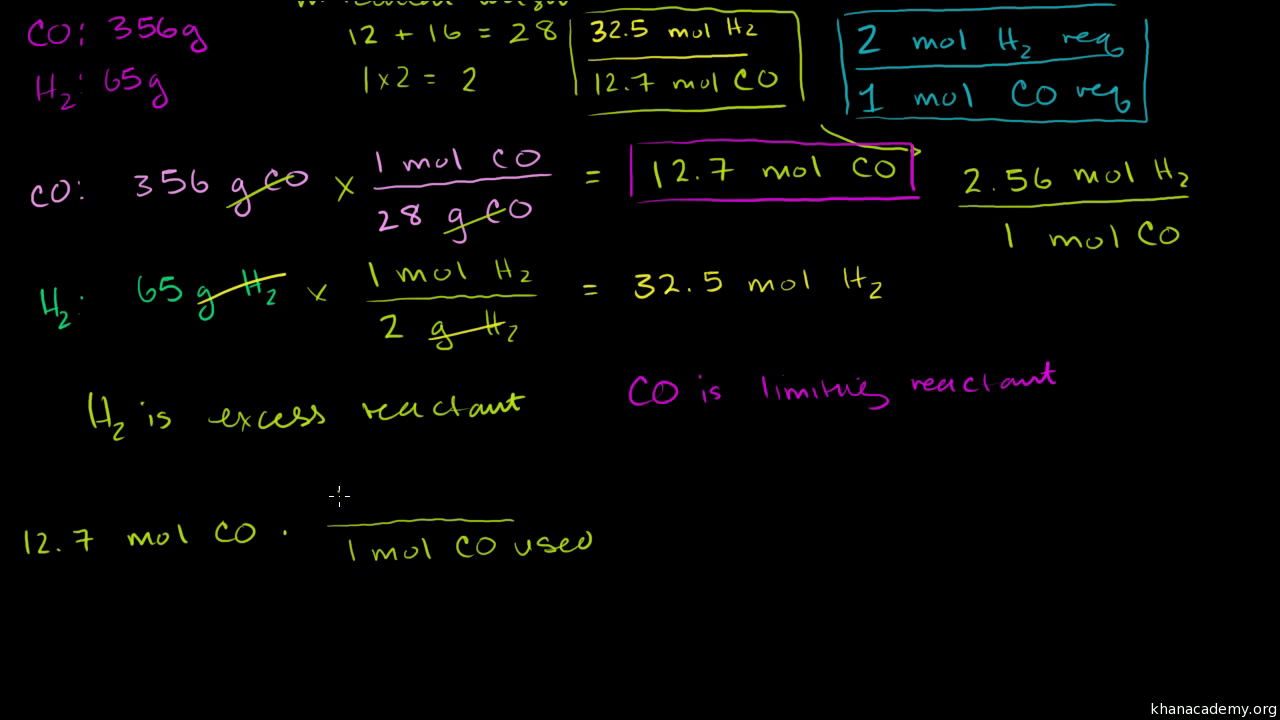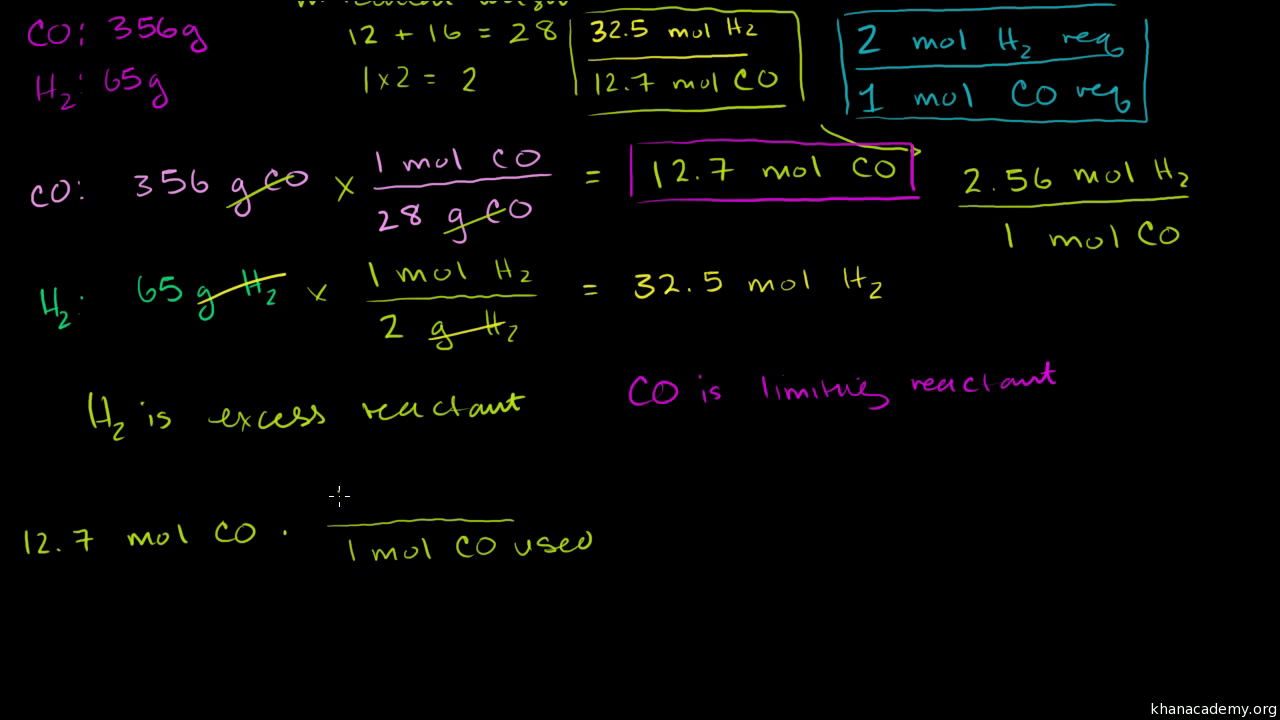
To solve stoichiometry problems with limiting reactant or limiting reagent:
- Figure out which of the reactants is the limiting reactant or limiting reagent.
