
Role of Polysaccharides in Food, Digestion and Health - Academia.edu
Polysaccharides derived from plant foods are major components of the human diet, with limited contributions of related components from fungal and algal sources. In particular, starch and other storage carbohydrates are the major sources of energy in
Role of polysaccharides in food, digestion, and health - PubMed
Polysaccharides derived from plant foods are major components of the human diet, with limited contributions of related components from fungal and algal sources. In particular, starch and other storage carbohydrates are the major sources of energy in all diets, while cell wall polysaccharides are the …
Dietary roles of non-starch polysaccharides in human nutrition: a ...
Nonstarch polysaccharides (NSPs) occur naturally in many foods. The physiochemical and biological properties of these compounds correspond to dietary fiber. Nonstarch polysaccharides show various physiological effects in the small and large intestine and therefore have important health implications …
How do polysaccharides store energy?
While the enzymes that produce energy only work on the monosaccharides stored in a polysaccharide, polysaccharides typically fold together and can contain many monosaccharides in a dense area. Further, as the side chains of the monosaccharides form as many hydrogen bonds as possible with themselves, water cannot intrude the molecules, making them hydrophobic. This property allows the molecules to stay together and not dissolve into the cytosol. This lowers the sugar concentration in a cell, and more sugar can then be taken in. Not only do polysaccharides store the energy, but they allow for changes in the concentration gradient, which can influence cellular uptake of nutrients and water.
How are monosaccharides formed?
All polysaccharides are formed by the same basic process: monosaccharides are connected via glycosidic bonds. When in a polysaccharide, individual monosaccharides are known as residues. Seen below are just some of the many monosaccharides created in nature. Depending on the polysaccharide, any combination of them can be combined in series.
What is the role of polysaccharides in plants?
Cellular Support. By far one of the largest roles of polysaccharides is that of support. All plants on Earth are supported, in part, by the polysaccharide cellulose. Other organisms, like insects and fungi, use chitin to support the extracellular matrix around their cells.
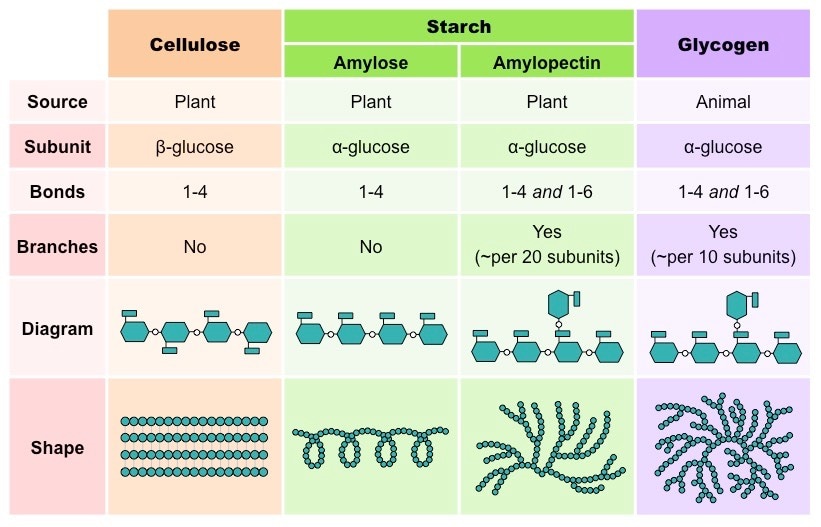
How are glycogen and starch different?
This means the monosaccharides can be quickly extracted from the polysaccharide and be utilized for energy. The only difference between starch and glycogen is the number of branches that occur per molecule. This is caused by different parts of the monosaccharides forming bonds, and different enzymes acting on the molecules. In glycogen a branch occurs every 12 or so residues, while in starch a branch occurs only every 30 residues.
Why is it important to brush and floss?
There are monosaccharides present in most foods which can feed the bacteria, and allow them to store energy in dextrans and create plaque. However, the digestive process starts in the saliva, and as the food stays in your mouth, it continues to release monosaccharides that allow for the growth of bacteria. That is why it is important to brush and floss regularly.
