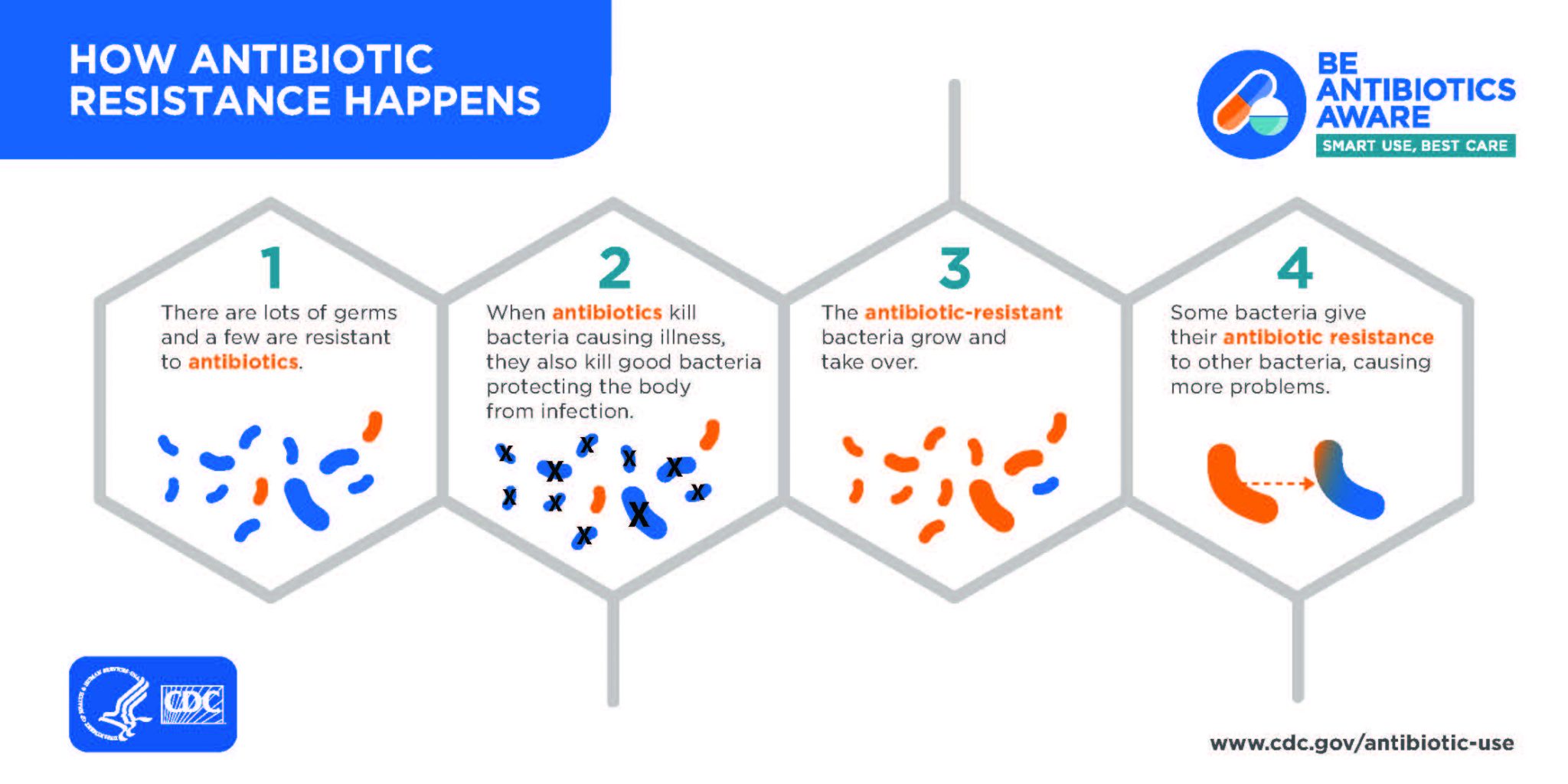
How to prevent antibiotic resistance:
- Judicious antibiotic use: The doctors must suggest the appropriate antimicrobial drug, with the exact dose, at the right time, and for the right duration.
- Surveillance and infection control: We should maintain good hygiene to prevent microbial infection. ...
- Use of specific antibiotics: Certain antibiotics kill only specific strains of bacteria. ...
What can you do to help stop antibiotic resistance?
Top tips for preventing the spread of antibiotic resistance
- Wash your hands properly using soap regularly. ...
- Cover your mouth with a tissue when sneezing or coughing and dispose of the tissue immediately. ...
- If your symptoms are mild (e.g. ...
- Don’t ask your doctor for antibiotics if you have a cold or the flu, or any other viral or fungal infections. ...
- Take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
How to minimise antibiotic resistance?
