What is double strand DNA denaturation and how is it done?
Double strand DNA denaturation of the sperm and FISH probes is carried out after incubation at high temperature (70°C–74°C). After denaturation, both DNAs are coincubated and hybridized to form a duplex of complementary strands.
How do you denature DNA fragments?
Among all the physical methods applied, the direct probe sonication was the most effective way to denature the DNA fragments. Among chemical methods, 60% DMSO was the most adequate denaturation method since it does not cause full renaturation during DNA hybridization.
How can the two strands of DNA be separated?
The separated strands can recombine and form the same base pairs responsible for maintaining the double helix. The two strands of the double helix can be separated by heating DNA samples. This process is called denaturation.
How is DNA denatured by heat?
DNA Denaturation through Heat. DNA can be denatured through heat in a process that is very similar to melting. Heat is applied until the DNA has unwound itself and separated into two single strands. Once the strands have been separated, the DNA will then be cooled back down to a stable temperature.
What are the factors cause denaturation of DNA?
Note 2: Denaturation can occur when proteins and nucleic acids are subjected to elevated temperature or to extremes of pH, or to nonphysiological concentrations of salt, organic solvents, urea, or other chemical agents.
What happens when double-stranded DNA is heated?
Heat denaturation of DNA, also called melting, causes the double helix structure to unwind to form single stranded DNA. When DNA in solution is heated above its melting temperature (usually more than 80 °C), the double-stranded DNA unwinds to form single-stranded DNA.
How is DNA denatured?
DNA can be denatured through heat in a process that is very similar to melting. Heat is applied until the DNA has unwound itself and separated into two single strands. Once the strands have been separated, the DNA will then be cooled back down to a stable temperature.
Which of the following conditions promotes denaturation of double stranded DNA?
In the above methods, the heating at high temperature (e.g., 95°C) is the most common way to denature dsDNA, particularly for polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Similar questions and discussions
Are there any differences of dsDNA, ssDNA or RNA when performing a agarose gel electrophoresis or PAGE?
Related Publications
To erect a main span of a bridge across the entrance of one of the busiest container orts in the world without causing disruption is a complex operation. Stonecutters Bridge, Hong Kong, was also the second longest cable-stayed span in the world with a unique twin box deck design that was being erected through a typhoon season.
How can we monitor DNA denaturation?
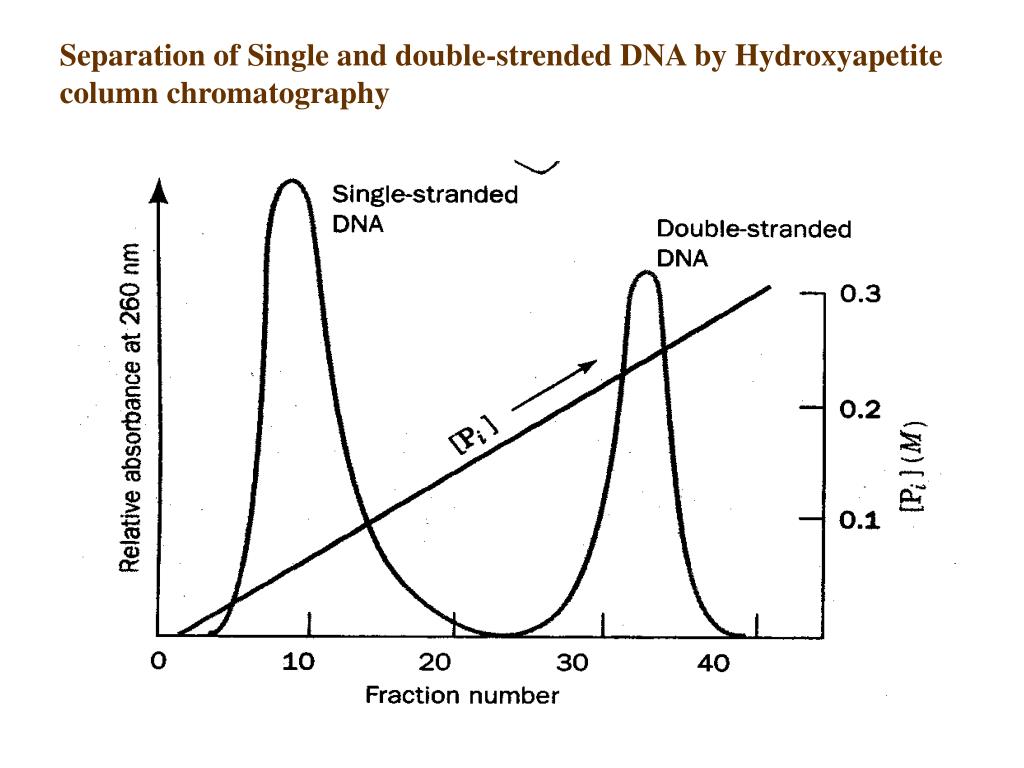
The heat denaturation of DNA, also called melting, can be monitored experimentally by observing the absorption of ultraviolet light. The bases absorb light in the 260-nm-wavelength region. As the DNA is heated and the strands separate, the wavelength of absorption does not change, but the amount of light absorbed increases (Figure 9.18).
