
Threats
- Intensive urban growth can lead to greater poverty, with local governments unable to provide services for all people.
- Concentrated energy use leads to greater air pollution with significant impact on human health.
- Automobile exhaust produces elevated lead levels in urban air.
- Large volumes of uncollected waste create multiple health hazards.
What are the negative effects of urbanization on the environment?
urbanization. As a consequence, the urban environment, particularly in large cities, is deteriorating very rapidly. Some important environmental problems are discussed below: A. Over Exploitation of Natural Resources Due to high population density and expensive life style, the rate of consumption of natural resources (e.g. water,
What are some of the environmental benefits of urbanization?
Environmental Benefits Of Urbanization. A new kind of building technology is emerging as an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional building methods. This technology produces structures which are highly efficient in terms of the amount of material used in their construction, require no permanent foundations, can be relocated easily ...
What are positive effects of urbanization?
What are good things about urbanization?
- Convenience is one of the many reasons why people choose to move to the city. …
- A lot of companies and industries are in the city and not in the country. …
- The best schools can be found in city areas. …
- Some get better Housing. …
- Better Social Life. …
- Better Healthcare Services.
What are the pros and cons of urbanization?
Pros And Cons Of Urbanization – Poor Living Conditions
- Land insecurity – Slums are usually located on land, not owned by the slum dwellers. ...
- Poor living conditions – Crowding and lack of sanitation. ...
- Unemployment – Since the number of people aspiring for jobs is more than jobs available, unemployment is a natural outcome of the situation.
- Crime – Slum conditions make maintenance of law and order difficult. ...
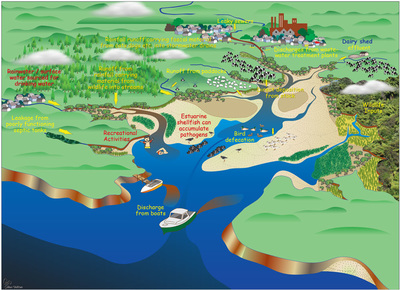
How does Urbanisation change the environment?
Urban areas can grow from increases in human populations or from migration into urban areas. Urbanization often results in deforestation, habitat loss, and the extraction of freshwater from the environment, which can decrease biodiversity and alter species ranges and interactions.
What are the effects of urban change?
Poor air and water quality, insufficient water availability, waste-disposal problems, and high energy consumption are exacerbated by the increasing population density and demands of urban environments. Strong city planning will be essential in managing these and other difficulties as the world's urban areas swell.
What are 5 negative effects of urbanization?
Negative effects of urbanisation: Development of Slums. Water and Sanitation Problems. Poor Health and Spread of Diseases. Traffic Congestion.
What are the main causes of environmental problems in urban areas?
Urban environmental problems are mostly inadequate water supply, wastewater, solid waste, energy, loss of green and natural spaces, urban sprawl, pollution of soil, air, traffic, noise, etc.
What are examples of urban change?
Urban change: deindustrialisation, decentralisation, rise of service economy. Urban decline -The deterioration of the inner city often caused by lack of investment and maintenance. It is often but not exclusively accompanied by a decline in population numbers, decreasing economic performance and unemployment.
What causes urban change?
The two causes of urbanisation are natural population increase and rural to urban migration. Urbanisation affects all sizes of settlements from small villages to towns to cities, leading up to the growth of mega-cities which have more than ten million people.
How does urbanization cause pollution?
Due to urbanisation, factories and industries are springing up in different places, and the number of vehicles on the road is increasing. The air and gases emitted from the factories and vehicles contaminate the atmosphere, thus leading to pollution.
What were 3 negatives of urbanization?
Some of the major health problems resulting from urbanization include poor nutrition, pollution-related health conditions and communicable diseases, poor sanitation and housing conditions, and related health conditions.
What problems are caused by urbanization?
The problems associated with urbanization are: High population density, inadequate infrastructure, lack of affordable housing, flooding, pollution, slum creation, crime, congestion and poverty.
How do cities affect the environment?
Cities are responsible for around 75% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, with transport, buildings, energy, and waste management being among the largest contributors. Thus, cities have a critical role to play in the fight against climate change and the global effort to meet the objective of the Paris Agreement.
