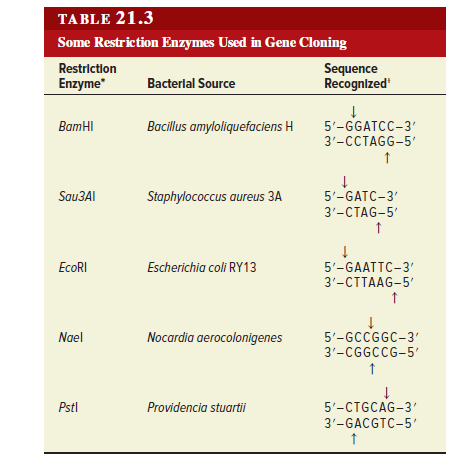
- Restriction enzymes are DNA-cutting enzymes. ...
- Many restriction enzymes make staggered cuts, producing ends with single-stranded DNA overhangs. ...
- DNA ligase is a DNA-joining enzyme. ...
- In DNA cloning, restriction enzymes and DNA ligase are used to insert genes and other pieces of DNA into plasmids.
Why is my restriction enzyme not cutting DNA?
Unexpected cleavage pattern—other
- The restriction enzyme tube or reaction buffer tube may be contaminated with a second enzyme. ...
- Another cause might be contamination of the DNA substrate. ...
- In rare cases, it may be possible that there are unexpected recognition sites in the substrate DNA. ...
- Finally, some restriction enzymes have degenerate recognition sites. ...
Why do we use restriction enzymes?
Restriction enzymes can be used to map DNA fragments or the entire genome, thus determining the specific order of the restriction enzyme sites in the genome. Restriction enzymes are also frequently used to verify the identity of a specific DNA fragment, based on the known restriction enzyme sites sequence that it contains. An extremely important use of restriction enzymes has been in the generation of recombinant DNA molecules.
What is the function of a restriction enzyme?
Restriction enzymes (endonucleases) are an important class of enzymes that protect bacteria from viral invasion. Restriction enzymes bind to non-methylated DNA of the virus at specific, often palindromic sequences, and cuts the DNA, destroying the virus. Bacteria methylate their own DNA to protect itself from endonucleases.
Why are restriction enzymes not cut own DNA?
But restriction enzyme can't cut their own genome or DNA; because bacterial genome has a gene which is known as DAM gene by which a spacefic type of enzyme is produced which is known as methylases which is responsible for the methylation on their own DNA as a result restriction enzyme can not cut their own DNA.....
How are restriction enzymes useful in gene cloning?
In DNA cloning, restriction enzymes and DNA ligase are used to insert genes and other pieces of DNA into plasmids.
What type of restriction enzyme is used in gene cloning?
Type II EnzymesType II Enzymes They produce discrete restriction fragments and distinct gel banding patterns, and they are the predominant class used in the laboratory for routine DNA analysis and gene cloning.
Which restriction enzyme is mostly used in cloning and why?
Type 2 restriction enzymes are used for cloning because they generally cut the DNA at a specific position within the recognition site. Further reading: Plasmid.
How are restriction enzymes used?
ProcedureSelect restriction enzymes to digest your plasmid. ... Determine an appropriate reaction buffer by reading the instructions for your enzyme. ... In a 1.5mL tube combine the following: ... Mix gently by pipetting.Incubate tube at appropriate temperature (usually 37 °C) for 1 hour.More items...
What is the function of restriction enzymes?
A restriction enzyme is a protein isolated from bacteria that cleaves DNA sequences at sequence-specific sites, producing DNA fragments with a known sequence at each end. The use of restriction enzymes is critical to certain laboratory methods, including recombinant DNA technology and genetic engineering.
How do restriction enzymes cut DNA sequences?
Restriction enzymes cut DNA bonds between 3′ OH of one nucleotide and 5′ phosphate of the next one at the specific restriction site. Adding methyl groups to certain bases at the recognition sites on the bacterial DNA blocks the restriction enzyme to bind and protects the bacterial DNA from being cut by themselves.
What are the different types of restriction enzymes?
Traditionally, four types of restriction enzymes are recognized, designated I, II, III, and IV, which differ primarily in structure, cleavage site, specificity, and cofactors.
What is an example of a restriction enzyme?
SmaI is an example of a restriction enzyme that cuts straight through the DNA strands, creating DNA fragments with a flat or blunt end. Other restriction enzymes, like EcoRI, cut through the DNA strands at nucleotides that are not exactly opposite each other.
What is the role of a restriction enzyme in molecular cloning quizlet?
What is the role of restriction enzymes in preparing a clone? What is the primary purpose of gene cloning? The purpose is often to yield large quantities of either an individual gene or its protein product after gene expression.
Why are sticky ends better than blunt ends?
Sticky ends are better than blunt ends because they facilitate ligation by DNA ligase by forming hydrogen bonds between complementary bases of the other strand. The efficiency of ligation is much higher for sticky ends.
How Does Restriction Enzyme Cloning Work?
