
Lac operon Notes
- Lac operon contains genes involved in metabolism.
- The genes are expressed only when lactose is present and glucose is absent.
- The operon is turned on and off in response to the glucose and lactose levels: catabolite activator protein and lac repressor.
- The lac repressor blocks the transcription of the operon. In the presence of lactose, it stops acting as a repressor.
How does the lac operon work?
Let's take a look at how this works. The lac operon contains three genes: lacZ, lacY, and lacA. These genes are transcribed as a single mRNA, under control of one promoter.
What happens when lactose is not present in the lac operon?
When lactose is not available, the lac repressor binds tightly to the operator, preventing transcription by RNA polymerase. However, when lactose is present, the lac repressor loses its ability to bind DNA. It floats off the operator, clearing the way for RNA polymerase to transcribe the operon. Upper panel: No lactose. When lactose is absent, the
What is the function of the lac repressor and the cap?
Two regulators turn the operon "on" and "off" in response to lactose and glucose levels: the lac repressor and catabolite activator protein (CAP). The lac repressor acts as a lactose sensor. It normally blocks transcription of the operon, but stops acting as a repressor when lactose is present.
What genes are involved in lactose utilization?
Regulation of genes for lactose utilization. lac repressor, catabolite activator protein, and cAMP. The lac operon of E. coli contains genes involved in lactose metabolism. It's expressed only when lactose is present and glucose is absent.
How the lac operon is turned on?
So the lac >operon is turned on when the allolactose molecules bind to repressor protein. Hence the correct answer is option 'D' i.e, repressor protein.
What turns the lac operon off?
The lac operon turns off when the repressor protein binds to the operator site, thereby inhibiting RNA polymerase to bind the to operator and express the genes which regulate the metabolism of lactose.
How does lactose turn on the lac operon?
A repressor protein binds the operator (control) region upstream of the operon preventing transcription. When lactose is present outside the cell, it crosses the cell membrane and acts as an inducer of the operon. It does so once lactose is broken down to create allolactose.
How does lac operon switched on and switched off Class 12?
The correct option is B lactose is present and it binds to the repressor. Switch on of lac operon: Lac operon switches on in the presence of an inducer like allolactose or lactose in the following way: Lactose binds to the repressor and prevents it from binding to the operator.
How is the lac operon turned off when lactose is not present?
Genes whose expression is not regulated are called constitutive genes. In the absence of lactose the lac repressor blocks the expression of the lac operon by binding to the DNA at a site, called the operator that is downstream of the promoter and upstream of the transcriptional initiation site.
What happens to the lac operon When lactose is present and glucose is absent?
If, however, glucose is absent and lactose becomes the only available carbon source, the picture changes. Lactose still prevents the repressor from binding to the operator region. But in addition, the lack of glucose leads to a rise in cyclic AMP (cAMP) concentration.
What happens when the lactase gene is turned on?
The LCT gene mutations change single protein building blocks (amino acids) in the lactase enzyme or result in an enzyme that is abnormally short. The mutations are believed to interfere with the function of the lactase enzyme, leading to undigested lactose in the small intestine and causing severe diarrhea.
How is the lac operon regulated quizlet?
The lac operon is regulated by specific protein which turn it on when it is an environment where the food source is lactose, it would begin to turn the lactose into digestible galactose and glucose. When it is not around lactose on the other hand, it is switched off by proteins that bind to DNA and block transcription.
How are inducible operon turned on?
Operons may be inducible or repressible It turns on only when the sugar lactose is present (and other, preferred sugars are absent). The inducer in this case is allolactose, a modified form of lactose.
Which regulates the switching on and off of lac operon?
An inducer regulates the switching on and off of lac operon. 2.
Is responsible for switching on and off the lac operon?
So, the correct answer is 'Regulator gene.
How does the repressor control switching on and off the expression of structural genes?
A molecule, that regulates gene expression by binding to repressor to prevent the transcription, is inducer. Allolactose serves as inducer in the lac operon and binds to the repressor and decreases the repressor's affinity for the operator site; thereby facilitating transcription.
Is lac operon on or off?
The lac operon contains an operator, promoter, and structural genes that are transcribed together and are under the control of the catabolite activator protein (CAP) or repressor. The lac operon is not activated and transcription remains off when the level of glucose is low or non-existent, but lactose is absent.
What happens to lac operon when glucose is present?
Glucose therefore stops activation of the lac operon (a cluster of coordinately regulated genes involved in lactose catabolism), which prevents lactose use and leads to preferential use of glucose.
How does glucose affect lac operon?
Concerning the mechanisms that lead to the inhibition of the lac operon expression, it widely has been believed that glucose inhibits lac expression by reducing the level of cAMP and therefore by depriving the lac operon of a transcriptional activator (CRP–cAMP) necessary for its expression.
