What is radar and how it works?
Here's a summary of how radar works: Magnetron generates high-frequency radio waves. Duplexer switches magnetron through to antenna. Antenna acts as transmitter, sending narrow beam of radio waves through the air. Radio waves hit enemy airplane and reflect back. Antenna picks up reflected waves during a break between transmissions.
Is it possible to generate any waveform in radar?
Thus, it is possible to generate any waveform, ranging from ultra-short pulses for classical pulse radar, via intrapulse modulation (with subsequent pulse compression) to all forms of modulation of frequency modulated continuous wave radar (FMCW radar). The processing of an I & Q - phase- detector is arranged reverse virtually.
What are radar waves made up of?
As implied by the term electro-magnetic radiation, the radar waves are made up of both electric and magnetic fields. When a wave is transmitted into free space from an antenna, the orientation of the electric [E] field with respect to the plane of the earth's surface determines the polarization of the wave.
What is the speed of a radar wave?
Radar waves travel through the atmosphere at roughly 300,000 km per second (the speed of light). The range to a target is determined by measuring the time that a radar signal takes to travel out to the target and back.
How do radar waves work?
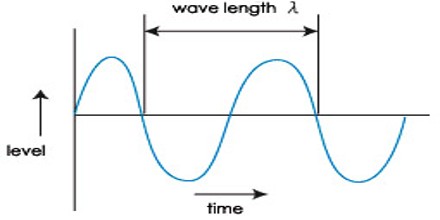
RADAR is fundamentally an electromagnetic sensor used to detect and locate objects. Radio waves are radiated out from the radar into free space. Some of the radio waves will be intercepted by reflecting objects (targets). The intercepted radio waves that hit the target are reflected back in many different directions.
What waves do radar use?
Radar systems transmit electromagnetic or radio waves. Most objects reflect radio waves, which can be detected by the radar system.
What are the 3 components of a radar?
Radar ComponentsAntenna Unit (Antenna + Motor) : Antenna that radiates waves, Motor that rotates the Antenna.Transceiver Unit: Unit generating waves and processing the signal.Processing Unit: Unit processing signals from radar components and external devices.More items...
Does radar use radio waves?
Radar data can be used to determine the structure of storms and to help with predicting severity of storms. Energy is emitted in various frequencies and wavelengths from large wavelength radio waves to shorter wavelength gamma rays. Radars emit microwave energy, a longer wavelength, highlighted in yellow.
What frequency do radars use?
between 400 MHz to 36 GHzMost radars, in practice, operate between 400 MHz to 36 GHz; however, there are some notable exceptions. The optical and radio portions of the electromagnetic spectrum occupy positions coincidental with two important transparent bands in the Earth's atmosphere and ionosphere.
Can radar detect humans?
Doppler radar cannot detect humans who are stationary or walking across the radar's field of view. The radar can only detect the motion components that are directed towards to or away from the radar.
What principle is used in radar?
The basic principle behind radar is simple - extremely short bursts of radio energy (traveling at the speed of light) are transmitted, reflected off a target and then returned as an echo. Radar makes use of a phenomenon we have all observed, that of the ECHO PRINCIPLE.
What are the five 5 components of a radar?
five main components associated with ground penetrating radar systems are the transmitter, antenna, receiver, signal processing and display components.
Why do radars spin?
Why do Radars Spin? Radar dishes spin to enable them to scan a wide area with greater focus by moving the position of the target being scanned. They also have different scanning modes that can be used depending on what they are tracking, whether stationary objects or moving ones.
Is radar a sound or light?
Radar and lidar (LY-dahr) rely on echoes, too. Only they don't use sound waves. Instead, these two technologies use radio waves or light waves, respectively. Both are examples of electromagnetic radiation.
Do radars work in space?
Radar (and other light-based detection systems) works in space but decreases in usefulness with distance. Active omnidirectional systems are only good for one's immediate area.
What are the 2 types of radar?
Radars can be classified into the following two types based on the type of signal with which Radar can be operated.Pulse Radar.Continuous Wave Radar.
Which waves is used in SONAR?
A common use of ultrasound is in SONAR. Ultrasonic waves are used in SONAR instead of audible sound waves.
