
Some of the common strong acids and bases are listed here. The relative strengths of acids may be determined by measuring their equilibrium constants in aqueous solutions. In solutions of the same concentration, stronger acids ionize to a greater extent, and so yield higher concentrations of hydronium ions than do weaker acids.
What is the strongest acid and base?
You should commit the strong acids to memory:
- HCl: hydrochloric acid
- HNO 3: nitric acid
- H 2 SO 4: sulfuric acid
- HBr: hydrobromic acid
- HI: hydroiodic acid
- HClO 4: perchloric acid
What are all the strong acids and bases?
What are Strong Acids and their List?
- Hydrochloric acid (denoted by the chemical formula HCl)
- Hydrobromic acid (denoted by the chemical formula HBr)
- Hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid (denoted by the chemical formula HI)
- Sulfuric acid (denoted by the chemical formula H2SO4)
- Nitric acid (denoted by the chemical formula HNO3)
- Chloric acid (denoted by the chemical formula HClO3)
What is stronger acid or base?
They both conduct electricity depending on the dissociation of ions. Acids have a pH lesser than 7.0 and the lower it is, the stronger the acid becomes. Bases have a pH between 7 and 14. Higher the pH value, stronger will be the base. A pH level of 7 is a neutral substance which is water.
How to distinguish strong and weak acids?
Strength of Acids and Bases
- Strong Acids. Strong acids completely dissociate in water, forming H + and an anion. ...
- Weak Acids. A weak acid only partially dissociates in water to give H + and the anion. ...
- Strong Bases. Strong bases dissociate 100 percent into the cation and OH - (hydroxide ion). ...
- Weak Bases. Examples of weak bases include ammonia, NH 3, and diethylamine, (CH 3 CH 2) 2 NH. ...
What are the factors affecting the relative strength of acids and bases?
Even though acid strength is usually due to all three of these factors, bond polarity, bond strength, and conjugate base stability, when we look at examples, we're only gonna consider one or two factors that are the main contributors to acid strength.
What determines the strength of bases?
The greater the ability of a species to accept a H+ from another species, the greater its base strength. Organic chemists customarily compare the strength of bases using the strengths of their conjugate acids, measured as pKa.
How is acid strength determined?
The bond strength of an acid generally depends on the size of the 'A' atom: the smaller the 'A' atom, the stronger the H-A bond. When going down a row in the Periodic Table (see figure below), the atoms get larger so the strength of the bonds get weaker, which means the acids get stronger.
How is the strength and weakness of acids and bases determined?
If the acid or base conducts electricity strongly, it is a strong acid or base. If the acid or base conducts electricity weakly, it is a weak acid or base.
How to determine the relative strength of an acid?
The relative strengths of acids may be determined by measuring their equilibrium constants in aqueous solutions. In solutions of the same concentration, stronger acids ionize to a greater extent, and so yield higher concentrations of hydronium ions than do weaker acids.
What is the relationship between a strong base and a hydroxide ion?
A strong base, such as one of those lying below hydroxide ion, accepts protons from water to yield 100% of the conjugate acid and hydroxide ion. Those bases lying between water and hydroxide ion accept protons from water, but a mixture of the hydroxide ion and the base results.
What is the ionization of weak acids?
The Ionization of Weak Acids and Weak Bases. Many acids and bases are weak; that is, they do not ionize fully in aqueous solution. A solution of a weak acid in water is a mixture of the nonionized acid, hydronium ion, and the conjugate base of the acid, with the nonionized acid present in the greatest concentration.
What is a weak acid?
A solution of a weak acid in water is a mixture of the nonionized acid, hydronium ion, and the conjugate base of the acid, with the nonionized acid present in the greatest concentration. Thus, a weak acid increases the hydronium ion concentration in an aqueous solution (but not as much as the same amount of a strong acid).
What is the solution of a weak base in water?
At equilibrium, a solution of a weak base in water is a mixture of the nonionized base, the conjugate acid of the weak base, and hydroxide ion with the nonionized base present in the greatest concentration.
What is the reaction of strong bases to water?
Strong bases react with water to quantitatively form hydroxide ions. Weak bases give only small amounts of hydroxide ion. The strengths of the binary acids increase from left to right across a period of the periodic table (CH 4 < NH 3 < H 2 O < HF), and they increase down a group (HF < HCl < HBr < HI).
Which acid is the strongest in water?
Strong acids, such as HCl, HBr, and HI, all exhibit the same strength in water. The water molecule is such a strong base compared to the conjugate bases Cl −, Br −, and I − that ionization of these strong acids is essentially complete in aqueous solutions.
What is the relative strength of an acid?
The relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or base is termed strong; if relatively little ionization occurs, the acid or base is weak. As will be evident throughout the remainder of this chapter, ...
How to measure acid strength?
To measure the differences in acid strength for “strong” acids, the acids must be dissolved in a solvent that is less basic than water. In such solvents, the acids will be “weak,” and so any differences in the extent of their ionization can be determined.