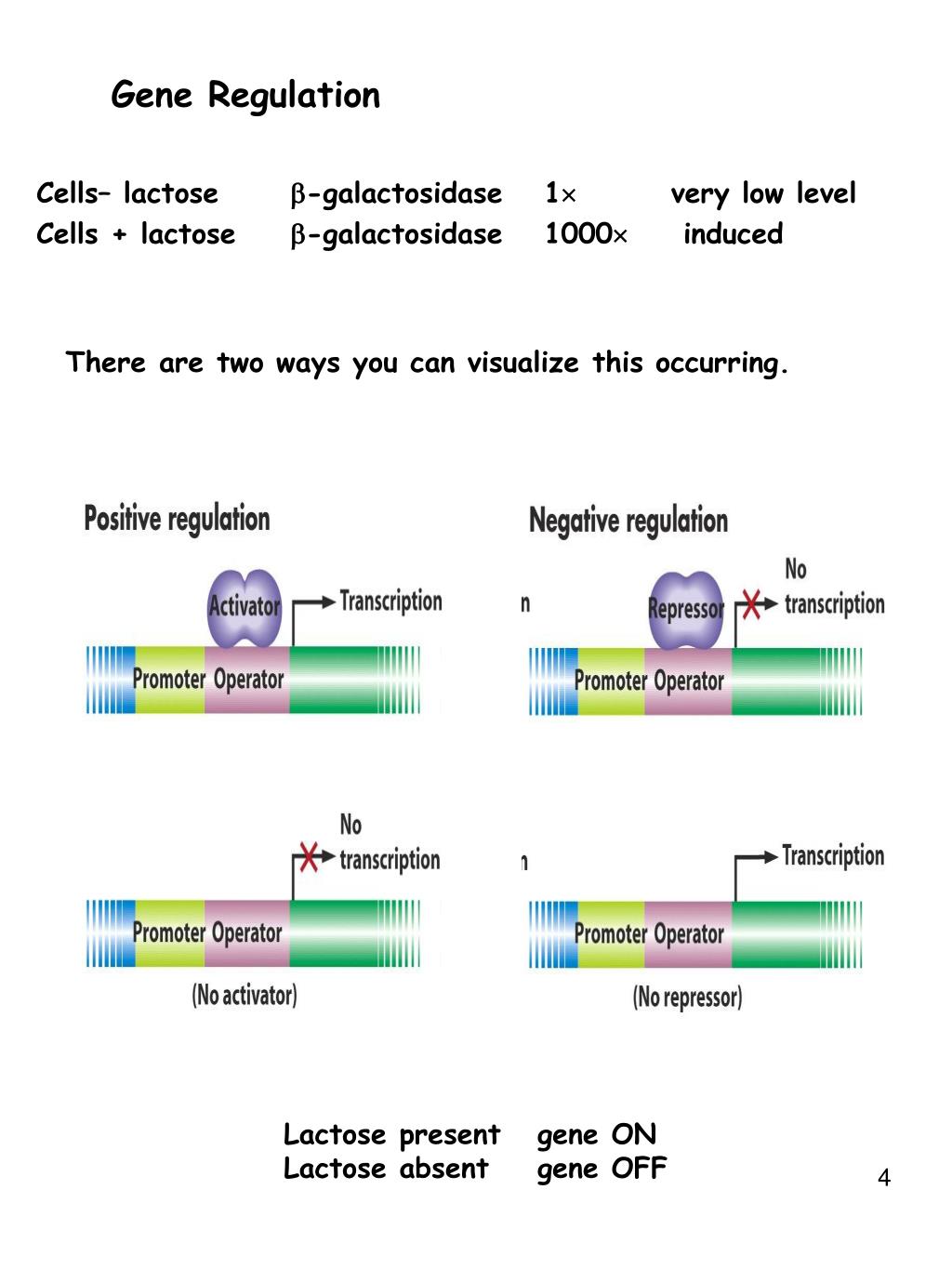
How is the lac operon affected by negative control?
Explanation: The lac operon exhibits both systems. It is a negative control system because expression is typically blocked by an active repressor (the lac repressor) that turns off transcription. The lac repressor binds to the operator region and negatively controls (prevents) transcription.
What are the genes in the lac operon?
The lac operon has three genes that are co regulated, lac Z, lac Y and lac A, they lie adjacent to each other on the operon in that order. Upstream of the lac Z gene is a regulatory promoter/operator region. The promoter region is involved in gene expression, it is where the RNA polymerase will bind to start the process of gene expression.
How does the Lac operon work?
The lac operon also shows you how cellular logic works best—it’s EASY to build binary switches (the two repressor here are both on/off, as is the CRP/CAP/lac activator machine). Binary is easy. Anything else is hard. So to handle two inputs (lactose, glucose) the lac repressor employs TWO different DNA binding proteins, one handling each branch of the logic. Building a protein with 3 or more distinct states can be pretty tough (and therefore hard/unlikely to discover by evolution); ‘stacking’ many binary machines is relatively trivial.
What is the significance of the Lac operon?