Restriction enzymes digest the plasmid, you prepare an insert either from another plasmid or one you synthesized, and last, T4 DNA ligase ligates the plasmid and insert. Then, you transform the ligated plasmid into a bacterium (usually E. Coli ). The problem, of course, is that the devil is in the details.
What is restriction enzyme?
Restriction enzymes are also known as restriction endonucleases. The first of these enzymes was found by observing that a phage was able to be grown in one strain of bacteria, but not another ( 1 ). After investigation, it was discovered that the reason the phage growth was restricted (hence the name) was certain bacteria lines had the ability to chop up the phage DNA, preventing infection. Upon further study, an enzyme was found that was ultimately responsible for cutting the phage DNA not present in phage-susceptible bacteria lines.
How Does Ligation Work?
Once the source and destination DNA has been digested and cleaned it is ready to be ligated together. This is accomplished by using the enzyme T4 DNA ligase, which joins together double-stranded breaks of compatible DNA ends. The enzyme is capable of joining both blunt and sticky ends, though the efficiency of joining together blunt ends is much lower.
What enzymes are used in cloning?
Then, you guessed it, use restriction enzymes. Restriction enzyme cloning takes advantage of the site specificity of these enzymes. The enzymes only cut (or “digest”) at specific DNA sequences —usually plasmid DNA in cloning.
How to prevent a plasmid from re-ligating?
In order to prevent the plasmid from re-ligating, a phosphatase is used to remove phosphate groups from the ends of the plasmid DNA. DNA ligases require the presence of phosphate groups on the ends of DNA. Therefore, with those phosphate groups missing from the plasmid DNA, ligation will only be possible using the phosphates on the insert sequence.
What is the heart of cloning?
At the heart of cloning are restriction enzymes . Restriction enzymes are a common tool in any molecular biology lab. Need to know how large your plasmid is? Cut it with a restriction enzyme. Need to chop your genomic DNA into smaller pieces for a southern hybridization or to prepare a library? Use a restriction enzyme. Need to put a piece of DNA into a vector (i.e., cloning)? Then, you guessed it, use restriction enzymes.
What is required for DNA ligase?
DNA ligases require the presence of phosphate groups on the ends of DNA. Therefore, with those phosphate groups missing from the plasmid DNA, ligation will only be possible using the phosphates on the insert sequence.
What is a restriction enzyme?
A restriction enzyme is a DNA-cutting enzyme that recognizes specific sites in DNA. Many restriction enzymes make staggered cuts at or near their recognition sites, producing ends with a single-stranded overhang. If two DNA molecules have matching ends, they can be joined by the enzyme DNA ligase.
Where are restriction enzymes found?
Restriction enzymes are found in bacteria (and other prokaryotes). They recognize and bind to specific sequences of DNA, called restriction sites. Each restriction enzyme recognizes just one or a few restriction sites. When it finds its target sequence, a restriction enzyme will make a double-stranded cut in the DNA molecule.
What is the enzyme that seals the gap between two DNA molecules?
If two DNA molecules have matching ends, they can be joined by the enzyme DNA ligase. DNA ligase seals the gap between the molecules, forming a single piece of DNA. Restriction enzymes and DNA ligase are often used to insert genes and other pieces of DNA into plasmids during DNA cloning.
How is recombinant plasmid produced?
Right: recombinant plasmid produced when gene goes in backwards ("pointing" back towards the promoter that is already in the plasmid). Restriction digests and ligations like this one are performed using many copies of plasmid and gene DNA. In fact, billions of molecules of DNA are used in a single ligation!
Why are blunt-ended fragments harder to ligate together?
However, blunt-ended fragments are harder to ligate together (the ligation reaction is less efficient and more likely to fail) because there are no single-stranded overhangs to hold the DNA molecules in position.
How does DNA ligase work?
How does DNA ligase do this? Using ATP as an energy source, ligase catalyzes a reaction in which the phosphate group sticking off the 5’ end of one DNA strand is linked to the hydroxyl group sticking off the 3’ end of the other. This reaction produces an intact sugar-phosphate backbone.
Why do enzymes leave sticky ends?
Sticky ends are helpful in cloning because they hold two pieces of DNA together so they can be linked by DNA ligase. Not all restriction enzymes produce sticky ends.
What enzyme to use to cut vector?
Note: If you are using blunt ends or a single enzyme to cut the vector, you will need to use a phosphatase to prevent re-circularization of the vector. CIP (calf alkaline phosphatase) or SAP (shrimp alkaline phosphatase) are commonly used. Follow the manufacturer's instructions.
What DNA polymerase to use for blunt end ligation?
Note: If you are doing a blunt-end ligation, use T4 DNA Polymerase or Klenow DNA Polymerase I for 3' overhang removal and 5' overhang fill-in. Use mung bean nuclease for both 3' and 5' overhang removal. Follow the manufacturer's instructions.
Can you use more than one restriction enzyme?
Note : If you are using more than one restriction enzyme, depending on the buffers needed or your cloning strategy, you may need to digest with individual enzymes sequentially.