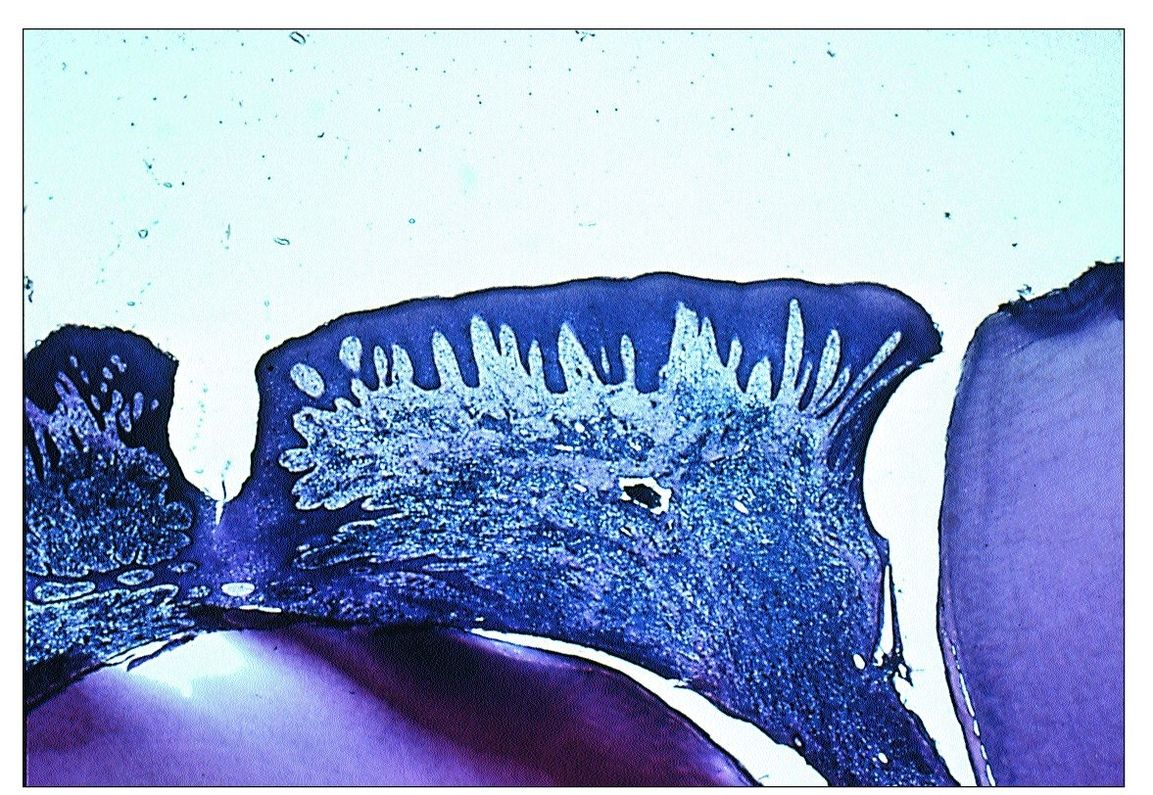
- Acute open pulpitis may become quiescent and enter a chronic phase in high tissue resistance and low virulent organism.
- Early minimal pulpitis can be treated by pulpotomy with CA ( OH)2 lining for calcify bridge
- Root canal filling with inert materials is used for more severe cases.
What are the treatment options for pulp polyps in permanent teeth?
See the list below: Treatment of a pulp polyp in a permanent tooth includes either root canal therapy or extraction of the tooth. The more conservative pulpotomy treatment has been successful in selected cases when only the coronal pulp is affected.
Which medications are used in the treatment of a pulp polyp?
Systemic medications are not recommended for the management of a pulp polyp. Antibiotics are not prescribed for the treatment of the pulp polyp, despite a bacterial component. However, an antibiotic paste mixture is used within the canals of the infected tooth when the revascularization process is performed for the treatment of the nonvital tooth.
How do you get rid of a pulp polyp?
The pulp polyp is remedied by curetting the new connective tissue mass from the pulp holding cell and also carrying out endodontic therapies on the remaining tooth root structures, assuming the interradicular ground remains undamaged. Extraction can be an accepted remedy alternative.
Is extraction of a pulp polyp without treatment a good idea?
Extraction can be an accepted remedy alternative. There is absolutely no malignant change and the lesion is not going to automatically regress. Leaving a pulp polyp without treatment can lead to a number of problems. Contamination of the adjoining gingival tissue mass and also abscess could appear.