Summary
The two strands of the double helix can be separated by heating DNA samples. This process is called denaturation.
How does DNA denaturation work?
If the temperature is slowly decreased in the solution where the DNA had been denatured, the DNA chains will spontaneously reanneal and the original double helix structure is restored. This process can be followed in a spectrophotometer at 260 nm and the temperature/absorbency relationship can be described by a curve that is the opposite of the denaturation curve shown in Fig. 6.14. The DNA renaturation resulting from slow cooling is called reannealing. When the complementary strands meet, they completely reconstitute the double helix.
What happens to DNA when it is unwinded?
DNA unwinding is initiated only if a functional oligomeric helicase is formed. Significantly, partial dissociation of the oligomeric helicase during unwinding leaves an inactive Rep monomer, resulting in a stalled complex. This stalled complex can be resolved in two ways.
What is DNA unwinding?
A DNA unwinding element (DUE) is an A + T-rich sequence ranging from 30 to > 100 bp in length in which the duplex DNA is prone to unpairing (also called melting or unwinding).
How are stalled replication forks protected, stabilized, and restarted?
How stalled replication forks are protected, stabilized, and restarted requires the involvement of many proteins and is the subject of much debate, but in addition to the essential protein-protein interactions required, the mechanistic consequences of the protein-DNA interactions should also be considered.
How much DNA is found in mammals?
Finally, a third fraction of the DNA that in mammals comprises about 60% of total DNA, corresponds to sequences only found in one to three copies ( single copy DNA) that anneal very slowly. In bacteria, almost all the DNA exists as single copy DNA. Hybridization.
What is the name of the fragments of DNA that are repeated many times?
In mammalian DNA preparations, fragments exist that are repeated many times (presenting hundreds of thousands to millions of copies), which are called highly repetitive DNA segments. Portions of highly repetitive DNA of more than 6 bp in length are also designated as satellite DNAs.
Why is the annealing time shorter?
When a given DNA has segments with the same sequence (repetitive sequences), the annealing time is shorter because the chance that one chain meets a complementary one is greater. In contrast, DNA sections with unique sequences require a longer time to find its complementary strand to reform the double helix.
When preparations of double-stranded DNA are denatured and allowed to renature, the rate of
When preparations of double-stranded DNA are denatured and allowed to renature, the rate of renaturation can give valuable information about the complexity of the DNA if there are repetitive sequences in the DNA, it shows less complexity in comparison to its total length, but the complexity is equal to its total length if all sequences are unique.
What happens when DNA is heated to 90°C?
If a DNA solution is heated to approximately 90°C or above there will be enough kinetic energy to denature the DNA completely causing it to separate into single strands. This denaturation is very abrupt and is accelerated by chemical reagents like urea and formamide.
What is the temperature at which DNA is melted?
It is defined as temperature at which 50% of the DNA is melted.
What does the abruptness of the transition mean?
