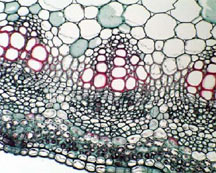
Does celery have xylem and phloem?
Each tube you see in the celery stem is in fact a collection of very thin tubes, called Xylem and Phloem! Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots up, while Phloem transports sugars made in the leaves during photosynthesis to the rest of the plant.
How are xylem and phloem arranged in plants?
In the shoots of higher plants, xylem and phloem tissues are arranged into vascular bundles. The particular distribution of these tissues within the vascular bundle is distinctive, but can vary among plants [10].
Are the strings of celery xylem or phloem?
Besides xylem (water-conducting) and phloem (food-conducting) tissues, which together are called vascular bundles, celery contains collenchyma tissue, which provides support for the plant.
What plant structure is celery?
Celery has a stem. A single celery plant has lots of stems actually. Most plants and trees have stems which are sometimes referred to as stalks.” The Cook's Thesaurus lists celery as a 'Stalk Vegetable'.
Which type of plant has its xylem and phloem arranged in a circle?
The herbaceous stem is composed of vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) arranged in a circle around a central core of spongy tissue made up of parenchyma cells, called the pith.
What is the arrangement of xylem and phloem in roots?
In monocot roots, the xylem and phloem are arranged in a circular pattern surrounding the central pith. In dicot roots, their xylem is located centrally and is surrounded by bundles of phloem.
Where is the phloem in celery?
Xylem and phloem arrange themselves in vas- cular bundles. Cutting a cross-section through stem usually shows the xylem on the inner side of the vascular bundle in a stem, while the phloem is found on the outer side of the vascular bundle.
Why do celery have strings?
Celery is made up of collenchyma cells, which contain vast amounts of water. The thick walls that store it are the cause of that characteristic crunch. However, the collenchyma tissue is also what we recognize as celery strings.
What kind of cells are the strings inside the celery?
The “strings” of a celery stalk are an example of collenchyma cells. Sclerenchyma cells also provide support to the plant, but unlike collenchyma cells, many of them are dead at maturity. There are two types of sclerenchyma cells: fibers and sclereids.
Where is the vascular tissue in celery?
In celery, vascular tissue is found in many small, circular bundles. In broccoli, vascular tissue is found in one large ring near the outer edge of the stem. 3. Xylem, since it carries water from the roots to the rest of the plant (see Introduction).
What are the veins in celery called?
Within the stalks of celery there are tiny vertical tubes. This vascular tissue in plants is called xylem. These tiny tubes draw up water using capillary action.
How does the arrangement of xylem and phloem in stems differ from that in roots?
In dicot stems, the xylem is located inside the cambium ring while the phloem is outside the cambium ring. In monocot roots, the xylem and phloem are arranged in a circular pattern surrounding the central pith. In dicot roots, their xylem is located centrally and is surrounded by bundles of phloem.
Where are xylem and phloem located in plants?
Where are the xylem and phloem located? The xylem is located towards the adaxial surface of the leaf, whereas, phloem is located towards the abaxial surface of the leaf.
How does the placement of xylem and phloem change between the root stem and leaf?
- In the roots, xylem and phloem are in the centre to withstand stretching forces. - In the stems, they are arranged in bundles near the edge to resist compression and bending forces. - They are grouped together into veins and vascular bundles as they pass through leaves.
How do you identify xylem and phloem?
1:202:28Xylem and Phloem - Transport in Plants | Biology | FuseSchoolYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe xylem vessels are made of elongated dead cells that are impermeable to water and have wallsMoreThe xylem vessels are made of elongated dead cells that are impermeable to water and have walls containing lignin a woody material.
Where do phloem and xylem grow?
Phloem and xylem grow around the inner layer of pith with phloem cells on the outside of the xylem. Vascular bundles from stems meet at the base of the stem to merge with the root stele. Last edited: 26 August 2020.
What is the function of the xylem?
The xylem is responsible for keeping a plant hydrated. Xylem sap travels upwards and has to overcome serious gravitational forces to deliver water to a plant’s upper extremities, especially in tall trees. Two different types of cells are known to form the xylem in different plant groups: tracheids and vessel elements.