Is pulp polyp common?
Pulp polyp is rare in middle aged adults but it is more common in teeth of children and adolescents, in which the pulp tissue have a high resistance and a good blood supply.
Is Pulp polyps cancerous?
Most polyps are benign, meaning they're noncancerous. But because they are due to abnormal cell growth, they can eventually become malignant, or cancerous.
How are pulp polyps diagnosed?
To differentiate from a polyp of gingival origin, the pulp polyp may be lifted from the walls of the cavity with an excavator revealing the presence of the pedicle with very little or no discomfort experienced by the patient.
Is pulp polyp vital tooth?
The pulp polyp, also known as chronic hyperplastic pulpitis or proliferative pulpitis, is a type of inflammatory hyperplasia. It occurs in a vital tooth with a good blood supply when the pulp has been exposed to caries or trauma (13).
Are pulp polyps harmful?
Pulp polyps are usually asymptomatic. Direct pressure during mastication may cause mild-to-moderate tenderness. Localized bleeding may occur when the soft tissue is manipulated or traumatized.
Is it normal to find polyps during endoscopy?
When they are found during an endoscopy, there are usually several of them, and they appear as small, smooth flat bumps. These polyps rarely develop into cancer. Fundic gland polyps are often associated with proton pump inhibitor use. In those cases, the doctor may recommend that the patient stop taking the medication.
Do pulp polyps bleed?
Pulp polyps are usually asymptomatic. Direct pressure during mastication may cause mild-to-moderate tenderness. Localized bleeding may occur when the soft tissue is manipulated or traumatized.
How do you stop a pulp polyp from bleeding?
If bleeding stops: Irrigate with NaOCl and leave in the canals and pulp chamber for 10–15 minutes. Dry and place Ca(OH)2 in the canals and close. If bleeding does not stop: Place sterile water in the canals for 10–15 minutes, to stop the breakdown of pulpal tissues.
How do you get rid of gingival polyps?
Gingival polyp are cut using an excavator and restoration cavity using composite. Conclusion: Eugenol exerts a beneficial action on anti-inflammatory so could reduce the edema of gingival soft tisuue. The treatment acceptance but the expected results are still not maximal so that it still needs to excision.
Can pulpitis spread?
With irreversible pulpitis, the pulp is no longer able to heal itself. Your body's immune system breaks down the dead tissue. Still, if there is too much infection and dead tissue for your immune system to handle, an abscess can form. The infection may spread to the surrounding bone or other areas of the body.
How long does a pulpotomy take?
A pulpotomy takes about 30 minutes to complete from start to finish. A member of the dental team will first numb the area to ensure that your child won't feel any pain or discomfort during the procedure. The endodontist will remove the damaged pulp from the tooth before sterilizing the area to remove all the infection.
How is irreversible pulpitis diagnosed?
Teeth with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis may be difficult to diagnose because the inffammation has not yet reached the periapical tissues, thus resulting in no pain or discomfort to percussion. In such cases, dental history and thermal testing are the primary tools for assessing pulpal status.
What polyps are cancerous?
Neoplastic polyps include adenomas and serrated types. These polyps have the potential to become cancer if given enough time to grow. Most of these colon polyps are called adenomas. Serrated polyps may also become cancerous, depending on their size and location in the colon.
How do you know if colon polyps are cancerous?
Most polyps are benign (not cancerous). Your doctor can tell if a colon polyp is cancerous during a colonoscopy by collecting tissue to biopsy. The results of the biopsy are typically sent to your doctor within a week. Only 5% to 10% of all polyps become cancerous.
What does a cancerous polyp look like?
Polypoid polyps look like a mushroom, but flop around inside the intestine because they are attached to the lining of the colon by a thin stalk. Sessile polyps do not have a stalk, and are attached to the lining by a broad base.
What happens if a uterine polyp is cancerous?
If your polyps have cancer cells, you may need surgery to take out your entire uterus, called a hysterectomy.
How to treat a pulp polyp in a tooth?
Treatment of a pulp polyp in a permanent tooth includes either root canal therapy or extraction of the tooth. The more conservative pulpotomy treatment has been successful in selected cases when only the coronal pulp is affected.
What is a Pulp Polyp?
Pulp polyps involving the primary, first, and second mandibular molars in a young child with extensive dental caries. Pulp polyp involving the permanent second mandibular molar in a young adult with multiple carious teeth.
Can you take antibiotics for a pulp polyp?