How do polysaccharides affect the concentration gradient?
Not only do polysaccharides store the energy, but they allow for changes in the concentration gradient, which can influence cellular uptake of nutrients and water.
What is the difference between cellulose and starch?
The only difference between cellulose and starch is the configuration of the glucose used.
How Should You Consume Aloe Vera?
Popular in many forms, you can find aloe vera in products like lotions, gels, creams, juices, and capsules. If you really want to experience the full effect of all this plant has to offer, you'll need to ingest it. [ 9] There are a variety of aloe vera juices available, but many of these fail to provide a significant amount of the key nutrients that make aloe vera so beneficial. The same is true of many capsulated forms of aloe vera. One other concern with products like these is that they may contain amounts of an aloe compound called aloin, which serves as an extremely potent laxative. As you might imagine, biting into a freshly cut leaf would pose the same risk.
What are the two types of energy stores?
There are two types of polysaccharides that the body uses for storing energy: starch and glycogen Starches serve as short-term energy stores and are made from a mixture of amylose and amylopectin. Some common dietary starches include rice, potatoes, wheat, and corn. Glycogen, on the other hand, acts more like a long-term storage option. Glycogen is mainly produced by the liver and muscles, but it can also be made during a process called glycogenesis, which occurs in both the brain and stomach.
Why are polysaccharides important?
Polysaccharides are critical when it comes to proper nutrition because they comprise the complex carbohydrates that, for many, serve as the body’s primary energy source. Every bodily function relies on carbohydrates for energy. But, while the body can produce some energy, it’s certainly not enough to sustain itself.
What are polysaccharides in nutrition?
Close. Polysaccharides are molecular strands that contain multiple monosaccharide or disaccharide units. Think of these as simple sugars linked by glycosidic bonds. When it comes to nutrition, polysaccharides play a huge role in the body.
What are some examples of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides, sometimes called “glycans”, have two roles: some, like starch or glycogen, help store the energy we gain from consuming food. Others help with cell structure. One common example of a polysaccharide used for storage is cellulose. [ 1]
Which polysaccharides show hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activity in mice with experimentally?
Jia, X. et al. Polysaccharides from Laminaria Japonica Show Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Activities in Mice with Experimentally Induced Diabetes. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 239 (12).
Is aloe vera good for you?
Because aloe vera is so rich in important nutrients, including those unique to the species, such as acemannan, it supports overall health in several ways. Of course, adding aloe vera to your diet isn’t really as simple as breaking off a leaf and taking a bite.
What are Polysaccharides?
The linear or branched chains formed by the joining of monosaccharide units with glycosidic linkages are called polysaccharides. So, polysaccharides are the polymers of monosaccharides. The monosaccharide units are linked with each other by glycosidic bonds.
What are the two main parts of a plant's storage polysaccharide?
Storage polysaccharides act as reserve food material while structural polysaccharides form the major part of structures such as cell walls, fibrous tissue and exoskeleton. Starch and glycogen are the storage polysaccharides in plants and animals, respectively.
What is the branched part of starch?
Amylopectin is the branched part of starch where α – D – glucose subunits are linked with each other by α – 1, 6 glycosidic linkage. vi. The branching appears approximately per 20 to 30 glucose residues in the chain. vii. Starch is hydrolyzed rapidly with amylase enzymes found in saliva and the small intestine. viii.
What are the two main functions of polysaccharides?
Chitin is an example of a structural polysaccharide in animals. Thus, storage of energy and structure formation are the two main functions of polysaccharides.
What are the components of a cell wall?
Bacterial cell walls and cell membranes contain a variety of polysaccharides and carbohydrate derivatives together called bacterial polysaccharides. Bacterial polysaccharides include peptidoglycans, lipopolysaccharides and exopolysaccharides. Peptidoglycan is the major constituent of the bacterial cell wall.