Ways to reduce antibiotic resistance
- Only take antibiotics when necessary.
- Treat specific bacteria with specific antibiotics.
- High hospital hygiene levels, including regular hand washing by staff and visitors.
- Patients who are infected with antibiotic resistant strains of bacteria should be isolated from other patients.
How do you reduce antibiotic resistance?
- Wash the right way. There is some concern that the triclosan in antibacterial soaps could lead to resistance, and its not clear whether theyre any more effective than scrubbing for ...
- Buy organic. ...
- Dont take an antibiotic unless you absolutely have to. ...
- Ask for the shortest course of antibiotics. ...
- Speak out. ...
Is antibiotic resistance a threat to life?
Antibiotic resistance raises medical expenses, lengthens hospital stays, and raises fatality rates. The world urgently needs to modify how antibiotics are prescribed and used. Antibiotic resistance will always be a danger, even if new medications are developed. Vaccination, hand washing, safer sex, and excellent food hygiene are all examples of ...
What does "raised without antibiotics" mean?
Concerned with antibiotic-related labeling, Consumers Union—Consumer Reports’ advocacy arm— sent a letter to Tom Vilsack, head of the USDA, for clarifications regarding certain claims found on food packaging, such as “No Antibiotic Growth Promotants,” “Antibiotic Free,” and “No Antibiotic Residues.” Vilsack responded that “raised without antibiotics” means no antibiotics were used in the animal’s feed or water, or via injections, over the course of its life.
What does "no antibiotics added" mean?
The USDA’s Food Safety and Inspection Service lists “no antibiotics added” as an acceptable term for meat and poultry labels. The term may be used on labels “for meat or poultry products if sufficient documentation is provided by the producer to the Agency demonstrating that the animals were raised without antibiotics.”.
How many people die from antibiotics in a year?
These microscopic “superbugs” sicken up to 2 million Americans a year and kill at least 23,000, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Why are antibiotics given to animals?
of all antibiotics sold in the U.S. are given to food animals for growth promotion and disease prevention . Antibiotics are the only kinds of drugs whose use by one life form affects the health of another, and the more they’re used, the less effective they become.
What stores have antibiotic free meat?
Chains such as Trader Joe’s, Whole Foods, Kroger, Costco, and Safeway offer antibiotic-free meats. If you can’t find them at your neighborhood store, ask the grocer to consider carrying these items.
How to take care of yourself naturally?
Anna Julien, an emergency care physician, tells her patients, “Your body will naturally take care of this if you take care of yourself: Sleep more, get more fluids, take a day or two off work to recover, and stop running around stressing yourself out over the little things.”
What percentage of ground turkey is drug resistant?
Last year, the FDA. announced drug-resistant bacterial contamination in 81 percent of ground turkey, 69 percent of pork chops, 55 percent of ground beef, and 39 percent of chicken sampled in grocery stores.
Why is bacterial resistance important?
The most important part of this is that bacterial resistance is essentially a numbers game: the more humans try to kill bacteria with antibiotics, and the more different antibiotics they use, the more opportunities bacteria have to develop new genes to resist those antibiotics . The less we use, the less bacteria can develop and share resistance.
What is the CDC's system for tracking antibiotic resistance?
One of the most important steps in tackling resistance is tracking it. The CDC have set up a system called the National Antimicrobial Monitoring System (NARMS).
How many people will die from antibiotic resistance in 2050?
If left unchecked, antibiotic resistance could lead to 10 million deaths by 2050 worldwide, costing some £66 trillion.
How many people die from antibiotics?
It’s hard to say for sure, but the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that in the US alone there are about 23,000 people who die every year from antibiotic-resistant infections. For example, they estimate that resistance to antibiotics that treat Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) causes almost 500,000 infections in the US every year, which lead to about 15,000 deaths. (But Amanda Jezek, a spokesperson specialising in policy and government relations at the Infectious Diseases Society of America, a group that represents many of the country’s infectious disease doctors and scientists, says the overall number of deaths is a conservative estimate and likely higher.
Is there a single antibiotic left to treat bacterial infections?
If we continue at this rate without intervention, we may find that there is not a single antibiotic left to treat any type of bacterial infection.
Which country is more likely to use antibiotics?
According to Dr Marc Sprenger, director of the antimicrobial programme at the WHO, much of Europe is three times more likely to use antibiotics than their fellow European countries Sweden or the Netherlands, where they are used only occasionally. “This has nothing to do with more people getting sick.
Is antibiotic resistance the end of modern medicine?
It’s been dubbed “the end of modern medicine”. BBC Future asked experts to explain how we might avoid the worst effects of antibiotic resistance – a grand challenge of our age.
What happens when you are infected with antibiotic resistance?