Why microwaves are used in radar?
Microwaves are used in radars because they can pass through any object. The frequency of the microwaves lies between infrared waves and radio waves and covers a high range of frequencies. So, the microwaves are used in the radar.
Does the Doppler radar use microwaves?
Doppler Radar, Scatterometers, and Radar Altimeters are examples of active remote sensing instruments that use microwave frequencies.
How do radars detect planes?
RADAR stands for Radio Detection And Ranging. A radar system detects other aircraft, ships, or other objects and the speed and direction in which they travel by sending out a pulse of high-frequency electromagnetic waves. This pulse goes out ahead of the aircraft until it encounters an object and reflects off of it.
What is radar?
Radar systems detect the presence, direction or range of aircraft, ships or other, usually moving objects. This is achieved by sending pulses of hi...
Are EMF emissions dangerous?
Radars usually operate at radio frequencies (RF) between 300 MHz and 15 GHz. They generate EMFs that are called RF fields. RF fields within this pa...
When are humans exposed to dangerous amounts of radio frequencies?
The power that radar systems emit varies from a few milliwatts (police traffic control radar) to many kilowatts (large space tracking radars). Howe...
Where are radars used?
Some of the common types of radars encountered in daily life include the following. Air traffic control radars are used to track the location of ai...
What are the possible health effects of radar?
Most studies conducted to date examined health effects other than cancer. They probed into physiological and thermoregulatory responses, behavioura...
What international standards regulate radar?
Exposure limits for RF fields are developed by international bodies such as the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNI...
What other protective measures are in place?
The aim of protective measures is to eliminate or reduce human exposure to RF fields below acceptable limits. An extensive program of measurement s...
In summary
RF fields cause molecules in tissue to vibrate and generate heat. Heating effects could be expected if time is spent directly in front of some rada...
How does pulsed radar work?
In the pulsed radar system, the electromagnetic waves are emitted from the antenna in short bursts. That is to say, the waves are interrupted for a period of time so that the wave can reach a reflecting target and a portion of the energy can return to the same antenna before the next burst of waves is transmitted.
Why does my radar delay?
In older model radars, this delay is due to the recovery time of the T/R tube (duplexer). In the WSR-88D, the computer controls both the firing of the transmitter (each and every pulse) and the protection of the receiver during transmitter bursts. After sensing that the high-power energy has diminished in the waveguide, the computer then allows the receiver to be activated.
What is the WSR-88D radar?
That system is the WSR-88D, a radar and communications system that was literally born out of the minds of Hiser and others. In order to ensure a solid foundation from which to study the WSR-88D system, a measure of knowledge of the fundamental principles of radar is a necessity.
How to tell if radar antenna is a sidelobe?
However, you should also see a ragged, relatively dim "ring" of light around the central bright spot. This is a sidelobe. All weather radar antennas have several sidelobes, separated by specific angles relative to the center of the main beam. The power in these lobes is considerably less than the power focused into the main beam (primary lobe), but still is sufficient to result in unwanted radar echoes from targets, especially those that are close to the radar antenna.
What is a carrier wave?
A "carrier" wave is transmitted, upon which is superimposed a certain modulating signal which we hear or see on our receiving equipment. For the purpose of our discussion of reflected waves, the modulating signals which are a part of a CW wave may be disregarded. We will "modulate" in radar, but rather than in the usual way, a radar wave will be transmitted in an on-and-off manner. While the radar transmitter is "on", the wave which is emitted may be thought of as a CW wave, and therefore will conform to the principles in the following discussion.
How does a flashlight work?
The "beam" of energy is accomplished by using an antenna which focuses the radar energy onto a parabolic reflector. A common analogy to this is found in an ordinary flashlight. The polished reflector found in a flashlight has the effect of directing the light waves in a concentrated "beam".
What does radar mean in the NWS?
RADAR is an acronym for Radio Detection And Ranging. In all of the radar units which have been (and are being) utilized by the NWS, a great deal more than simply "detection" and "ranging" have taken place.
How does radar work?