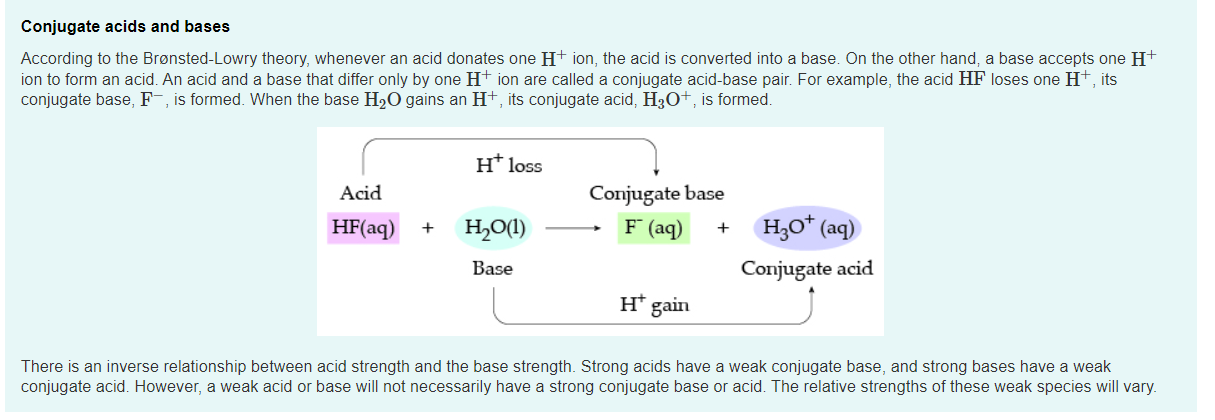
What is the relationship between the strengths of a conjugate acid and a base?
The relative strengths of acids and bases are reflected in the magnitudes of their ionization constants; the stronger the acid or base, the larger its ionization constant. A reciprocal relation exists between the strengths of a conjugate acid-base pair: the stronger the acid, the weaker its conjugate base.
What is the name of the weak base that partially ionizes?
Species listed between water and its conjugate base, hydroxide ion, are weak bases that partially ionize. Species listed below hydroxide ion are strong bases that completely ionize in water to yield hydroxide ions (i.e., they are leveled to hydroxide).
What is a strong acid?
An acid is classified as “strong” when it undergoes complete ionization, in which case the concentration of HA is zero and the acid ionization constant is immeasurably large ( Ka ≈ ∞). Acids that are partially ionized are called “weak,” and their acid ionization constants may be experimentally measured.
What is the chapter on chemical equilibria?
The chapter on chemical equilibria introduced several types of equilibrium calculations and the various mathematical strategies that are helpful in performing them. These strategies are generally useful for equilibrium systems regardless of chemical reaction class, and so they may be effectively applied to acid-base equilibrium problems. This section presents several example exercises involving equilibrium calculations for acid-base systems.
Is water a solvent or a reactant?
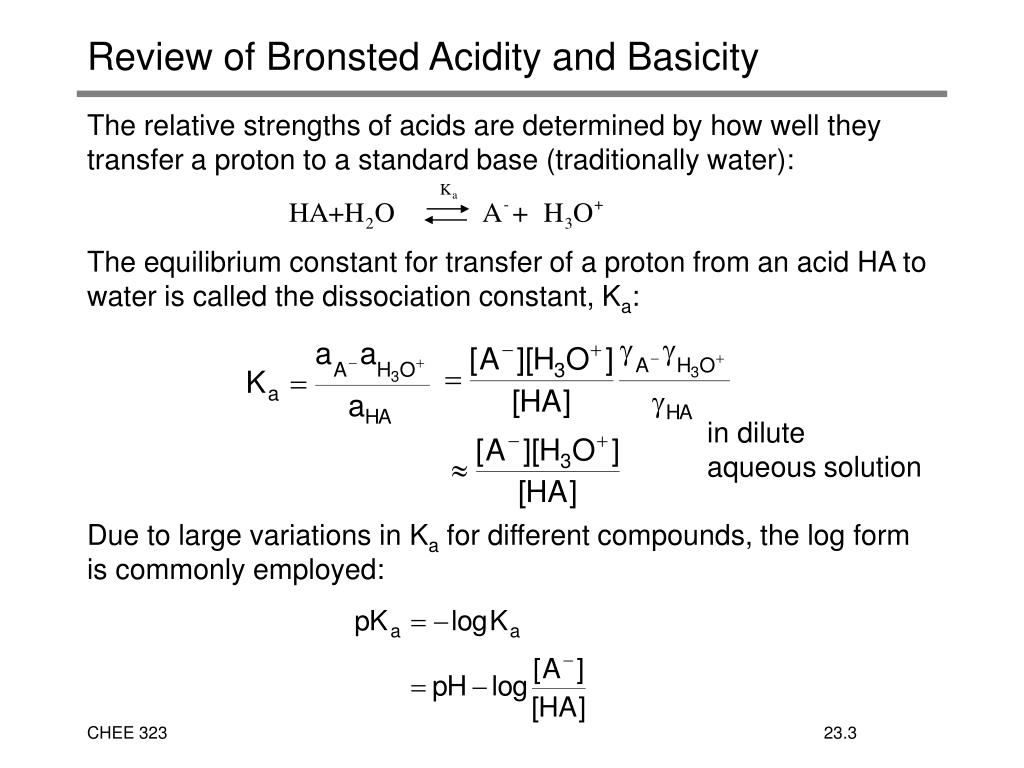
Although water is a reactant in the reaction, it is the solvent as well, so we do not include [H 2 O] in the equation. The larger the Ka of an acid, the larger the concentration of and A − relative to the concentration of the nonionized acid, HA, in an equilibrium mixture, and the stronger the acid. An acid is classified as “strong” ...
