
Film thickness can be measured on a UV-Visible spectrophotometer by using the interference effect of light. Constructive and destructive interferences between light reflected from
What are the factors that affect thin film interference?
The thickness of the film relative to the wavelength of light is the other crucial factor in thin-film interference. Ray 2 in (Figure) travels a greater distance than ray 1. For light incident perpendicular to the surface, ray 2 travels a distance approximately 2 t farther than ray 1.
Is thin-film interference constructive or destructive?
To know whether interference is constructive or destructive, you must also determine if there is a phase change upon reflection. Thin-film interference thus depends on film thickness, the wavelength of light, and the refractive indices.
What happens when light hits a thin film?
Light striking a thin film is partially reflected (ray 1) and partially refracted at the top surface. The refracted ray is partially reflected at the bottom surface and emerges as ray 2. These rays interfere in a way that depends on the thickness of the film and the indices of refraction of the various media.
What is the refractive index of thin film of uniform thickness?
3. The refractive index of the thin soap film of uniform thickness is 1.4. Find the smallest thickness of the film that gives on the inteference maximum in the reflected light of wavelength 5460 amstrong fall at normal incidence. Maximum interference in the reflected light, in case of thin-film interference, expressed as
How do you find the thickness of thin film interference?
3:325:14Physics - Interference of Light (6 of 8) The Thin Film: Oil - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBy the shift here and no shift over there solving. This for T we get T is the lambda divided by 4n.MoreBy the shift here and no shift over there solving. This for T we get T is the lambda divided by 4n.
How can you measure the thickness of a thin layer?
The best way to measure the thickness is the cross section using Fesem or SEM. The second way using Afm by covering a portion of the substrate using metal after that you measure the difference in the highest, this difference will be the thickness.
How does interference occur in thin films?
Thin film interference occurs when light waves reflecting off the top and bottom surfaces of a thin film interfere with one another. This type of interference is the reason that thin films, such as oil or soap bubbles, form colorful patterns.
Which measurement technique is commonly used to find the thickness of thin films?
The techniques chosen for this comparison are widely used in thin film characterization and are as follows: stylus profilometry, interferometry, ellipsometry, spectrophotometric measurements and X-ray microanalysis. The comparison is performed for areas where more than one technique can be used.
Which type of method is used for the measurement of thickness?
In the field of industrial ultrasonic testing, ultrasonic thickness measurement (UTM) is a method of performing non-destructive measurement (gauging) of the local thickness of a solid element (typically made of metal, if using ultrasound testing for industrial purposes) based on the time taken by the ultrasound wave to ...
How is film thickness calculated?
You measure mass of the film before and after deposition. you will know the the mass of the film (M). You know the area of the film (A) and density (d) of the film material. By using following relation you can find out thickness (t): t = M/Ad. or you can use needle and from penetrate you can be know the thickness.
Why is it called thin film interference?
This is known as thin-film interference, because it is the interference of light waves reflecting off the top surface of a film with the waves reflecting from the bottom surface. To obtain a nice colored pattern, the thickness of the film has to be on the order of the wavelength of light.
Why is there no interference in thick film?
For a layer which is a couple of wavelengths thick, all colours will interfere destructively under the same angle. However when the layer is 1000 wavelengths thick, one colour will interfere constructively, while the other interferes destructively. The interference pattern will thus be lost.
What is the thickness of thin film?
This means that a film of thickness 10 microns can be considered as a thin film when it interacts with infrared light of wavelengths few microns to several tens of microns, but if the same film interacts with ultraviolet light say wavelength less than 0.3 micron, then this film cannot be considered as thin film.
Which of the following method is used to measure the thickness of opaque film?
The advantage of optical measurement methods is that they are usually non-invasive and precise. The thickness range is from nanometer to micrometer in most of the interferometry methods. For films thicker than micron, confocal microscopy can be used for thicknesses up to a few hundred microns.
