Which test is used for detection of bacteria?
Techniques like straining of isolated bacteria, motility testing, Biochemical testing, Serological tests, Phage typing, identification disc testing, Semiautomated and Automated identification system & Molecular techniques are used for bacterial identification.
How Can infections be diagnosed?
AdvertisementBlood tests. A technician obtains a sample of blood by inserting a needle into a vein, usually in the arm.Urine tests. This painless test requires you to urinate into a container. ... Throat swabs. ... Stool sample. ... Spinal tap (lumbar puncture).
How are viruses and bacteria diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Bacterial and Viral Infections But your doctor may be able to determine the cause by listening to your medical history and doing a physical exam. If necessary, they also can order a blood or urine test to help confirm a diagnosis, or a "culture test" of tissue to identify bacteria or viruses.
How do doctors know if you have bacterial infection?
Tests that are frequently performed to help us with the diagnosis of a bacterial infection include a complete blood count and cultures of fluid that we are concerned about. This may include a blood culture, urine culture, or spinal culture (which requires a spinal tap).
Can a blood test detect infection?
Blood cultures are procedures done to detect an infection in the blood and identify the cause. Infections of the bloodstream are most commonly caused by bacteria (bacteremia) but can also be caused by yeasts or other fungi (fungemia) or by a virus (viremia).
What are the types of diagnosis?
In reality, a diagnostic procedure may involve components of multiple methods.Differential diagnosis. Main article: Differential diagnosis. ... Pattern recognition. ... Diagnostic criteria. ... Clinical decision support system. ... Other diagnostic procedure methods.
Where can you find bacteria?
Bacteria are found in every habitat on Earth: soil, rock, oceans and even arctic snow. Some live in or on other organisms including plants and animals including humans. There are approximately 10 times as many bacterial cells as human cells in the human body.
How do you collect bacteria samples?
Sampling ProtocolsUse sterile swabs. ... Remove the outer packaging of the sterile swab.It is often recommended to follow the instructions on the outer packaging to moisten the swab before sampling to help improve collection efficiency. ... Swab the area of concern. ... Return the swab into the tube.
What causes bacterial infection?
Bacteria must enter your body for them to cause an infection. So you can get a bacterial infection through an opening in your skin, such as a cut, a bug bite, or a surgical wound. Bacteria can also enter your body through your airway and cause infections like bacterial pneumonia.
Can blood test detect bacterial infection?
A bacteria culture is a test to identify whether you have a bacterial infection. It can be performed on a sample of blood, stool, urine, skin, mucus or spinal fluid. Using this type of test, a healthcare provider can identify what caused an infection and determine the most effective treatment.
What are 5 diseases caused by bacteria?
Other serious bacterial diseases include cholera, diphtheria, bacterial meningitis, tetanus, Lyme disease, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
Are bacterial infections serious?
Serious bacterial infections are a major cause of death in hospitals and healthcare settings. Bacteria can enter the body through wounds and surgery sites, ventilators and catheters, leading to pneumonia, urinary tract, abdominal and bloodstream infections.
What test shows infection in the body?
A blood culture test helps your doctor figure out if you have a kind of infection that is in your bloodstream and can affect your entire body. Doctors call this a systemic infection. The test checks a sample of your blood for bacteria or yeast that might be causing the infection.
What are the 5 signs of infection?
Know the Signs and Symptoms of InfectionFever (this is sometimes the only sign of an infection).Chills and sweats.Change in cough or a new cough.Sore throat or new mouth sore.Shortness of breath.Nasal congestion.Stiff neck.Burning or pain with urination.More items...
What is the nursing diagnosis for infection?
Risk for Infection Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis and Interventions. Risk for infection is a NANDA nursing diagnosis that involves the alteration or disturbance in the body's inflammatory response, which allows microorganisms to invade the body and cause infection. It is a common problem in people with low immune system.
What are the 4 types of infections?
The four different categories of infectious agents are bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. When studying these agents, researchers isolate them using certain characteristics: Size of the infectious agent.
How to diagnose BV?
Diagnosing BV involves four steps: A review of your medical history. A pelvic exam. Performing a pH test to check the level of acidity in the vagina. Taking a sample of vaginal secretions to check for the presence of bacteria by either looking for "clue cells" or using a gram stain technique.
What grade is considered a definitive diagnosis for bacterial vaginosis?
Grades seven through 10 can be considered a definitive diagnosis for bacterial vaginosis.
What is a grade 2 bacterial vaginosis?
Grade 2: Lactobacilli mixed with Gardnerella and/or Mobiluncus bacteria. Grade 3: Few lactobacilli and mostly Gardnerella and/or Mobiluncus. Grade 3 can be considered a definitive diagnosis for bacterial vaginosis.