Radar signals are reflected especially well by materials of considerable electrical conductivity —such as most metals, seawater, and wet ground. This makes the use of radar altimeters possible in certain cases. The radar signals that are reflected back towards the radar receiver are the desirable ones that make radar detection work. If the object is moving either toward or away from the transmitter, there will be a slight change in the frequency of the radio waves due to the Doppler effect .
What is the process of directing radio waves towards objects?
Radar relies on its own transmissions rather than light from the Sun or the Moon, or from electromagnetic waves emitted by the target objects themselves, such as infrared radiation (heat). This process of directing artificial radio waves towards objects is called illumination, although radio waves are invisible to the human eye as well as optical cameras.
How does a radar jammer affect radars?
Jammers have an added effect of affecting radars along other lines of sight through the radar receiver's sidelobes ( sidelobe jamming ).
Why is my radar cluttering?
Adjusting the timing between when the transmitter sends a pulse and when the receiver stage is enabled will generally reduce the sunburst without affecting the accuracy of the range, since most sunburst is caused by a diffused transmit pulse reflected before it leaves the antenna. Clutter is considered a passive interference source , since it only appears in response to radar signals sent by the radar.
What is radar system?
A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the object (s).
What is a radar antenna?
For other uses, see Radar (disambiguation). Long-range radar antenna, used to track space objects and ballistic missiles. Radar of the type used for detection of aircraft. It rotates steadily, sweeping the airspace with a narrow beam.
What does brightness indicate on radar?
Brightness can indicate reflectivity as in this 1960 weather radar image (of Hurricane Abby ). The radar's frequency, pulse form, polarization, signal processing, and antenna determine what it can observe.
Why does Radar Use Radio Waves?
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic waves that travel at the speed of light and have no mass. The high speed of electromagnetic waves is ideal for quickly travelling long distances to assess distant objects with minimal delay.
How are Radar Waves Generated?
Radio waves that are used by radar are created by a piece of equipment called a magnetron. The magnetron is a very high-powered vacuum tube and works as a self-excited microwave oscillator. The magnetron uses crossed electric and magnetic fields to generate the high-power output required in radar equipment.
Radar Frequency Bands
Radars are instruments that use electromagnetic, or radio, waves to detect objects. Most objects reflect radio waves, which can be detected by a radar system. The radiated frequency of a radar system is determined by the purpose for which it’s being used.
How does radar work?
When people use radar, they are usually trying to accomplish one of three things: 1 Detect the presence of an object at a distance - Usually the "something" is moving, like an airplane, but radar can also be used to detect stationary objects buried underground. In some cases, radar can identify an object as well; for example, it can identify the type of aircraft it has detected. 2 Detect the speed of an object - This is the reason why police use radar. 3 Map something - The space shuttle and orbiting satellites use something called Synthetic Aperture Radar to create detailed topographic maps of the surface of planets and moons.
What is the difference between radio waves and radar?
Radar therefore uses radio waves instead of sound. Radio waves travel far, are invisible to humans and are easy to detect even when they are faint.
Why is radar hard to detect?
Because the echo of the sound would be very faint, it is likely that it would be hard to detect. Radar therefore uses radio waves instead of sound. Radio waves travel far, are invisible to humans and are easy to detect even when they are faint. Advertisement.
What are the two things that are easy to understand in the realm of sound?
All three of these activities can be accomplished using two things you may be familiar with from everyday life: echo and Doppler shift. These two concepts are easy to understand in the realm of sound because your ears hear echo and Doppler shift every day. Radar makes use of the same techniques using radio waves.
Why does the sound of an echo have a higher pitch than the original sound?
Some of the sound waves will bounce off the car (an echo). Because the car is moving toward you, however, the sound waves will be compressed. Therefore, the sound of the echo will have a higher pitch than the original sound you sent. If you measure the pitch of the echo, you can determine how fast the car is going.
What is radar used for?
Air traffic control uses radar to track planes both on the ground and in the air, and also to guide planes in for smooth landings. Police use radar to detect the speed of passing motorists. NASA uses radar to map the Earth and other planets, ...
What is the laser used to measure speed?
Police are now using a laser technique to measure the speed of cars. This technique is called lidar , and it uses light instead of radio waves. See How Radar Detectors Work for information on lidar technology. Advertisement.