Which methods are good optical or mechanical for film thickness measurements and why?
A very precise method is x-ray reflectometry. you can get the film thickness from simulations of the data very accurate with errors of less than 0.1 nm. It works fine for all the materials you use, polymers, oxids and sulfide.
How is thickness of polymer film measured?
All Answers (262) You can use the gravimetric method if you know the density and mass of the coated material by the relation density=mass/area*thickness. One can determine the weight of the coated material simply by taking the weight difference of the sample after coating and before coating.
What is the thickness of the Mentle?
about 2,900 kilometersThe mantle is about 2,900 kilometers (1,802 miles) thick, and makes up a whopping 84% of Earth's total volume.
What does a profilometer measure?
A profilometer/roughness gauge is a measuring device used to capture 2D or 3D data on the surface of a sample in order to measure roughness, flatness, or other critical 2D and 3D dimensions.
Which of the following instrument is being used to measure the thickness of the oxide thin films?
Ellipsometry should work for your films as long as their thickness is lower than 100 nm.
Which methods are good optical or mechanical for film thickness measurements and why?
A very precise method is x-ray reflectometry. you can get the film thickness from simulations of the data very accurate with errors of less than 0.1 nm. It works fine for all the materials you use, polymers, oxids and sulfide.
Abstract
An optical method for directly measuring the thickness of a thin transparent film has been proposed by means of multi-wave laser interference at many incident angles, and confirmed experimentally by means of equipment made on an experimental basis.
1. Introduction
Transparent, protective ceramic coatings have been applied to various materials such as electronic circuits and a building's outer wall tiles.
2. Principle of the method
Fig. 1 illustrates the principle of measurement using the multi-wave interference of a single wavelength on a single layer, i.e., a single film in air.
3. Experimental results
A preliminary experiment was carried out by means of a numerical calculation. Fig. 2 shows the results for Eqs. (1), (4a), and (4b) for h =5 μm, λ =0.65 μm and n =1.4 (1−j3×10 −3 ), respectively. As is shown, the light intensity received on a silicon photodiode R varies with θ in the manner of sin-wave. Further, Eq.
4. Discussion
As was shown in , , the thickness can be determined experimentally when two successive values of Θ i, k−1 and Θ i, k are obtained for Eq. (8), and when three successive values of Θ i, k−1, Θ i, k and Θ i, k+1 are obtained for Eq. (9). This restricts the smallest measurable thickness of the film, i.e., the resolution of this method.
5. Conclusion
The optical method for directly measuring the thickness of a thin transparent film has been proposed by means of multi-wave laser interference for many incident angles, and was confirmed experimentally by means of equipment made on an experimental basis.
How to see thin film interference?
Another example of thin-film interference can be seen when microscope slides are separated (see (Figure) ). The slides are very flat, so that the wedge of air between them increases in thickness very uniformly. A phase change occurs at the second surface but not the first, so a dark band forms where the slides touch. The rainbow colors of constructive interference repeat, going from violet to red again and again as the distance between the slides increases. As the layer of air increases, the bands become more difficult to see, because slight changes in incident angle have greater effects on path length differences. If monochromatic light instead of white light is used, then bright and dark bands are obtained rather than repeating rainbow colors.
How to know if interference is constructive or destructive?
To know whether interference is constructive or destructive, you must also determine if there is a phase change upon reflection. Thin-film interference thus depends on film thickness, the wavelength of light, and the refractive indices.
Why do the rainbow colors of constructive interference repeat?
The rainbow colors of constructive interference repeat, going from violet to red again and again as the distance between the slides increases. As the layer of air increases, the bands become more difficult to see, because slight changes in incident angle have greater effects on path length differences.
What would happen if a bubble was illuminated with pure red light?
Significance If the bubble were illuminated with pure red light, we would see bright and dark bands at very uniform increases in thickness. First would be a dark band at 0 thickness, then bright at 122 nm thickness, then dark at 244 nm, bright at 366 nm, dark at 488 nm, and bright at 610 nm. If the bubble varied smoothly in thickness, like a smooth wedge, then the bands would be evenly spaced.