What are the bonds between polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are polymers of simple sugars linked with each other by covalent bonds called glycosidic bonds.
Where is starch hydrolyzed?
Starch is hydrolyzed rapidly with amylase enzymes found in saliva and the small intestine. viii. The amylose is naturally present in a coiled fashion. In such a state, it has spaces to accommodate the iodine molecules which form amylose-iodine complexes.
What are the three main types of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds. Three important polysaccharides, starch, glycogen, and cellulose, are composed of glucose. Starch and glycogen serve as short-term energy stores in plants and animals, respectively. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of ten or up to several thousand monosaccharides arranged in chains. Think of these as simple sugars linked by glycosidic bonds. When it comes to nutrition, polysaccharides play a huge role in the body. Polysaccharides have two roles: some, like starch or glycogen, help store the energy we gain from consuming food. Others help with cell structure. The most common monosaccharides in polysaccharides are glucose, fructose, galactose and mannose.
What are some examples of polysaccharides?
Examples of Polysaccharides: 1. Starch. An energy source from glucose units that are widely obtained from plants. Many starches are cereal grains, bread, pasta, pastries, cookies, potatoes, tapioca, wheat, oats, rye, barely, rice and yams to name a few. They are a polysaccharide energy source when digested in the body.
How many polysaccharides are in a chain?
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of ten or up to several thousand monosaccharides arranged in chains. Think of these as simple sugars linked by glycosidic bonds. When it comes to nutrition, polysaccharides play a huge role in the body.
Why are polysaccharides important?
Polysaccharides are critical when it comes to proper nutrition because they comprise the complex carbohydrates that, for many, serve as the body's primary energy source. Every bodily function relies on carbohydrates for energy. But, while the body can produce some energy, it's certainly not enough to sustain itself.
What is the most abundant organic molecule on earth?
2. Cellulose. A structural polysaccharide in plants that when consumed, it acts as a dietary fiber. Cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule on earth, since it is the main component of plant cell walls.
What are the benefits of cellulose in the body?
Non-digestible polysaccharides or dietary fiber, such as cellulose, promote the passage of food through the gut and thus help maintain bowel regularity.
How many calories are in starch?
They are a source of energy; they provide about 4 Calories per gram.
What is cellulose in food?
Cellulose is another polysaccharide commonly found in foods. Cellulose provides a protective covering and/or structure to fruits and vegetables and their seeds. It gives foods a crunchy texture and is undigestible in the body. However, cellulose does act as a source of dietary fiber, adding bulk to your stool and helping to maintain regular digestive processes. Many fruits and vegetables contain some aspect of cellulose, including in the skins of apples and pears, in the covering of whole grains like wheat bran and in plant leaves like spinach. Seeds and nuts also contain cellulose.
What is the prefix for carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates can be divided into several categories: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. Chemically speaking, the prefix before "saccharides" indicates how many saccharide chains are attached to the molecule. Polysaccharides have many chains and must be broken down into smaller portions before they can be fully digested.
What are some examples of starch?
Starch food sources often are referred to as "starchy carbohydrates" and include foods like corn, potatoes and rice. Other examples include bread, cereal and pasta. These foods are the most common form of carbohydrates in your diet, comprising an estimated one-third of the foods you eat. The body breaks starches down into glucose, ...
How many calories are in kale pesto?
This amazing kale pesto is only 210 calories and anti-oxidant rich!
What fruits and vegetables contain cellulose?
Many fruits and vegetables contain some aspect of cellulose, including in the skins of apples and pears, in the covering of whole grains like wheat bran and in plant leaves like spinach. Seeds and nuts also contain cellulose. Advertisement.
Do polysaccharides taste sweet?
Although polysaccharides are a form of sugar, many of their food sources rarely taste sweet. Video of the Day.
Is carrot a soluble fiber?
carrots are a source of soluble fiber. Image Credit: Alicja Bochenek/iStock/Getty Images. Pectin is a compound that helps to form a gel-like substance when broken down in the body. Food sources that contain pectin also are known as soluble fiber sources.