How are radio waves produced?
The radio waves used by radar are produced by a piece of equipment called a magnetron . Radio waves are similar to light waves: they travel at the same speed—but their waves are much longer and have much lower frequencies. Light waves have wavelengths of about 500 nanometers (500 billionths of a meter, which is about 100–200 times thinner than a human hair), whereas the radio waves used by radar typically range from about a few centimeters to a meter—the length of a finger to the length of your arm—or roughly a million times longer than light waves.
How does radar work in an airplane?
An airplane's radar is a bit like a torch that uses radio waves instead of light. The plane transmits an intermittent radar beam (so it sends a signal only part of the time) and, for the rest of the time, "listens" out for any reflections of that beam from nearby objects. If reflections are detected, the plane knows something is nearby—and it can use the time taken for the reflections to arrive to figure out how far away it is. In other words, radar is a bit like the echolocation system that "blind" bats use to see and fly in the dark.
What is radar?
We can see objects in the world around us because light (usually from the Sun) reflects off them into our eyes. If you want to walk at night, you can shine a torch in front to see where you're going. The light beam travels out from the torch, reflects off objects in front of you, and bounces back into your eyes. Your brain instantly computes what this means: it tells you how far away objects are and makes your body move so you don't trip over things.
How does radar use radio?
Whether it's mounted on a plane, a ship, or anything else, a radar set needs the same basic set of components: something to generate radio waves, something to send them out into space, something to receive them, and some means of displaying information so the radar operator can quickly understand it.
Who invented radar?
Radar can be traced back to a device called a Telemobiloskop (sometimes written French-style, Télémobiloscope ), invented in 1904 by German electrical engineer Christian Hülsmeyer (1881–1957). After hearing about a tragic collision between two ships, he figured out a way to use radio waves to help them see one another when the visibility was poor.
Why isn't radar used in submarines?
Photo by courtesy of US Department of Energy. One place radar isn't used is to help submarines as they navigate underwater. Electromagnetic waves don't travel readily through dense seawater (that's why it's dark in the deep ocean).
What is radar used for?
Radar was originally developed to detect enemy aircraft during World War II, but it is now widely used in everything from police speed-detector guns to weather forecasting. Let's take a closer look at how it works!
What is the inner structure of a radar signal?
The inner structure of the transmitted signal is usually called the Radar Waveform . The general term includes both the very simple pulse modulation (so-called “Keyed ON/OFF”- Modulation) and non-linearly internally modulated transmit pulses that are generated in a complicated manner. These signals may have a complex structure for a pulse compression radar.
How does a waveform generator work?
It permits generating predefined waveforms by driving the amplitudes and phase shifts of carried microwave signals. SAW devices , which were the mainstay of pulse compression in the 1980s, were also the prime mechanism for waveform generation when used as expanders. Since these waveform signals are used as a reference for the receiver channels too, there are high requirements for the time and frequency stability.
Why does the measured signal look like the signal on testpoint 3?
But the measured signal looks like the signal on testpoint 3 because the oscilloscope cannot show the phase shifts. Testpoint 1. The “in-phase” part of the waveform you can measure at this testpoint. Testpoint 2. The “quadrature” part of the waveform you can measure at this testpoint. Testpoint 3.
How many timesteps are there in a sine wave?
The whole waveform is divided into 2048 timesteps. For every timestep a 8-bit voltage value is stored in this programmable memory. This memory provides the sine wave (the “In-Phase” signal) representing the amplitude-information of the waveform. Cosine- PROM
What is the middle of a pulse?
The frequency-modulated waveform is upconverted to the IF now. The middle of the pulse is (instead of the former zero) the nominal intermediate frequency (IF). Testpoint 4
What is the finally waveform?
The finally waveform is constructed of e.g. 2048 discrete voltage steps here. Its values of amplitude and phase are stored in programmable memories (PROMs) . A change of the waveform is only possible by replacing the PROMs by the manufacturer.
How does a D/A converter work?