The abruptness of the transition indicates that the DNA double helix is highly cooperative structure, held together by many reinforcing bonds. The melting of DNA can be followed spectrophotometrically by monitoring the absorbance of DNA at 260 nm. T m is analogous to the melting point of crystal. The T m value depends on the nature of the DNA.
Why does DNA have a high viscosity?
The solutions of native DNA exhibit high viscosity because of the relatively rigid double helical, long and rod like character of DNA molecule. Denaturation causes a marked decrease in viscosity. If melted DNA is cooled it is possible to reassociate the separated strands, a process known as renaturation.
Does rapid cooling reverse denaturation?
DNA (50-60%) is renatured. Rapid cooling does not rever se denaturation, but if the cooled solution is again heated and then cooled slowly, renaturation takes place.
Does DNA have a T-m or G-C?
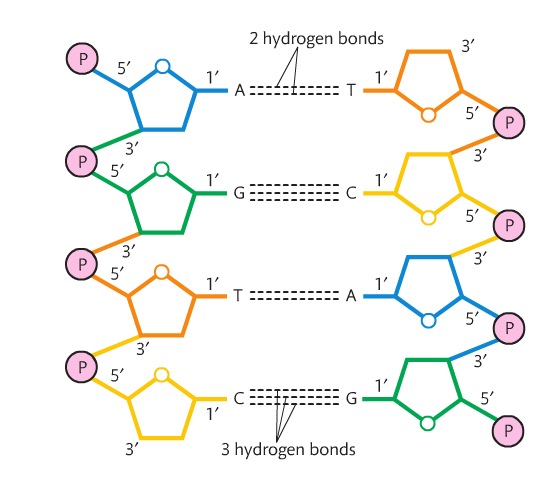
In fact, the T m of DNA from many species varies linearly with G—C content. This relationship between T m and G—C content arises due to guanine and cytosine form three hydrogen bonds when base paired, whereas adenine and thymine form only two. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is DNA denaturation?
In general the process of “denaturation” or “denaturing the biomolecule” encourage losing the structure. For example, denaturation of protein or DNA loses various levels of structure.
Techniques to Denature DNA
One of the most common techniques to denature, (theoretically or more precisely) to unwind the dsDNA is by heat. And is commonly practiced in routine lab experiments. At higher heat or temperature >90℃, hydrogen bonds between dsDNA break and produce two separate single strands.
Applications of DNA denaturation
Many different assays use the “process” DNA denaturation for various purposes and studies.
Wrapping up
Unlike NaOH, the majority of chemical denaturants work in PCR with heat, meaning it alters the melting temperature. Denaturing DNA has significant importance in the downstream application, however, to get good results, DNA should denature completely.
What is Denaturation of DNA
During the replication of DNA and other different phenomenon in which active participation of DNA is observed with the separation of strands of DNA double helix.
Renaturation of DNA
Segregated strands of DNA start to anneal immediately when temperature drops below the T m value. This annealing cycle is often called as renaturation. The property of denaturation and renaturation is very important for the optimum biological functioning of the DNA.
Thermal Denaturation of DNA
DNA can be denatured through heat and this process is same as melting. The sample is heated until the DNA unwinding and the separation of two strands. When the strands have been separated, the DNA will then, at that point be allowed to reach a steady temperature.
DNA Denaturation through NaOH Treatment
Besides heating the DNA sample, Chemicals like NaOH can also be used to achieve denaturation of DNA. A specific concentration of NaOH can be utilized to denature DNA. As the amount of NaOH utilized is lowered, the denaturation will take longer time than expected – yet the DNA can in any case be completely denatured.
DNA Denaturation through Salt
A high amount of salt in the medium will make DNA normally denature, given the right ratio of salt. DNA denaturation using salt is like denaturation using organic solvents. generally, DNA denaturation using salt can’t be renatured.
Which PCR step causes the denaturation of double stranded DNA
Separation of DNA strands take place in denaturation step of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) which is described in the following steps:
Effect of urea on DNA denaturation
Like Thermal and pH induced denaturation of DNA, Urea also possess the capability to denature DNA. Urea in high amounts addresses a problematic condition for nucleic acid structures. Since urea is hydrogen-bond donor as well as acceptor, it can undoubtedly denature nucleic acids.