How does urban environment affect health?
An estimated 91% of people in urban areas breathe polluted air. Poorly designed urban transport systems create a range of threats including road traffic injuries, air and noise pollution and barriers to safe physical activity – all leading to higher levels of noncommunicable disease and injuries.
What is urban environmental pollution?
Definition. Although there is not a universally accepted definition, the concept of urban pollution refers to the presence or introduction in cities and urban areas of poisonous or harmful substances. Urban pollution may come from natural sources, but the most detrimental are those emissions related to human activities ...
What are the effects of urbanization on the society?
In addition, urbanization has many adverse effects on the structure of society as gigantic concentrations of people compete for limited resources. Rapid housing construction leads to overcrowding and slums, which experience major problems such as poverty, poor sanitation, unemployment and high crime rates.
How does urbanization affect society?
But when poorly planned, urbanization can lead to congestion, higher crime rates, pollution, increased levels of inequality and social exclusion. Inequality within cities has economic, spatial and social dimensions.
What are the economic effects of urbanisation?
Cities infrastructure is much greater than that of rural areas, increasing economic output, individuals can take advantage of the proximity, diversity and access to surrounding areas. Transportation links, such as roads busses, and trains, results in greater access for residents.
What were some of the positive effects of urbanization?
Finally, the higher standard of living associated with urbanization provides people with better food, education, housing, and health care. Urban growth generates revenues that fund infrastructure projects, reducing congestion and improving public health.
How does water runoff affect the environment?
This will result in more infrastructures and waterways that were supposed to be natural are now used to drain off the run off water. In urban areas that are highly-urbanized, the rain becomes surface runoff. This run off from these urbanized areas can cause channel erosion, habitat damage to the animals, and clogged stream channels. These changes in the water cycle have great effects on the atmosphere. For example, clean water will be harder to find for fish, humans, and other wildlife.
How does acidification affect the environment?
Such acidification may cause sudden shifts in water chemistry. It increases the concentration of substances like aluminum which would be toxic to some fish. It may also affect the forests by influencing the soil. It weakens the trees ' natural defenses, making them more exposed to diseases.
How does runoff affect storm water?
Runoff from such concretized surfaces has a high velocity in flow during and after rainfall, which increases storm water in drainage systems in built-up areas. This increases peak flow and overland flow volume and decreases natural groundwater flow as percolation is near impossible and evapotranspiration. Urban runoff has increased pollution and contamination of water bodies in the environment, which leads to serious environmental consequences (Parkinson, et al, 2010). The traditional model of storm water management is based on a misconception by people which the main aim is to drain urban runoff as quick as possible from the environment through channels and pipes and this increases peak flows and costs of storm water management in urban system. This type of solution has been observed to promote or transfer flood problems from one section of the basin of an urban area to another section. Urban runoff most time contains large amount of solids and higher concentration of metals and other toxic components during the flowing process as a result of not treating them before discharge (Parkinson, et al,…show more content…
Why is water pollution important?
People are pollution waters everywhere. They gut polluted water into some river from some factory, due to global warming, etc. (The Importance of Clean Water) Well, water pollution affect the condition for human life and quality of living by when drinking polluted water, polluted water come into your body, and global warming. Global warming hear like kind of air pollution but Water pollution
Why is Puget Sound so polluted?
The Puget Sound is polluted, largely because of people’s actions. Efforts to clean up pollution are already underway, but the problem of pollution still persists. The Department of Ecology says that “a major contributor of these toxic pollutants entering the Sound is the stormwater that runs off our highways, roads, driveways, roofs, parking lots, disturbed soils, and other developed surfaces” (“Threats to Puget Sound”). When there is rain, the rain
What is water pollution?
Water pollution is when there is a build of one or more substances in water to such an extent that it causes problems for animals or plants. This form of pollution has increased as the population of this town has increased. There are two different ways in which water pollution can occur: • If pollution occurs from a single location such as a discharge pipe attached to a factory it is known as point-source pollution. • A great deal of pollution happens not from one source but from many different scattered sources. This is known as nonpoint-source pollution.