What are NSPs made of?
NSPs are made up of the hexose sugars glucose, galactose and mannose, the deoxy-hexoses rhamnose and fucose, glucuronic and galacturonic acids, and the pentose sugars arabinose and xylose (Bach-Knudsen, 2001). NSPs may be broadly grouped into classes (based on Waldron et al., 2003).
Where are amylopectin and amylose deposited?
Amylose and amylopectin are deposited within specialized plastids (called amyloplasts) in highly organized granules which vary in their abundances, sizes, and shapes between different species (Tester et al., 2004).
Where are arabinoxylans found?
Arabinoxylans are generally found in monocot cell walls, particularly grasses , and consist of a (1→4)-β-linked D-xylose unit backbone which is substituted with L-arabinose at either the 3 or the 2 and 3 positions. Further modifications of these chains may occur, including the feruloylation of monosubstituted arabinose units, which may lead to oxidative cross-linking of cell wall components. Arabinoxylans from wheat grain are of particular interest as they constitute the principle source of fiber in flour (and make up ˜70% of the cell wall polysaccharide) (Fincher and Stone, 1986). Water-soluble arabinoxylans have profound effects on processing properties (including bread making as discussed by Courtin and Delcour, 2002) owing to their water holding capacity and effect on viscosity. The water solubility is strongly related to the degree of branching (substitution), the more branched arabinoxylans are more soluble than less branched arabinoxylans (Izydorcryk and Biliadris, 1995). The solubility of arabinoxylan in wheat and other cereal grain may also be affected by feruloylation, which occurs at the 5 position of arabinose units. This substitution with ferulic acid allows the formation of cross-links, by oxidation of ferulate present on adjacent AX chains to give dehydrodimers (diferulates). Such cross-linked arabinoxylans may be important components of water-insoluble arabinoxylans, particularly in cereal brans. Substitution may also occur with p-coumaric acid, but at a lower frequency than with ferulic acid.
What are the main storage carbs in plants?
Starch is the major storage carbohydrate in plants, and the major source of calories in many plant organs and foods. Its biophysical properties also have major impacts on food texture and other properties. Although available starch is readily digested in the small intestine, resistant starch (RS) and cell wall polysaccharides (or nonstarch polysaccharides, NSPs) are not digested, but are the major components of dietary fiber and are fermented by the colon microbiota to produce short chain fatty acids (SCFAs). NSPs provide a rigid structure surrounding plant cells and therefore affect the release and digestion of the cell contents. Table 1provides a summary of the major types of plant-derived carbohydrate in the human diet.
What is pectin used for?
Like many of the polysaccharides described here, they are used in the food industry as gelling and thickening agents.
What are the three main types of pectic polysaccharides?
Three major pectic polysaccharides are recognized; homogalacturonan (HG), rhamnogalacturonan-I (RG I), and rhamnogalacturonan-II (RG II) (Willats et al., 2006). HG comprises (1→4)-α-linked D-galacturonic acid units with occasional rhamnose residues, up to 200 units long. RG I has a backbone of repeats of the disaccharide (1→4)-α-D-galacturonic acid (1→2)-α-L-rhamnose (up to approximately 10 units long; Thibault et al., 1993). The rhamnose residues may be substituted with (1→4)-β-galactan, branched arabinan, and/or arabinogalactan side chains. The nonbranched HG regions are commonly referred to as “smooth” while the branched regions are referred to as “hairy.” RG II has a HG backbone decorated with side branches (designated A–D), which consist of 12 different sugars and 20 different linkages (Mohnen, 2008). RG II is a very minor component of plant cell walls and has an extremely complex chemical structure including some very rare sugars (Voragen et al., 1995). The different pectic polysaccharides are not separate molecules, but consist of covalently linked domains (Harholt et al., 2010). Similarly to arabinoxylan, ferulylation of arabinose in pectin may also occur, as for instance, in sugar beet pectin. Another important feature in the chemical structure of the pectic polysaccharides is the presence of methyl esters at the carboxylic groups of the galacturonic acid as well as acetylated hydroxyl groups. The extent to which these modifications occur has a large influence on the aqueous solubility of the polysaccharide as well as its solution properties. If more than 50% of the carboxyl groups are methylated, the pectin is referred to as high methoxyl (HM) pectin and if less than 50% are methylated then the pectin is referred to as low methoxyl (LM) pectin. Pectins make up around 35% of primary cell walls of dicotyledonous and nongraminaceous monocots (Mohnen, 2008; Willats et al., 2006; Carpita, 1996).