When antibiotics don't work, the result can be. longer illnesses.
What are some examples of bacteria resistant to antibiotics?
Examples of the types of bacteria that have become resistant to antibiotics include those that cause skin infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, sexually transmitted diseases and respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia. In cooperation with other government agencies, the Food and Drug Administration ...
Why do we need antibiotic labeling?
Antibiotic labeling contains required statements in several places advising health care professionals that these drugs should be used only to treat infections that are believed to be caused by bacteria. Labeling also encourages health care professionals to counsel patients about proper use.
What is the term for the disease that occurs when bacteria change in a way that reduces or eliminates the effectiveness?
Misuse and overuse of these drugs, however, have contributed to a phenomenon known as antibiotic resistance. This resistance develops when potentially harmful bacteria change in a way that reduces or eliminates the effectiveness of antibiotics.
What is the FDA's role in labeling antibiotics?
FDA has also encouraged the development of new drugs, vaccines, and improved diagnostic tests for infectious diseases.
Why should patients not demand antibiotics?
Patients should not demand antibiotics when a health care professional says the drugs are not needed. Health care professionals should prescribe antibiotics only for infections they believe to be caused by bacteria.
When is it important to take antibiotics?
When you are prescribed an antibiotic to treat a bacterial infection, it's important to take the medication exactly as directed. Here are more tips to promote proper use of antibiotics. Take the antibiotics as prescribed. It's important to take the medication as prescribed by your doctor, even if you are feeling better.
How many people die from antibiotic resistance each year?
Antibiotic resistance can affect people of all ages in all countries. It is estimated that 5.7 million people, most in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), die each year from treatable infectious diseases. Many lives could have been saved if antibiotics had worked and been available.
How have antibiotics contributed to the world?
Antibiotics have become the cornerstone for the treatment of infectious diseases and contributed significantly to the dramatic global health development during the last 70 years. Millions of people now survive what were previously life-threatening infections. But antibiotics are finite resources. Misuse has led to antibiotic resistance (ABR) and reduced efficacy within just a few years of introduction of each new antibiotic [ 1 ]. The problem was foreseen by Alexander Fleming in his Nobel speech in 1945 when he concluded that ´ the time may come when penicillin can be bought by anyone in the shops. Then there is the danger that the ignorant man may easily underdose himself and by exposing his microbes to non-lethal quantities of the drug make them resistant´. But, as late as in 1968, the US Surgeon General William H Stewart stated that ´ it is time to close the book on infectious diseases and declare the war against pestilence won´ [ 2 ].
Why is epidemiology important?
Data on the epidemiology of ABR and infectious diseases are essential to inform our understanding of the patterns of use and misuse of antibiotics and their consequences [ 17 ].
Does stewardship reduce antibiotic resistance?
A recent systematic review of eight stewardship programmes found no solid evidence of their effectiveness in reducing antibiotic resistance in hospital settings. This is attributed mainly to suboptimal study designs and heterogeneous program features, preventing the pooling of studies [ 72 ].
Is antibiotic use in maternity units important?
Access to antibiotics is critical in maternity units. Preventable maternal or neonatal mortality is still unacceptably high in LMICs where many women do not have access to skilled health care and hygienic birthing facilities. However, we lack information on antibiotic use in these settings [ 32 ].
Why are antibiotics given to livestock?
Antibiotics are given to livestock (like cattle, pigs, and chickens) as preventative treatment or to increase growth. While the use of antibiotics in food is not directly linked to antibiotic resistance in bacteria that pose medical problems for humans, researchers are beginning to learn that antibiotics in the waste system can cause selection ...
What is the word for a substance that weakens or destroys bacteria?
show/hide words to know. Antibiotic: a substance that weakens or destroys bacteria. Antibiotic resistant: when a group of bacteria can no longer be harmed or killed by a certain antibiotic...... more (link is external) Immunostimulant: a drug or nutrient that increases immune function...... more (link is external)
What is the term for a substance that provides immune memory using antigens, or dead or weak viruses or bacteria?
Vaccine: a substance that provides immune memory using antigens, or dead or weak viruses or bacteria, instead of from an infection.
Should we increase research into alternatives to antibiotics?
We should increase research into alternatives to antibiotics. Antibiotics are not the only way that we can fight bacteria, but they do seem to have one of the greatest effects on bacterial evolution. This means antibiotics seem to cause resistance more quickly than other treatment options, like vaccines or other immunostimulants.
Should we increase research into the production of new antibiotics and use of old antibiotics?
We should increase research into the production of new antibiotics and use of old antibiotics. Medicine development is often slow and antibiotics are sometimes developed for specific bacteria strains and aren’t well tested on how they work on other bacteria. We need to learn more about how these medications can be used.