How do industrial corporations use water?
Industrial corporations have continuously used bodies of water to their advantage by having their factories use water as an energy source and trash bin. Toxic chemicals are released by these factories and sometimes directly dumped back into the water. Aquatic plants benefit from the carbon dioxide released by factories, but too much can harm the biodiversity of that ecosystem and other marine life and acidity levels will also rise. A bigger population means more consumption and as the human consumption has increased throughout the years, landfills have been overflowed by large amounts of trash. When liquids and other materials begin to degrade, they release a juice that can be toxic if consumed.
Why is city planning important?
Strong city planning will be essential in managing these and other difficulties as the world's urban areas swell.
How does energy use affect human health?
Concentrated energy use leads to greater air pollution with significant impact on human health. Automobile exhaust produces elevated lead levels in urban air. Large volumes of uncollected waste create multiple health hazards. Urban development can magnify the risk of environmental hazards such as flash flooding.
How can we reduce air pollution?
Reduce air pollution by upgrading energy use and alternative transport systems.
Why do people want to live in cities?
The promise of jobs and prosperity, among other factors, pulls people to cities. Half of the global population already lives in cities, and by 2050 two-thirds of the world's people are expected to live in urban areas. But in cities two of the most pressing problems facing the world today also come together: poverty and environmental degradation.
What are the causes of animal populations being inhibited?
Animal populations are inhibited by toxic substances, vehicles, and the loss of habitat and food sources.
How do urban areas affect the environment?
Many of the effects of urban areas on the environment are not necessarily linear. Bigger urban areas do not always create more environmental problems. And small urban areas can cause large problems. Much of what determines the extent of the environmental impacts is how the urban populations behave — their consumption and living patterns — not just how large they are.
How do urban populations interact with their environment?
Urban populations interact with their environment. Urban people change their environment through their consumption of food, energy, water, and land. And in turn, the polluted urban environment affects the health and quality of life of the urban population.
Why is there no research on urban areas?
Much of the research that needs to be done on the environmental impacts of urban areas has not been done because of a lack of data and funding. Most of the data that exist are at a national level. But national research is too coarse for the environmental improvement of urban areas. Therefore, data and research at the local level need to be developed to provide the local governments with the information they need to make decisions. Certainly the members of the next generation, the majority of whom will be living in urban areas, will judge us by whether we were asking the right questions today about their urban environments. They will want to know whether we funded the right research to address those questions. And they will also want to know whether we used the research findings wisely.
How do urban people differ from rural people?
People who live in urban areas have very different consumption patterns than residents in rural areas.10For example, urban populations consume much more food, energy, and durable goods than rural populations. In China during the 1970s, the urban populations consumed more than twice as much pork as the rural populations who were raising the pigs.11With economic development, the difference in consumption declined as the rural populations ate better diets. But even a decade later, urban populations had 60 percent more pork in their diets than rural populations. The increasing consumption of meat is a sign of growing affluence in Beijing; in India where many urban residents are vegetarians, greater prosperity is seen in higher consumption of milk.
How long have humans been an environmental force?
Human beings have become an increasingly powerful environmental force over the last 10,000 years.
Why do urban areas grow?
The growth in urban areas comes from both the increase in migration to the cities and the fertility of urban populations. Much of urban migration is driven by rural populations’ desire for the advantages that urban areas offer. Urban advantages include greater opportunities to receive education, health care, and services such as entertainment. The urban poor have less opportunity for education than the urban nonpoor, but still they have more chance than rural populations.7
How does urban migration affect fertility?
Urban fertility rates, though lower than rural fertility rates in every region of the world, contribute to the growth of urban areas. Within urban areas, women who migrated from rural areas have more children than those born in urban areas.8Of course, the rural migrants to urban areas are not a random selection of the rural population; they are more likely to have wanted fewer children even if they had stayed in the countryside. So the difference between the fertility of urban migrants and rural women probably exaggerates the impact of urban migration on fertility.
How does urban forest help the environment?