What are mixed-linked glucans?
Cereal mixed-linked β-glucans are glucose units linked (1→4)-β (as in cellulose) but interspersed with (1→3)-β-linkages. The (1→3)-β-linkages generally occur after three or four β-(1→4) linkages, but more extensive cellulose-like stretches of up to 20 (1→4)-β-linked residues have been reported in wheat bran (Li et al., 2006). The irregular linkage structure prevents the formation of an ordered crystalline structure, leading to the β-glucans being partially water soluble. Water-soluble mixed-linked β-glucans of barley (where they constitute ˜70% of endosperm cell wall polysaccharides (Fincher and Stone, 1986)) and oats are able to form viscous solutions and dispersions. In addition, b-glucans with (1→3)(1→6) linkages occur in fungi.
Terminology
Functions
- Depending on their structure, polysaccharides can have a wide variety of functions in nature. Some polysaccharides are used for storing energy, some for sending cellular messages, and others for providing support to cells and tissues. Many polysaccharides are used to store energy in organisms. While the enzymes that produce energy only work on the ...
Formation
- All polysaccharides are formed by the same basic process: monosaccharides are connected via glycosidic bonds. When in a polysaccharide, individual monosaccharides are known as residues. Seen below are just some of the many monosaccharides created in nature. Depending on the polysaccharide, any combination of them can be combined in series. Probably the most importa…
Mechanism
- The structure of the molecules being combined determines the structures and properties of the resulting polysaccharide. The complex interaction between their hydroxyl groups (OH), other side groups, the configurations of the molecules, and the enzymes involved all affect the resulting polysaccharide produced. A polysaccharide used for energy storage will give easy access to the …
Chemistry
- The glycosidic bonds between monosaccharides consist of an oxygen molecule bridging two carbon rings. The bond is formed when a Hydroxyl group is lost from the carbon of one molecule, while the hydrogen is lost by the hydroxyl group of another monosaccharide. The carbon on the first molecule will substitute the oxygen from the second molecule as its own, and glycosidic bo…
Structure
- Cellulose and chitin are both structural polysaccharides that consist of many thousand glucose monomers combined in long fibers. The only difference between the two polysaccharides are the side-chains attached to the carbon rings of the monosaccharides. In chitin, the glucose monosaccharides have been modified with a group containing more carbon, nitrogen, and oxyge…
Causes
- When a glycogen or starch molecule is broken down, the enzymes responsible start at the ends furthest from the center. This is important, as you will notice that because of the extensive branching there are only 2 starting points, but many ends. This means the monosaccharides can be quickly extracted from the polysaccharide and be utilized for energy. The only difference bet…
Examples
- 2. Plants produce both the starch amylose, and the structural polymer cellulose, from units of glucose. Most animals cannot digest cellulose. Even ruminants such as cattle cannot digest cellulose and rely on symbiotic internal organisms to break the bonds of cellulose. However, all mammals produce amylase, an enzyme which can break down amylose. Why can amylase not b…
Properties
- B. The glycosidic bonds of cellulose are stronger. C. The extracellular matrix created by cellulose cannot be broken down.
Types
- 3. Hyaluronan is a molecule found in the joints of vertebrates that provides support by creating a jelly-like matrix to cushion the bones. Hyaluronan is created from several different monosaccharides bonded together in long chains. Which of the following describe hyaluronan? 1. Homopolysaccharide 2. Heteropolysaccharide 3. Polymer 4. Monomer