Why do healthcare providers investigate other causes of bacterial vaginosis?
Because the symptoms of bacterial vaginosis are similar to other infections, healthcare providers may investigate other causes if the test results are borderline or the clinical symptoms raise concerns about another condition.
What are the clinical criteria for bacterial vaginosis?
Clinical Criteria. A doctor can make a definitive diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis with one of two evaluative measures: the Amsel criteria or gram stain grading. The Amsel criteria take into account the physical findings alongside the result of the diagnostic tests.
What tests are done to check for vaginal acidity?
The evaluation would also include a pelvic exam, an analysis of vaginal secretions, and a pH test to check for vaginal acidity. In addition to lab tests, there are self-testing kits that allow you to check your vaginal pH and other markers of inflammation at home. 2. Illustration by Verywell.
What does a BV test look for?
The test is performed in two parts: The first test looks for evidence of an elevated vaginal pH.
Why do I need a bacteria culture test?
Your health care provider may order a bacteria culture test if you have symptoms of a bacterial infection. The symptoms vary depending on the type of infection.
How long does it take for a bacteria test to grow?
If there is an infection, the infected cells will multiply. Most disease-causing bacteria will grow enough to be seen within one to two days, but it can take some organisms five days or longer.
Will I need to do anything to prepare for the test?
There are many different types of bacteria culture tests. Ask your health care provider if you need to do anything to prepare for your test.
What is stool culture?
Stool Culture. Another name for stool is feces. Used to detect infections caused by bacteria or parasites in the digestive system. These include food poisoning and other digestive illnesses. Test procedure: You will provide a sample of your feces in a clean container as instructed by your health care provider.
What is a swab test?
These include bacterial pneumonia and bronchitis. Test procedure: You may be asked to cough up sputum into a special cup as instructed by your provider; or a special swab may be used to take a sample from your nose.
What is a bacteria culture?
Bacteria are a large group of one-celled organisms. They can live on different places in the body. Some types of bacteria are harmless or even beneficial. Others can cause infections and disease. A bacteria culture test can help find harmful bacteria in your body. During a bacteria culture test, a sample will be taken from your blood, urine, skin, ...
What is a urine test used for?
Used to diagnose a urinary tract infection and identify the bacteria causing the infection. Test procedure: You will provide a sterile sample of urine in a cup, as instructed by your health care provider.
Skin Culture
A skin culture is a test that is performed to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection. It is performed by obtaining a tissue specimen from the affected area. This can be done by scraping the outer layer of the skin with a sterile instrument.
Skin Biopsy
A skin biopsy is performed by removing part of the lesion by using a punch or a razor blade. Once the specimen has been removed, it is also placed into a sterile contained and sent to the lab for testing. After a diagnosis has been achieved, then a treatment can be provided.
Treatments
There are many different types of treatment for the infection. Some can be taken orally while others are topical, or placed on the skin. Topical creams are usually very effective in treating the skin because they are placed directly on the wound. Oral medications need to enter the blood stream before any kind of relief can be achieved.
How to diagnose bacteremia?
Bacteremia can be diagnosed using a blood culture. To do this, a sample of blood will be taken from a vein in your arm. It will then be sent to a lab to be tested for the presence of bacteria.
How do you know if you have a bloodstream infection?
However, see your doctor promptly if you experience a fever, chills, or shaking that comes on suddenly.
What is the term for the presence of bacteria in the bloodstream?
Strictly speaking, bacteremia refers to the presence of bacteria in the bloodstream. Bacteria can sometimes enter your bloodstream due to things like cleaning your teeth or undergoing a minor medical procedure.
What is it called when there are bacteria in your blood?
Bacteremia is when there are bacteria present in your bloodstream.
Why is it important to treat bloodstream infections with antibiotics?
Timely treatment of bloodstream infections with antibiotics is necessary to prevent complications. If you believe you have a bloodstream infection, be sure to get prompt medical attention.
Why does sepsis occur?
Sepsis occurs due to a strong immune response to an infection. This response can trigger changes in your body such as inflammation. These changes can be harmful and can lead to organ damage.
What does it mean to have a sputum culture?
sputum culture if you appear to have a respiratory infection or are using a breathing tube
What is the name of the tissue that is tested for bacterial infection?
Tissue. Cerebrospinal fluid. Mucus from the nose, throat, or genital area. Some samples sent for testing, such as sputum , stool, and mucus from the nose or throat, normally contain many types of bacteria that do not cause disease.
What is the diagnosis of infectious disease?
Diagnosis of Infectious Disease. Infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Doctors suspect an infection based on the person's symptoms, physical examination results, and risk factors. First, doctors confirm that the person has an infection rather than another type of illness.
Why do doctors do susceptibility testing?