- See how much product can be formed by using the maximum amount of the limiting reactant or limiting reagent.
- The excess reactant is what is left over after all of the limiting reactant has been used up.
How do you determine limiting reagent?
Strategy:
- Write the balanced chemical equation.
- Convert from mass of reactants and product to moles using molar masses and then use mole ratios to determine which is the limiting reactant.
- Calculate the percent yield by dividing the actual yield by the theoretical yield and multiplying by 100.
How to do limiting reagent problems?
to find the limiting reagent, take the moles of each substance and divide it by its coefficient in the balanced equation. The substance that has the smallest answer is the limiting reagent. You're going to need that technique, so remember it. By the way, did you notice that I bolded the technique to find the limiting reagent?
How to find the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction?
- It can be used in systems containing any number of reactants
- Balance the given chemical equation
- Convert all masses into moles
- Using Stoichiometry, calculate the amount of product by using each reactant individually
- Denote the reactant with the least amount of product as a limiting reagent
What are examples of limiting reactants?
Limiting reactant and reaction yields
- Limiting reactant and theoretical yield. It’s a classic conundrum: We have five hot dogs and four hot dog buns. ...
- Example 1: Using the limiting reactant to calculate theoretical yield. We can do so by converting both reactant masses to moles and then using one or more mole ratios from ...
- Percent yield. ...
- Example 2: Calculating percent yield. ...

How do you use limiting reactant in stoichiometry?
Calculate the number of moles of each reactant by multiplying the volume of each solution by its molarity. Determine which reactant is limiting by dividing the number of moles of each reactant by its stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation.
What is a limiting reactant and why is it important in stoichiometry?
The limiting reagent is the reactant that is completely used up in a reaction, and thus determines when the reaction stops. From the reaction stoichiometry, the exact amount of reactant needed to react with another element can be calculated.
How do you determine the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction?
How to find Limiting Reagent?When there are only two reactants, write the balanced chemical equation and check the amount of reactant B required to react with reactant A. ... The reactant which is in a lesser amount than is required by stoichiometry is the limiting reactant.More items...
What is the most important step in any stoichiometry problem?
the first step in any stoichiometric problem is to always ensure that the chemical reaction you are dealing with is balanced, clarity of the concept of a 'mole' and the relationship between 'amount (grams)' and 'moles'.
Why do we use limiting reactant?
The limiting reactant is the reagent (compound or element) to be totally consumed in a chemical reaction. Limiting reactant is also what prevents a reaction from continuing because there is none left. The limiting reactant may also be referred to as limiting reagent or limiting agent.
What is the purpose of limiting reagent?
The limiting reactant (or limiting reagent) is the reactant that gets consumed first in a chemical reaction and therefore limits how much product can be formed.
How will you identify the limiting reagent in reaction and how it controls the amount of product formed?
Method 1: Comparison of reactant amounts If the amount of B actually present exceeds the amount required, then B is in excess and A is the limiting reagent. If the amount of B present is less than required, then B is the limiting reagent.
How limiting reactant controls the amount of product formed?
A limiting reagent is a chemical reactant that limits the amount of product that is formed. The limiting reagent gives the smallest yield of product calculated from the reagents (reactants) available. This smallest yield of product is called the theoretical yield.
How do you do simple stoichiometry?
Almost all stoichiometric problems can be solved in just four simple steps:Balance the equation.Convert units of a given substance to moles.Using the mole ratio, calculate the moles of substance yielded by the reaction.Convert moles of wanted substance to desired units.
How do you solve stoichiometry solutions?