This D/A-Converter converts the 8-Bit data words into an analog voltage. All these timesteps got an different value of volta ge and these timesteps are stringed to a frequency together. The frequency can reach values from zero (DC) to 1 megahertz. The frequency changes during the pulse width from -ΔF/2 via zero to +ΔF/2 and gets its characteristic appearance. IF Sine Wave (CW)
How does radar extract Doppler frequency shift?
Radar can extract the Doppler frequency shift of the echo produced by a moving target by noting how much the frequency of the received signal differs from the frequency of the signal that was transmitted.
What is the average power of a radar?
The average power, rather than the peak power, is the measure of the capability of a radar system. Radars have average powers from a few milliwatts to as much as one or more megawatts, depending on the application. A typical pulse waveform transmitted by radar.
What is a moving target radar?
A form of pulse radar that uses the Doppler frequency shift to eliminate stationary clutter is called either a moving-target indication (MTI) radar or a pulse Doppler radar, depending on the particular parameters of the signal waveform.
How accurate is a radar?
The range accuracy of a simple pulse radar depends on the width of the pulse: the shorter the pulse, the better the accuracy. Short pulses, however, require wide bandwidths in the receiver and transmitter (since bandwidth is equal to the reciprocal of the pulse width). A radar with a pulse width of one microsecond can measure the range to an accuracy of a few tens of metres or better. Some special radars can measure to an accuracy of a few centimetres. The ultimate range accuracy of the best radars is limited by the known accuracy of the velocity at which electromagnetic waves travel.
How does Doppler frequency shift work?
The Doppler frequency shift can also be used to separate moving targets from stationary targets even when the echo signal from undesired clutter is much more powerful than the echo from the desired moving targets. A form of pulse radar that uses the Doppler frequency shift to eliminate stationary clutter is called either a moving-target indication (MTI) radar or a pulse Doppler radar, depending on the particular parameters of the signal waveform.
How long is a radar pulse?
Some radar pulse widths are even of nanosecond (10 −9 second) duration.
What is the angle of a radar antenna?
An aircraft-surveillance radar generally employs an antenna that radiates a “ fan ” beam, one that is narrow in azimuth (about 1 or 2 degrees) and broad in elevation (elevation beamwidths of from 20 to 40 degrees or more). A fan beam allows only the measurement of the azimuth angle.
Overview
Principles
A radar system has a transmitter that emits radio waves known as radar signals in predetermined directions. When these signals contact an object they are usually reflected or scattered in many directions, although some of them will be absorbed and penetrate into the target. Radar signals are reflected especially well by materials of considerable electrical conductivity—such as most metals, seawater, …
History
As early as 1886, German physicist Heinrich Hertz showed that radio waves could be reflected from solid objects. In 1895, Alexander Popov, a physics instructor at the Imperial Russian Navy school in Kronstadt, developed an apparatus using a coherer tube for detecting distant lightning strikes. The next year, he added a spark-gap transmitter. In 1897, while testing this equipment fo…
Applications
The information provided by radar includes the bearing and range (and therefore position) of the object from the radar scanner. It is thus used in many different fields where the need for such positioning is crucial. The first use of radar was for military purposes: to locate air, ground and sea targets. This evolved in the civilian field into applications for aircraft, ships, and automobiles.
In aviation, aircraft can be equipped with radar devices that warn of aircraft or other obstacles in …
Radar signal processing
One way to obtain a distance measurement is based on the time-of-flight: transmit a short pulse of radio signal (electromagnetic radiation) and measure the time it takes for the reflection to return. The distance is one-half the round trip time multiplied by the speed of the signal. The factor of one-half comes from the fact that the signal has to travel to the object and back again. Since r…
Engineering
A radar's components are:
• A transmitter that generates the radio signal with an oscillator such as a klystron or a magnetron and controls its duration by a modulator.
• A waveguide that links the transmitter and the antenna.
Regulations
Radar (also: RADAR) is defined by article 1.100 of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) as:
A radiodetermination system based on the comparison of reference signals with radio signals reflected, or retransmitted, from the position to be determined. Each radiodetermination system shall be classified by the radiocommunication service in which it operates permanently or temp…
Configurations
Radar come in a variety of configurations in the emitter, the receiver, the antenna, wavelength, scan strategies, etc.
• Bistatic radar
• Continuous-wave radar
• Doppler radar