Thus, susceptibility testing is done to determine how effective various antimicrobial drugs are against the specific microorganism infecting the person. This testing helps doctors determine which drug to use for a particular person's infection (see Selecting an Antibiotic ).
What is a nucleic acid test?
Most nucleic acid–based tests are designed to identify the presence of a microorganism (called qualitative testing). However, for certain infections, such as HIV and hepatitis C, tests can measure how much of the microorganism's genetic material is present (called quantitative testing) and thus determine how severe the infection is. Quantitative tests can also be used to monitor how well treatment is working.
What is an antibody test?
Antibody tests. Antibody tests are usually done on a sample of the infected person’s blood. They also can be done on samples of cerebrospinal fluid or other body fluids. Antibodies are substances produced by a person's immune system to help defend against infection.
How long does it take for antibodies to be detected?
The more dilutions it takes until the test is negative, the more antibody there was in the infected person's sample. Because it takes several days to weeks for the immune system to produce enough antibody to be detected, diagnosis of an infection may be delayed.
Why do we use cultures?
Cultures are often used for susceptibility testing. Once a microorganism has been grown in a culture, doctors add different antimicrobial drugs to see which ones kill the microorganism.
How do you know if you have bacterial pneumonia?
The most common symptoms of bacterial pneumonia are: a cough with thick yellow, green, or blood-tinged mucus. stabbing chest pain that worsens when coughing or breathing. sudden onset of chills severe enough to make you shake . fever of 102-105°F or above (fever lower than 102°F in older persons)
How to check if your white blood cell count is high?
Take a blood sample to determine if your white blood cell count is high, which usually indicates infection. Take a blood culture, which can help determine if the bacteria have spread to your bloodstream and also help identify the bacterium causing the infection.
How does bacterial pneumonia enter the body?
It can enter your lungs through inhalation or through your bloodstream. There is a vaccination for this type. Haemophilus influenzae is the second most common cause of bacterial pneumonia. This bacterium may live in your upper respiratory tract.
Can pneumonia cause a cell to not work properly?
Pneumonia can make it difficult for your body to get enough oxygen to your blood, which can cause cells to not work properly. Bacterial pneumonia can be mild or serious. The severity of your pneumonia depends on: the strength of the bacteria. how quickly you are diagnosed and treated. your age.
What are the symptoms of sepsis?
Fever. Low blood pressure. Increased heart rate. Difficulty breathing. Doctors also perform lab tests that check for signs of infection or organ damage. Doctors also perform specific tests to identify the germ that caused the infection that led to sepsis.
How to treat sepsis quickly?
Research shows that rapid, effective sepsis treatment includes: Giving appropriate treatment, including antibiotics . Maintaining blood flow to organs. Sometimes surgery is required to remove tissue damaged by the infection. Doctors and nurses should treat sepsis with antibiotics as soon as possible.
Can antibiotics help with sepsis?
Doctors and nurses should treat sepsis with antibiotics as soon as possible. Antibiotics are critical tools for treating life-threatening infections, like those that can lead to sepsis. However, as antibiotic resistance grows, infections are becoming more difficult to treat.
What is the gold standard test for bacterial overgrowth?
Although widely available, breath testing is less specific than other types of tests for diagnosing bacterial overgrowth. Small intestine aspirate and fluid culture. This is currently the gold standard test for bacterial overgrowth. To obtain the fluid sample, doctors pass a long, flexible tube ...
What tests can be done to check for fat?
In addition to these tests, your doctor may recommend blood testing to look for vitamin deficiency or a stool evaluation to test for fat malabsorption. In some cases, your doctor may recommend imaging tests, such as X-rays, computerized tomography (CT) scanning or magnetic resonance imaging ...
What is SIBO test?
In order to diagnose small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), you may have tests to check for bacterial overgrowth in your small intestine, poor fat absorption, or other problems that may be causing or contributing to your symptoms. Common tests include:
Why do doctors switch antibiotics?
Doctors may also switch among different antibiotics to help prevent bacterial resistance. Antibiotics wipe out most intestinal bacteria, both normal and abnormal. As a result, antibiotics can cause some of the very problems they're trying to cure, including diarrhea. Switching among different drugs can help avoid this problem.
How to treat bacterial overgrowth?
For most people, the initial way to treat bacterial overgrowth is with antibiotics. Doctors may start this treatment if your symptoms and medical history strongly suggest this is the cause, even when test results are inconclusive or without any testing at all. Testing may be performed if antibiotic treatment is not effective.
How to treat SIBO?
Treatment. Whenever possible, doctors treat SIBO by dealing with the underlying problem — for example, by surgically repairing a postoperative loop, stricture or fistula. But a loop can't always be reversed. In that case, treatment focuses on correcting nutritional deficiencies and eliminating bacterial overgrowth.
Can you take antibiotics for a loop in your intestine?