0:457:38How to Do Solution Stoichiometry Using Molarity as a Conversion FactorYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we're given 12.5 milliliters of HCL solution and then we're also given our molarity of our HClMoreSo we're given 12.5 milliliters of HCL solution and then we're also given our molarity of our HCl solution as well now whenever you see that molarity.
What is the first step when you are solving any stoichiometry problem?
Answer and Explanation: The first and critical step in any stoichiometric calculation is to have a balanced chemical equation.
What is the first step in solving stoichiometry problems?
We can tackle this stoichiometry problem using the following steps:Step 1: Convert known reactant mass to moles. ... Step 2: Use the mole ratio to find moles of other reactant. ... Step 3: Convert moles of other reactant to mass.
How limiting reactant controls the amount of product formed?
A limiting reagent is a chemical reactant that limits the amount of product that is formed. The limiting reagent gives the smallest yield of product calculated from the reagents (reactants) available. This smallest yield of product is called the theoretical yield.
Are limiting reactants present in all reactions?
There is always a limiting reagent, if at least one of the starting materials is in excess in the reaction mixture.
How can an understanding of the limiting reactant help manufacturing companies?
Limiting reactant is an important concept in any manufacturing process. A manufacturer knows they want to make a certain amount of a specific product, and will purchase the reactants accordingly.
Does the limiting reactant produce the least amount of product?
Another way is to calculate the grams of products produced from the given quantities of reactants; the reactant that produces the smallest amount of product is the limiting reactant (Approach 2).
How to find the limiting reagent of a substance?
take the moles of each substance and divide it by its coefficient in the balanced equation. The substance that has the smallest answer is the limiting reagent. 2) Let's say that again: to find the limiting reagent, take the moles of each substance and divide it by its coefficient in the balanced equation.
Which reagent is the lesser amount?
3) The water is the lesser amount; it is the limiting reagent.
What is reactant A?
Reactant A is a test tube. I have 20 of them.
How to determine the moles of product produced by each assumption?
Determine the moles of product produced by each assumption: Note: the first factor in each case converts grams of each reactant to moles. The second factor uses a molar ratio from the chemical equation to convert from moles of the reactant to moles of product.
What happens when a reaction is carried out with non-stoichiometric quantities of the reactants?
If the reaction is carried out with stoichiometric quantities of reactants, then all the reactants will be converted into products. On the other hand, when a reaction is carried out using non-stoichiometric quantities of the reactants, the product yield will be determined by the reactant that is completely consumed.
What is the limiting reagent of sulphur?
1 mole of sulphur reacts with 3 moles of fluorine to form 1 mole of sulphur hexafluoride and therefore 3 moles of sulphur reacts with 9 moles of fluorine to form 3 moles of sulphur hexafluoride. In this case, all available sulphur gets consumed and therefore it limits the further reaction. Hence sulphur is the limiting reagent and fluorine is the excess reagent. The remaining three moles of fluorine are in excess and do not react.
What is stoichiometry in chemistry?
Stoichiometry is the quantitative relationship between reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation in moles. The quantity of reactants and products can be expressed in moles or in terms of mass unit or as volume. These three units are inter convertible.
What is the relationship between a metron and a stoichiometric equation?
In Greek, stoicheion means element and metron means measure that is, stoichiometry gives the numerical relationship between chemical quantities in a balanced chemical equation. By applying the concept of stoichiometry, we can calculate the amount of reactants required to prepare a specific amount of a product and vice versa using balanced chemical ...
How many moles of hydrogen are required to produce 10 moles of ammonia?
N2(g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g) As per the stoichiometric equation, to produce 2 moles of ammonia, 3 moles of hydrogen are required.
What is the excess reagent left at the end of the reaction?
Excess reagent leftover at the end of the reaction is carbon dioxide.
How much ammonia reacts with CO2?
In a process, 646 g of ammonia is allowed to react with 1.144 kg of CO2 to form urea.
Which is lower, oxygen or reagent?
Oxygen is the lower value. It is the limiting reagent.
What is the molar ratio of importance?
The molar ratio of importance is nitrogen to hydrogen. It is 1:3.
How many molecules of hydrogen react with carbon?
one atoms of carbon reacts with two molecules of hydrogen
How many molecules of hydrogen and chlorine react?
c) 4 molecules of hydrogen and 5 molecules of chlorine react.
Is 19 good for limiting reagent?
Comment: when I was in the classroom, teaching the technique for determining the limiting reagent, I would warn against using the results of the division, in this case the 19 for the NaOH, in the next step of the calculation. The 19 is good only for determining the limiting reagent. You need to use the 57 in the next step.
Does oxygen run out before sucrose?
Since the oxygen required is greater than that on hand, it will run out before the sucrose. Oxygen is the limiting reagent.
Is chlorine gas a limiting reagent?
Seems pretty obvious that chlorine gas is the limiting reagent. In a situation like this, you don't have to finish the problem unless it's on a test and the teachers wants it finished!