Relative Strengths of Acids and Bases
We can rank the strengths of acids by the extent to which they ionize in aqueous solution. The reaction of an acid with water is given by the general expression:
Example
Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.125- M solution of nitrous acid (a weak acid), with a pH of 2.09.
Example
Use the Kb for the nitrite ion, NO2−, NO 2 −, to calculate the Ka for its conjugate acid.
What is the relative strength of an acid?
The relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or base is termed strong; if relatively little ionization occurs, the acid or base is weak. As will be evident throughout the remainder of this chapter, ...
How to measure acid strength?
To measure the differences in acid strength for “strong” acids, the acids must be dissolved in a solvent that is less basic than water. In such solvents, the acids will be “weak,” and so any differences in the extent of their ionization can be determined.
What is the relationship between the strengths of a conjugate acid and a base?
The relative strengths of acids and bases are reflected in the magnitudes of their ionization constants; the stronger the acid or base, the larger its ionization constant. A reciprocal relation exists between the strengths of a conjugate acid-base pair: the stronger the acid, the weaker its conjugate base.
What is the name of the weak base that partially ionizes?
Species listed between water and its conjugate base, hydroxide ion, are weak bases that partially ionize. Species listed below hydroxide ion are strong bases that completely ionize in water to yield hydroxide ions (i.e., they are leveled to hydroxide).
What is the nitrous acid concentration?
The nitrous acid concentration provided is a formal concentration, one that does not account for any chemical equilibria that may be established in solution. Such concentrations are treated as “initial” values for equilibrium calculations using the ICE table approach. Notice the initial value of hydronium ion is listed as approximately zero because a small concentration of H 3 O + is present (1 × 10 −7M) due to the autoprotolysis of water. In many cases, such as all the ones presented in this chapter, this concentration is much less than that generated by ionization of the acid (or base) in question and may be neglected.
What is the equilibrium constant of an acid?
The equilibrium constant for an acid is called the acid-ionization constant, Ka. For the reaction of an acid HA: the acid ionization constant is written: where the concentrations are those at equilibrium. Although water is a reactant in the reaction, it is the solvent as well, so we do not include [H 2 O] in the equation.
What is a strong acid?
An acid is classified as “strong” when it undergoes complete ionization, in which case the concentration of HA is zero and the acid ionization constant is immeasurably large ( Ka ≈ ∞). Acids that are partially ionized are called “weak,” and their acid ionization constants may be experimentally measured.
Reactions
- Acetic acid, CH3CO2H, is a weak acid. When we add acetic acid to water, it ionizes to a small extent according to the equation: Water also exerts a leveling effect on the strengths of strong bases. For example, the oxide ion, O2, and the amide ion, , are such strong bases that they react completely with water:
Mechanism
- giving an equilibrium mixture with most of the acid present in the nonionized (molecular) form. This equilibrium, like other equilibria, is dynamic; acetic acid molecules donate hydrogen ions to water molecules and form hydronium ions and acetate ions at the same rate that hydronium ions donate hydrogen ions to acetate ions to reform acetic acid molecules and water molecules. We …
Example
- Table 2 gives the ionization constants for several weak acids; additional ionization constants can be found in Appendix H. At equilibrium, a solution of a weak base in water is a mixture of the nonionized base, the conjugate acid of the weak base, and hydroxide ion with the nonionized base present in the greatest concentration. Thus, a weak base increases the hydroxide ion concentrat…
Chemistry
- giving an equilibrium mixture with most of the base present as the nonionized amine. This equilibrium is analogous to that described for weak acids.
Properties
- Strong acids, such as HCl, HBr, and HI, all exhibit the same strength in water. The water molecule is such a strong base compared to the conjugate bases Cl, Br, and I that ionization of these strong acids is essentially complete in aqueous solutions. In solvents less basic than water, we find HCl, HBr, and HI differ markedly in their tendency to gi...
Characteristics
- If the central atom, E, has a low electronegativity, its attraction for electrons is low. Little tendency exists for the central atom to form a strong covalent bond with the oxygen atom, and bond a between the element and oxygen is more readily broken than bond b between oxygen and hydrogen. Hence bond a is ionic, hydroxide ions are released to the solution, and the material be…