Why are military aircraft invisible to radar?
To save money on making military aircraft invisible to radar, an inventor decides to coat them with a nonreflective material having an index of refraction of 1.20, which is between that of air and the surface of the plane. This, he reasons, should be much cheaper than designing Stealth bombers.
When light reflects from a medium having an index of refraction greater than that of the medium in which it?
When light reflects from a medium having an index of refraction greater than that of the medium in which it is traveling, a phase change (or a shift) occurs.
Does phase change occur when reflecting from a medium of lower refractive index?
No phase change takes place when reflecting from a medium of lower refractive index ( (Figure) ). Because of the periodic nature of waves, this phase change or inversion is equivalent to in distance travelled, or path length. Both the path length and refractive indices are important factors in thin-film interference.
What is Thin Film Interference?
Thin-film interference is the phenomenon that is a result of lightwave being reflected off two surfaces that are at a distance comparable to its wavelength. When light waves that reflect off the top and bottom surfaces interfere with one another we see different coloured patterns. During this, the light reaches the boundary between two media and part of it gets reflected and some part gets transmitted.
How many waves are there in a thin film?
Thus, there are two waves emerging from a thin film – one wave reflected off the top surface of the film and the other reflected off the bottom surface.
What is the refractive index of soap solution?
In the reflected light, two dark consecutive overlapping fringes are observed corresponding to wavelengths 6.1 x 10-7 m and 6.0 x 10-7 m. The refractive index for soap solution is 4/3. Calculate the thickness of the film.
What happens to the light during constructive interference?
During constructive interference, the light of a particular wavelength increases in intensity whereas in destructive interference it decreases in intensity.
What is phase difference?
The phase difference is the difference in phase angle between two waves. Path difference is defined as the difference in actual distance travelled by the two waves.
Does light from the upper air-film interface move to the lower film-air interface?
Further, light from the upper air-film interface will keep moving to the lower film-air interface where it is reflected. Here, the phase of the reflected wave is not changed.
Is interference destructive or constructive?
The interference can be constructive or destructive depending on the phase difference between the two reflected light waves, resulting in the increase or decrease in the brightness of the reflected light.
What is thin film interference?
Thin film interference occurs between the light reflected from the top and bottom surfaces of a film. In addition to the path length difference, there can be a phase change.
How thick is a soap bubble?
A soap bubble is 100 nm thick and illuminated by white light incident perpendicular to its surface. What wavelength and color of visible light is most constructively reflected, assuming the same index of refraction as water?
What is thin film interference?
Thin film interference occurs between the light reflected from the top and bottom surfaces of a film. In addition to the path length difference, there can be a phase change.
How thick is a soap bubble?
1: A soap bubble is 100 nm thick and illuminated by white light incident perpendicular to its surface. What wavelength and color of visible light is most constructively reflected, assuming the same index of refraction as water?
What would happen if a bubble was illuminated with pure red light?
If the bubble was illuminated with pure red light, we would see bright and dark bands at very uniform increases in thickness. First would be a dark band at 0 thickness, then bright at 122 nm thickness, then dark at 244 nm, bright at 366 nm, dark at 488 nm, and bright at 610 nm. If the bubble varied smoothly in thickness, like a smooth wedge, then the bands would be evenly spaced.
Popular Answers (1)
I may add, that if you do not know the refractive index of your material you can measure the interference pattern perpendicularly to your film (as usually) and at other incident angle. You can then calculate refractive index from the shifts of extrema in your measured pattern.