The sustainable use of wood, food, and other goods provided by the local urban forest may also help mitigate climate change by displacing imports associated with higher levels of carbon dioxide emitted during production and transport. Urban wood is a valuable and underutilized resource. At current utilization rates, forest products manufactured from felled urban trees are estimated to save several hundred million tons of CO2over a 30-year period. Furthermore, wood chips made from low-quality urban wood may be combusted for heat and/or power to displace an additional 2.1 million tons of fossil fuel emissions per year (15).
How do urban forests help?
Urban forests help control the causes and consequences of climate-related threats. However, forests may also be negatively impacted by climate change.
What is local governance?
Local governance. Due to limited staff and budget resources, many cities rely on partnerships with private landowners, organized citizen groups, and nonprofit agencies in order to effectively manage urban ecosystems. In some areas, citizens participate in advisory commissions that provide input to local officials on policy and regulations governing urban forests. In others, partnerships promote innovative greening strategies that complement or augment existing programs (33, 34). Collaborative governance across traditional boundaries engages constituents, increases environmental and political awareness across generations, and enables communities to better address complex issues such as climate change (35, 36, 37).
How can trees help communities?
Adaptation. Incorporating climate resilience into tree planting and urban forest management plans helps improve the adaptive capacity of a community’s tree canopy. Planting a diverse mix of pest-tolerant, well-adapted, low-maintenance, long-lived, and drought-resistant trees ensures greater resilience (27, 28), while planting small groves of especially water-tolerant species in areas receiving peak volumes of stormwater runoff reduces flooding and pollutant transport (28). Establishing and adhering to a regular maintenance cycle can help protect cities from extreme weather events. Young trees must be pruned early and often to encourage development of strong branching structures that are less vulnerable to storm and wind damage, and hazardous or diseased trees must be removed (28). Although urban forests, like all other ecosystems, can never be totally invulnerable to climate change impacts, thoughtful management can improve resilience and help cities and communities better adapt to change.
What is urban forest cover?
Urban forest cover is a key mediating variable between climate change impacts and particularly vulnerable population demographics, such as the young, the elderly, and the poor. These populations often suffer disproportionate negative impacts from the multiple health hazards associated with climate change, especially when located near freeways, industry, rivers, landfills, and other areas with little green space. Developing a location-specific list of "climate smart" tree species and planting sites can serve as a useful first step towards increasing urban forest cover in these areas.
What is urban forest management?
Active urban forest management for climate change strengthens community resilience to climate change impacts (as well as other potential disasters), and creates more livable, desirable places to live, work and play.
Why are trees more attractive to pests?
The consequences of these population changes are compounded by the fact that hot, dry environments enrich carbohydrate concentrations in tree foliage, making urban trees more attractive to pests and pathogens (24).
What does reusing and recycling do to the environment?
By reusing and recycling items, we save energy (and the associated fossil fuels) that it would otherwise have taken to produce new items.
How does the ocean affect fish?
However, increased water temperatures and ever-increasing carbon dioxides concentrations mean that oceans are changing and becoming more acidic. This affects fish and other marine organisms living there. Coral reefs are particularly at risk. Sensitive coral species and algae are starved of oxygen, which leads to a dramatic bleaching and possibly even the death of the coral.
What are the services that ecosystems provide?
If our ecosystems suffer, the valuable services they provide will be compromised – these include clean air and water as well as nutrient replenishment – the key to productive soils.
Why do we need to plant trees?
We must plant as many trees as possible on Earth to sequester our carbon, and we also need to implement sustainable agriculture systems that store carbon in the soil.
What will happen to the world by the end of the century?
According to a recent study, by the end of the century, more than half of the world’s population will be exposed to increasingly stagnant atmospheric conditions, with the tropics and subtropics bearing the brunt of the poor air quality [3].
When did Greentumble change?
Greentumble Climate Change May 21, 2018. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has reported again and again on the grave effects of climate change. After years of scientific research and debate as well as efforts to mobilize governments across the world, global leaders signed up to the Paris Agreement.
What is the greatest cause of species extinction?
According to international experts, global warming is likely to be the greatest cause of species extinctions this century with estimates indicating that a 1.5°C average rise may put 20 to 30% of species at risk of extinction [4].