The significance of Lac operon is that it is under tight regulation and the genes are expressed only when lactose is available to E. coli. The regulation is under the control of regulatory DNA, which is not a part of the operon and has its own promoter, which encodes regulatory protein called repressor protein. This repressor protein binds onto a region in the Lac operon called the operator sequence. Operator sequence includes region of promoter and some region of LacZ sequence. When regulatory protein binds onto the operator sequence, RNA polymerase cannot bind to the promoter sequence and there would be no transcription of the structural genes.
What is an operon?
Operon is a group of several structural genes under the control of a single promoter. Promoter is the DNA sequence onto which RNA pol can bind and transcribe information on the DNA into RNA. When operons are transcribed it results in the formation of a polycistronic mRNA, i.e.m mRNA with several start codons. polycistronic mRNA results in translation of several structural proteins. Operons are found in prokaryotes. Originally discovered by Jacob and Monod, two French scientists, discovery of Lactose operon and its regulation earned them Nobel Prize.
What happens when lactose is present in the RNA polymerase?
At its most simple level what happens is that if lactose is present it will bind LacI, which will change its conformation (shape), making it unable to bind the operator . Once the operator is clear of LacI, RNA polymerase can bind the promoter and start transcription.
What is the primary energy source for the lac operon?
Lactose is the energy source for lac operon..but the primary energy source is the glucose . as long as there is glucose in the medium the bacteria uses it to produce energy. In the absence of glucose bacteria uses lactose.
Which molecule binds to the repressor molecule?
The lactose molecule binds to the repressor molecule which blocks the repressor to bind to the operator. As a result the RNA polymerase transcribes the structural genes.
What happens when a gene is turned off?
When a gene is turned off, it no longer provides the directions for making proteins. This means that the proteins needed to fulfill a particular job -- say, tolerate lactase -- aren't produced. Think about following driving directions on a GPS device in your car.
What is the process that turns genes off and on?
It all comes down to a process called gene regulation . This is how our genes are turned off and on, for minor things like hair color and vital functions like protection from cancer. Within our bodies, we house trillions of cells, all busily going about doing their jobs while we enjoy our days.
How does DNA methylation work?
The answer is through DNA methylation. During methylation, methyl groups -- a gang of one carbon and three hydrogens -- move in and plop down on our genes. The methyl group tells that gene how to behave [source: Weinhold ].
What is the purpose of healthy genes in gene therapy?
From a very basic level, in the new arena of gene therapy, healthy genes are added to areas where other genes have gone missing, have a mutation or are just "off.". The hope is that the healthy genes will jump-start what the silent or missing genes are supposed to be doing.
How do genes get red light?
The first way our genes get the big red or green light is through gene transcription. During transcription, the first step in reading the gene's directions and getting proteins made, the nucleus of the cell needs to figure out how to get its knowledge transferred.
How does regulation help cells?
Regulation can help our cells behave properly and aid us in adapting to our environment [source: National Center for Biotechnology Information ]. Now that you have a brief overview on genetic regulation from afar, find out what's happening inside a cell to turn genes off and on. Advertisement.
What is the study of how different environmental and lifestyle factors can alter how our genes behave?
Recent discoveries have unveiled another means of gene regulation. This new area of science is called epigenetics , the study of how different environmental and lifestyle factors can alter how our genes behave, without actually changing our genetic makeup [source: Science ].
What is the lac operon?
The lac operon of E. coli contains genes involved in lactose metabolism. It's expressed only when lactose is present and glucose is absent. Two regulators turn the operon "on" and "off" in response to lactose and glucose levels: the lac repressor and catabolite activator protein (CAP).
How many genes are in the lac operon?
The lac operon contains three genes: lacZ, lacY, and lacA. These genes are transcribed as a single mRNA, under control of one promoter.
What are the two proteins that regulate the glucose and lactose levels?
Two regulatory proteins are involved: One, the lac repressor, acts as a lactose sensor. The other, catabolite activator protein (CAP), acts as a glucose sensor. These proteins bind to the DNA of the lac operon and regulate its transcription based on lactose and glucose levels. Let's take a look at how this works.
What is the function of CAP?
Catabolite activator protein ( CAP) acts as a glucose sensor. It activates transcription of the operon, but only when glucose levels are low. CAP senses glucose indirectly, through the "hunger signal" molecule cAMP.
What genes regulate lactose utilization?
Regulation of genes for lactose utilization. lac repressor, catabolite activator protein, and cAMP.
Why is the lac repressor released from the operator?
The lac repressor is released from the operator because the inducer (allolactose) is present. cAMP levels are high because glucose is absent, so CAP is active and bound to the DNA. CAP helps RNA polymerase bind to the promoter, permitting high levels of transcription. operon occurs.
Which protein binds to the CAP binding site and promotes RNA polymerase binding to the promoter?
gene. The activator protein CAP, when bound to a molecule called cAMP (discussed later), binds to the CAP binding site and promotes RNA polymerase binding to the promoter. The. lac. repressor protein binds to the operator and blocks RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter and transcribing the operon.