All Answers (5)
If you have interference pattern in your transmittance spectra, take a look on this article. Best regards
Similar questions and discussions
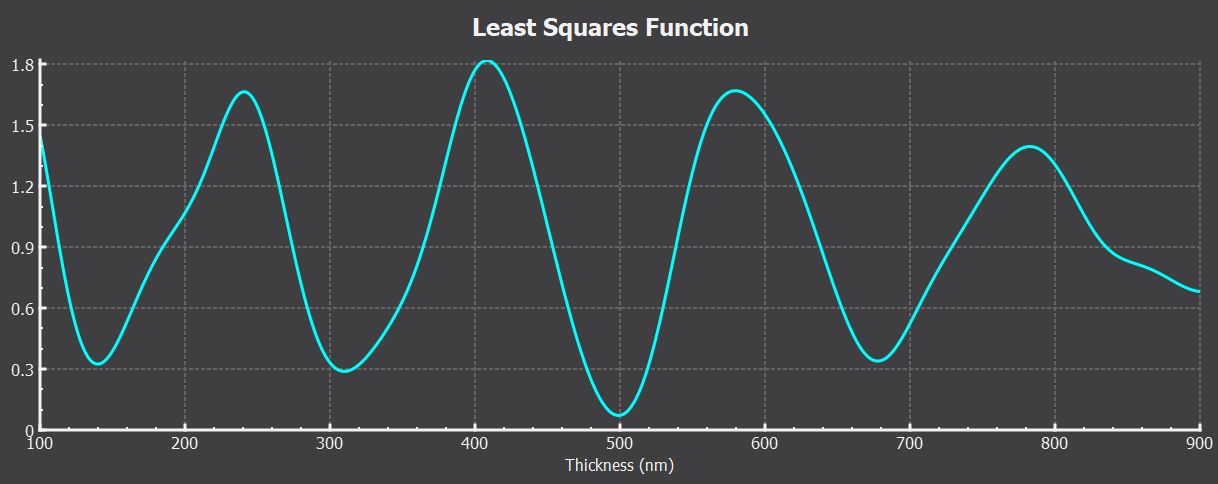
How we can measure thickness for thin film by using UV Visible Spectroscopy?
What is thin film interference?
Thin film interference occurs between the light reflected from the top and bottom surfaces of a film. In addition to the path length difference, there can be a phase change.
How thick is a soap bubble?
1: A soap bubble is 100 nm thick and illuminated by white light incident perpendicular to its surface. What wavelength and color of visible light is most constructively reflected, assuming the same index of refraction as water?
What would happen if a bubble was illuminated with pure red light?
If the bubble was illuminated with pure red light, we would see bright and dark bands at very uniform increases in thickness. First would be a dark band at 0 thickness, then bright at 122 nm thickness, then dark at 244 nm, bright at 366 nm, dark at 488 nm, and bright at 610 nm. If the bubble varied smoothly in thickness, like a smooth wedge, then the bands would be evenly spaced.
What Is Thin Film Interference?
Conditions For interference
Phase Difference and Path Difference
- The phase difference is the difference in phase angle between two waves. Path difference is defined as the difference in actual distance travelled by the two waves. The phase angle is the part of one complete wave cycle measured as a fraction of 2π (360 degrees) i.e the phase difference from one wave peak to the next is 2π (360 degrees).
Thin-Film interference Soap Bubble
- When we take a soap bubble, light waves travel through the air and hits the soap film. If we look at the refractive index of air it is 1(nair= 1) whereas the film will have an index larger than 1 (nfilm> 1). On the other hand, a 180° phase shift will be introduced in the reflected wave. It takes place at the upper boundary of the film. The shift occurs mainly because of the lower refractive index of t…
Thin-Film interference Problems and Solutions
- 1. A thin film of soap solution is illuminated by white light at an angle of incidence i = sin-1(4/5). In the reflected light, two dark consecutive overlapping fringes are observed corresponding to wavelengths 6.1 x 10-7 m and 6.0 x 10-7m. The refractive index for soap solution is 4/3. Calculate the thickness of the film. Given, µ = 4/3, λ1 = 6.1 x...