Systemic medications are not recommended for the management of a pulp polyp. Antibiotics are not prescribed for the treatment of the pulp polyp, despite a bacterial component. However, an antibiotic paste mixture is used within the canals of the infected tooth when the revascularization process is performed for the treatment of the nonvital tooth.
What is a pulp polyp?
This kind of polyp is mostly a result of an neglected cavity in a big tooth, for example the wisdom teeth. The pulp polyp is usually located in the main second molar or perhaps permanent initial molar, due to the fact these types of teeth are usually more probably compared to others to be significantly damaged by caries at an age once the apical blood circulation into the tooth continues to be excellent. This indicates it is actually mostly a condition of the very first decade of living, however later on lesions can happen.
Why do we use vital pulpotomy?
Vital pulpotomy procedure is used to take away contaminated parts of the pulp in an effort to stop nerve and tooth root deterioration. Here you can find a pulpotomy procedure steps. TOP Reasons for using Interdental Brushes and How to use Interdental Brushes Pure Facts about Pulp Stones.
How to treat a pulp polyp in a tooth?
Treatment of a pulp polyp in a permanent tooth includes either root canal therapy or extraction of the tooth. The more conservative pulpotomy treatment has been successful in selected cases when only the coronal pulp is affected.
What is pulp polyp?
The pulp polyp, also known as chronic hyperplastic pulpitis or proliferative pulpitis, is an uncommon and specific type of inflammatory hyperplasia that is associated with a nonvital tooth. Pulpal diseases are broadly divided into reversible and irreversible pulpitis and are based on the ability of the inflamed dental pulp to return ...
Why does pulpitis not occur?
Tissue necrosis with destruction of the microcirculation that usually accompanies irreversible pulpitis does not occur in part because of this lack of significant intrapulpal pressure. In young teeth in which the apex of the root is open, the risk of pulpal necrosis secondary to venous congestion is decreased.
What happens when the pulpal roof is exposed?
The large exposure of pulpal tissue to the oral environment and bacterial invasion results in a chronic inflammatory response that stimulates an exuberant granulation tissue reaction.
What causes a tooth to have a pulp polyp?
The pulp polyp is the result of both mechanical irritation and bacterial invasion into the pulp of a tooth that exhibits significant crown destruction due to trauma or caries. The mechanical causes that may stimulate this response include a tooth fracture with pulpal exposure or loss of a dental restoration. Usually, the entire dentinal roof is exposed with the crown of a carious tooth. The large exposure of pulpal tissue to the oral environment and bacterial invasion results in a chronic inflammatory response that stimulates an exuberant granulation tissue reaction.
What is the surface of a polyp?
The surface varies from pink and smooth to red and white and granular. Red and ulcerated lesions are vascular and bleed when manipulated. Polyps typically enlarge to fill the entire cavitated area or pulpal chamber of the tooth. Soft tissue may merge with the adjacent attached gingiva.
Is pulp polyp uncommon?
Pulp polyps are reportedly uncommon in the United States, and no epidemiologic studies specifically document the frequency of this entity. Although this lesion is reported to be uncommon with only isolated references in the literature, the true prevalence of this reactive pulpal disease is likely to be underestimated because it is a well-recognized sequela of extensive dental caries in children.
What is the best treatment for nasal polyps?
If you have nasal polyps and chronic sinusitis, your doctor may give you an injection of a medication called dupilumab (Dupixent) to treat your condition. This medication may reduce the size of the nasal polyps ...
How to treat a large nasal polyp?
Drug treatments may include: Nasal corticosteroids. Your doctor is likely to prescribe a corticosteroid nasal spray to reduce swelling and irritation. This treatment may shrink the polyps or eliminate them completely.
What is the procedure to remove polyps from the sinuses?
Your surgeon may also enlarge the openings leading from your sinuses to your nasal passages. Endoscopic surgery is usually performed as an outpatient procedure.
What is the test for nasal polyps?
The standard diagnostic test for cystic fibrosis is a noninvasive sweat test, which determines whether your child's perspiration is saltier ...
What to do if your sinuses are swollen?
Your doctor may prescribe drugs to treat conditions that contribute to long-term swelling in your sinuses or nasal passages. These may include antihistamines to treat allergies and antibiotics to treat a chronic or recurring infection.
What is a polyp in pulpitis?
Pulp Polyp, also called as Chronic Hyperplastic Pulpitis, or Proliferative pulpitis is a productive pulpal inflammation due to extensive carious exposure of any young pulpal tissue. This is a type of irreversible pulpitis, which is chronic and usually asymptomatic in nature.