What is the CDC's role in controlling antibiotic resistance?
CDC takes a major step to control antibiotic resistance. They hold a day to increase awareness about antibiotic resistance.
How many people will die from antibiotic resistance in 2050?
Antibiotic resistance is increasing in an alarming rate. Millions of people will die by 2050 due to increased antibiotic resistance. It has become a curse to the present human civilization. It is the time we should take major steps to halt it. First we should know how to prevent antibiotic resistance. Then we should find antibiotic alternatives ...
What is the best antibiotic for bacterial infection?
Phage is thought to be the best antibiotic alternative against bacterial infection. Phages kill specific bacterial strains that don’t cause any harm to host cells. They don’t kill beneficial bacteria too. Bacteria can’t acquire resistance to phage. Endolysin is a good example of antibiotic alternative.
What is the name of the bacterial toxin that kills the same bacterial species of producer bacteria?
Bacteriocins is a bacterial toxin that kill the same bacterial species of producer bacteria. Both gram positive bacteria and gram negative bacteria produces bacteriocins . Bacteriocins are of several types. These include lacticin, nisin and thuricin.
What are some alternatives to antibiotics?
There are a number of antibiotic alternatives to treat or prevent bacterial infection. For example, phage therapy is sometimes more advantageous over the antibiotics. Phage is thought to be the best antibiotic alternative against bacterial infection.
Why should we maintain good hygiene?
We should maintain good hygiene to prevent microbial infection. The most we should do is to avoid the use of antimicrobial drug. If we prevent the interaction of bacteria with antibiotics, we can control antibiotic resistance.
Why is it so hard to develop new antibiotics?
It has been great difficult to develop new antibiotics due shortage of funds or many other reasons. There is only way to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Why is it important to use antibiotics correctly?
Proper usage of antibiotics can contribute to therapeutic outcomes and the eradication of bacterial infections. Unnecessary and improper usage of antibiotics contributes to antibiotic resistance.
Why is it important to use antibiotics only for their intended purpose?
Antibiotics resistance occurs when the antibiotic created to eliminate the bacteria can no longer destroy them, making them permanent, so it is crucial to utilize antibiotics only for their intended purpose as prescribed by a certified healthcare professional.
How do antibiotics affect bacteria?
Antibiotics exert their effects by stopping bacterial growth (bacteriostatic) or by killing the bacteria (bactericidal), ultimately treating and preventing bacterial infection. Antibiotics can halt bacterial growth by interfering with their DNA replication, enzyme metabolism, and protein synthesis. (1)
Is antibiotic resistance better prevented?
Antibiotic resistance is better prevented via preventive measures such as those mentioned above than treated. Bacteria that have undergone a change (intrinsic resistance, acquired resistance, genetic change, and DNA transfer) to evade being eliminated by antibiotics become very challenging to treat.
Can antibiotics cause a mutant drug resistant strain?
Improper usage of antibiotics may result in the advancement of a resistant strain that can then be transmitted to others who may then acquire the mutant drug-resistant strain. (1)
Can antibiotic resistance cause pneumonia?
Antibiotic resistance can make treatable illnesses, such as bacterial pneumonia or meningitis, more troublesome to manage and treat.
Can antibiotics cause nonbeneficial effects?
The unnecessary treatment with antibiotics can result in nonbeneficial effects of therapy while still being susceptible to the medication’s adverse effects.

A Public Health Issue
- Antibiotic resistance is a growing public health concern worldwide. When a person is infected with an antibiotic-resistant bacterium, not only is treatment of that patient more difficult, but the antibiotic-resistant bacterium may spread to other people. When antibiotics don't work, the result can be 1. longer illnesses 2. more complicated illnesses 3. more doctor visits 4. the use of stron…
Antibiotics Fight Bacteria, Not Viruses
- Antibiotics are meant to be used against bacterial infections. For example, they are used to treat strep throat, which is caused by streptococcal bacteria, and skin infections caused by staphylococcal bacteria. Although antibiotics kill bacteria, they are not effective against viruses. Therefore, they will not be effective against viral infections such as colds, most coughs, many ty…
Follow Directions For Proper Use
- When you are prescribed an antibiotic to treat a bacterial infection, it's important to take the medication exactly as directed. Here are more tips to promote proper use of antibiotics. 1. Take the antibiotics as prescribed.It's important to take the medication as prescribed by your doctor, even if you are feeling better. If treatment stops too soon, and you become sick again, the remai…
What FDA Is Doing
- FDA combating antibiotic resistance through activities that include 1. Approval of certain new antibiotics. Since 2015, FDA approved new antibiotics that can treat certain resistant bacteria. Health care professional are encouraged to use the new antibiotics appropriately and for some antibiotics, use only in patients who have limited or no other t...