What is the vascular bundle of a plant?
One xylem and one phloem are known as a ‘vascular bundle’ and most plants have multiple vascular bundles running the length of their leaves, stems, and roots. Xylem tissue is used mostly for transporting water from roots to stems and leaves but also transports other dissolved compounds. Phloem is responsible for transporting food produced ...
What is SAP in plants?
What is commonly referred to as ‘sap’ is indeed the substances that are being transported around a plant by its xylem and phloem.
How does photosynthesis occur in leaves?
Photosynthesis in leaves requires a lot of water from the xylem and produces a lot of sugar for the phloem. The xylem and phloem enter a plant’s leaves via their petiole – a short stalk that connects a leaf to a branch. With the exception of lycophytes, veins divide multiple times in a leaf which creates a good spread of veins ...
Where are vascular bundles arranged in a eudicot?
In eudicots, vascular bundles are arranged in a ring within the stem. Each vascular bundle is orientated with the xylem on the interior and the phloem on the outside of the xylem. In monocots, the vascular bundles are scattered throughout the stem rather than being arranged in a circle.
How does the sap in a phloem work?
Sap within the phloem simply travels by diffusion between cells and works its way from leaves down to the roots with help from gravity. The phloem is made from cells called ‘sieve-tube members’ and ‘companion cells’.
What is the Xylem?
Mature xylem consists of elongated dead cells, arranged end to end to form continuous vessels (tubes). Mature xylem vessels: contain no cytoplasm. are impermeable to water. have tough walls containing a woody material called lignin.
What is the phloem vessel?
Phloem consists of living cells arranged end to end. Unlike xylem, phloem vessels contain cytoplasm, and this goes through holes from one cell to the next.
Which leaves move water from the roots to the leaves?
Xylem moves water from roots to the leaves, and phloem moves food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. During transpiration water evaporates from the leaves and draws water from the roots.
What are the two parts of a plant that transport water, nutrients, and minerals?
Xylem and phloem. Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant, while phloem transports sucrose and amino acids between the leaves and other parts of the plant. Xylem and phloem in the centre of the plant root.
Which tissue transports water from the roots upwards to the leaves of the plant?
The vascular tissue system in plants is the transport system made up of two primary specialized tissues: xylem, which carries water from the roots upwards to the leaves of the plant as it is needed for photosynthesis, and phloem, which carries glucose/ manufactured food from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
What are the molecules that plants use to make CO2?
This means that plants are able to harness the energy of the sun to turn CO2 from the air into the carbon-based molecules of life — carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Which is larger, Xylem or Phloem?
Xylem fibres are smaller. Phloem fibres are larger. Found In. They are present in roots, stems and leaves. They are present in stems and leaves, which later transports and grow in roots, fruits and seeds. Movements. These tissues move in a Unidirectional. (only in one direction – upward direction)
Where is the xylem located?
The xylem is located towards the adaxial surface of the leaf, whereas, phloem is located towards the abaxial surface of the leaf.
Why is the phloem important?
Phloem is also important as the xylem tissues for the vascular system of plants. The main activity of this tissue is to transport nutrients and food from leaves to other growing parts of plants. The term phloem is derived from the Greek word – φλοιός (phloios), meaning bark.
What is a phloem tissue?
Xylem tissues are the tubular-shaped structure, with the absence of cross walls. This tissue resembles the shape of a star. Phloem tissues are tubular-shaped, elongated, structures with the presence of walls with thin sieve tubes. Location. It is located in the centre of the vascular bundle.
What is a dead xylem cell?
Xylem cells are made up of a long chain of dead cells known as vessel elements. The vessel elements have no organelles. The components of xylem tissues are highly lignified and scalarified. Hence, xylem cells are considered dead.
What are the elements of the tracheid?
It consists of tracheids, vessel elements, xylem parenchyma, xylem sclerenchyma and xylem fibres. It consists of four elements: companion cells, sieve tubes, bast fibres, phloem fibres, intermediary cells and the phloem parenchyma. Transports soluble mineral nutrients and water molecules from the roots to the aerial parts of the plant.
What are the features of vascular plants?
Essentially, a vascular plant has specialized features that help it to absorb water and minerals from the soil. These include special tissues such as xylem and phloem.