What is the appearance of polypoid tissue?
Appearance of Polypoid tissue – A fleshy, reddish mass fills most of the pulp chamber or extends beyond the tooth structure. Polypoid tissue is less responsive when compared to normal pulp tissue. Radiographs show a large, open cavity with direct access to the pulp chamber. Response is seen on electric pulp testing too.
Is pulpitis asymptomatic or chronic?
This is a type of irreversible pulpitis, which is chronic and usually asymptomatic in nature. It is characterized by development of granulation tissue, covered by epithelium and it results from irritation for a long time.
How to treat a pulp polyp in a tooth?
Treatment of a pulp polyp in a permanent tooth includes either root canal therapy or extraction of the tooth. The more conservative pulpotomy treatment has been successful in selected cases when only the coronal pulp is affected.
What causes a pulp polyp?
Causes of a pulp polyp include the following: Carious tooth with significant loss of tooth structure. Loss of a dental restoration that results in pulpal exposure. Fractured tooth due to trauma with a pulpal exposure. Pulpal tissue with access to a good blood supply.
Why does my tooth have a pulp polyp?
The pulp polyp is the result of both mechanical irritation and bacterial invasion into the pulp of a tooth that exhibits significant crown destruction due to trauma or caries. The mechanical causes that may stimulate this response include a tooth fracture with pulpal exposure or loss of a dental restoration. Usually, the entire dentinal roof is ...
What happens when the pulpal roof is exposed?
The large exposure of pulpal tissue to the oral environment and bacterial invasion results in a chronic inflammatory response that stimulates an exuberant granulation tissue reaction.
Why does pulpitis not occur?
Tissue necrosis with destruction of the microcirculation that usually accompanies irreversible pulpitis does not occur in part because of this lack of significant intrapulpal pressure. In young teeth in which the apex of the root is open, the risk of pulpal necrosis secondary to venous congestion is decreased.
Do dental polyps occur in developing countries?
International data. Pulp polyps are uncommon in countries with routine access to dental care, but they are encountered more frequently in developing countries. In a study of Vietnamese refugees who sought dental care, the prevalence of pulp polyps was 6%.
Is there a risk of recurrence of a polyp?
No risk for recurrence exists once definitive treatment has been rendered. Morbidity/mortality. Pulp polyps tend to be asymptomatic and are not associated with any significant morbidity or mortality except for gross caries destruction with premature tooth loss in many cases. Complications.
Acute Pulpitis Signs and Symptoms
Usually, a large carious lesion or a defective restoration with recurrent caries is present.
Chronic Pulpitis Signs and Symptoms
Pain is not a prominent feature though it may be dull, mild and often intermittent.
Treatment of Chronic Pulpitis
As in acute phase but extraction may be necessary when RCT is not feasible.
What is Pulp polyp?
The pulp polyp, also known as proliferative pulpitis, is an uncommon and specific type of inflammatory Hyperplasia that is associated with a non-vital tooth.
What is the best way to check for uterine polyps?
If your doctor suspects you have uterine polyps, he or she might perform one of the following: Transvaginal ultrasound. A slender, wand-like device placed in your vagina emits sound waves and creates an image of your uterus, including its interior.
Can you treat small polyps on their own?
Watchful waiting. Small polyps without symptoms might resolve on their own. Treatment of small polyps is unnecessary unless you're at risk of uterine cancer. Medication. Certain hormonal medications, including progestins and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, may lessen symptoms of the polyp.
Can a hysteroscopy reveal a polyp?
Hysteroscopy allows your doctor to examine the inside of your uterus. Endometrial biopsy. Your doctor might use a suction catheter inside the uterus to collect a specimen for lab testing. Uterine polyps may be confirmed by an endometrial biopsy, but the biopsy could also miss the polyp. Most uterine polyps are noncancerous (benign).
Is a polyp benign or non-benign?
Most uterine polyps are noncancerous (benign). However, some precancerous changes of the uterus (endometrial hyperplasia) or uterine cancers (endometrial carcinomas) appear as uterine polyps. Your doctor will likely recommend removal of the polyp and will send a tissue sample for lab analysis to be certain you don't have uterine cancer.
Can uterine polyps recur?
If a uterine polyp contains cancerous cells, your doctor will talk with you about the next steps in evaluation and treatment. Rarely, uterine polyps can recur. If they do, you might need more treatment.