But bacteria can return when the antibiotic is discontinued, so treatment may need to be long term. Some people with a loop in their small intestine may go for long periods without needing antibiotics, while others may need them regularly.
What test can detect C difficile toxin B?
Several main types of lab tests exist, and they include: Polymerase chain reaction. This sensitive molecular test can rapidly detect the C. difficile toxin B gene in a stool sample and is highly accurate. GDH/EIA. Some hospitals use a glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) test in conjunction with an enzyme immunoassay (EIA) test.
How to test for C difficile?
This test (flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy) involves inserting a flexible tube with a small camera on one end into your colon to look for areas of inflammation or abnormal tissue.
What age can you take antibiotics for C difficile?
Are older than 65. Are taking other antibiotics for a different condition while being treated with antibiotics for C. difficile infection. Have a severe underlying medical disorder, such as chronic kidney failure, inflammatory bowel disease or chronic liver disease. Treatment for recurrent disease may include:
What type of scan is used to diagnose C. difficile?
If your doctor is concerned about possible complications of C. difficile infection, he or she may order an abdominal X-ray or a computerized tomography (CT) scan , which provides images of your colon. The scan can detect the presence of complications such as:
What is the procedure to check for C. difficile?
If your doctor is concerned about possible complications of C. difficile, he or she may order an abdominal X-ray or a computerized tomography (CT) scan, which provides images of your colon. The scan can detect the presence of complications such as thickening of the colon wall, expansion of the bowel or, more rarely, a hole (perforation) in the lining of your colon.
Can C. difficile cause a person to get sick again?
difficile get sick again, either because the initial infection never went away or because they've been reinfected with a different strain of the bacteria.
Can antibiotics be used for recurrent infections?
Antibiotic therapy for recurrence may involve one or more courses of a medication. In general, guidelines recommend not repeating the same therapy used for an initial infection for a recurrent infection. The effectiveness of antibiotic therapy declines with each subsequent recurrence.
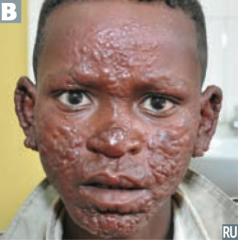
Symptoms
Causes
- The transmission (passing) of bacteria is what causes bacterial infections. You can become exposed to bacteria from other people, the environment, or by eating or drinking contaminated food or water. Anyone can get sick when exposed to bacteria. But having a weakened immune system puts you at a higher risk of severe bacterial infections. Certain conditions and medicatio…
Types of Bacterial Infections
- The severity of bacterial infections can vary widely and depends on the type of bacteria involved. On one hand, there are relatively minor illnesses like strep throat and ear infections. But bacterial infections can also cause potentially life-threatening conditions like meningitis and encephalitis. Common bacterial infections include: 1. Salmonella is an infection often linked to food poisonin…
Treatment
- Bacterial infections often get better quickly on their own without treatment. That said, you may need prescription antibiotics to treat your bacterial infection.6 Untreated bacterial infections can spread or linger, causing major health problems. Although it's rare, untreated bacterial infections can even be life-threatening. Symptoms like fever, pain, swelling, coughing, or dehydration migh…
Summary
- Bacterial infections are incredibly common and are also quite different from one to another. The type of bacteria involved, its cause, location, and timing all influence the course of your infection. Even symptoms vary a great deal. Some infections can worsen and cause severe complications. Even diagnosis and treatment options depend on the specific infection you may have.
A Word from Verywell
- You're likely going to have at least a few bacterial infections throughout your life. These infections can cause a range of symptoms and effects. Your doctor can use diagnostic testing to determine which specific infection you have. Sometimes, you may need prescription medicine, such as antibiotics, to treat your condition. Using an antibiotic "just in case" you have a bacterial infectio…
At-Home Tests
Labs and Tests
- The diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis typically involves four parts: 1. Your medical history is reviewed to check whether you have had past vaginal infections, including sexually transmitted ones. 2. A pelvic examis performed to visually check for signs of infection. 3. A pH test, performed with a paper test strip, is used to measure vaginal acidity...
Clinical Criteria
- A healthcare provider can make a definitive diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis with one of two evaluative measures: the Amsel criteria or gram stain grading. The Amsel criteria take into account the physical findings alongside the result of the diagnostic tests. Using these criteria, BV can be confirmed when three of the following four conditions are met:4 1. There is a whitish or y…
Differential Diagnoses
- Because the symptoms of bacterial vaginosis are similar to other infections, healthcare providers may investigate other causes if the test results are borderline or the clinical symptoms raise concerns about another condition. Differential diagnoses for BV may include:6 1. Candidiasis (a yeast infection caused by the Candida fungus) 2. Trichomoniasis (a sexually transmitted infecti…