
Examples of Checks and Balances
- The President may veto a law passed by Congress. Congress may then override the veto if a minimum of two-thirds of members of both the House of Representatives and the Senate vote to do so. ...
- Supreme Court may declare a law passed by Congress unconstitutional. Because judges of the Supreme Court are appointed by the President, the power here is balanced between all three branches.
What is meant by checks and balances in government?
What are the specific checks and balances on each arm of government?
- The Judiciary The Judiciary includes judges and the courts. The role of the Judiciary is to interpret the law and to judge whether the law applies in individual cases. ...
- The Executive The Executive includes ministers and the government departments, agencies, and statutory bodies they are responsible for. ...
- The Legislature
Why are there checks and balances in government?
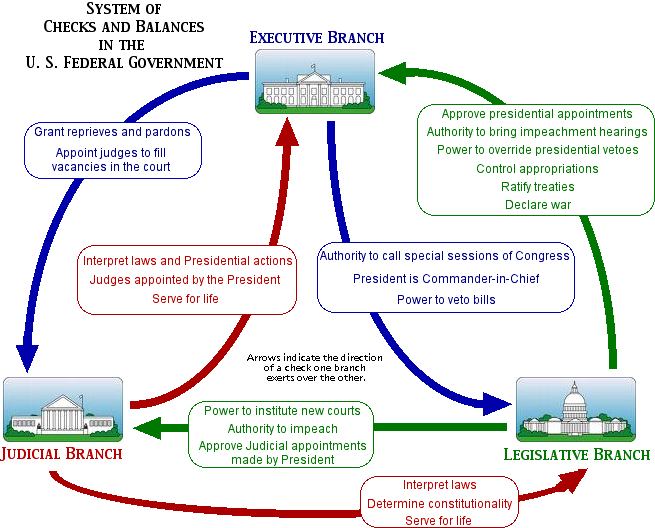
The system of checks and balances was established to make sure that parts of our government did not abuse their powers. Each branch, including the legislative, executive, and judicial, has its own unique set of powers and responsibilities to initiate change and to serve as checks, or limits, on the powers of the other branches.
How does the system of government checks and balances work?
With checks and balances, each of the three branches of government can limit the powers of the others. This way, no one branch becomes too powerful. Each branch “checks” the power of the other branches to make sure that the power is balanced between them.
How do government checks and balances work?
Checks and balances is a method set in place so that no branch of the government can become to powerful by allowing each branch to limit the powers of the others. This is accomplished by each branch checking the powers of the other branches to ensure the balance between all three.
What are three examples of checks and balances?
Some examples of checks and balances in use are:In 1973, President Richard Nixon vetoed the legislative branch's passing of the War Powers Act. ... U.S. v Alvarez is a court case that involved all three branches. ... In 1998, the House of Representatives voted to impeach President Bill Clinton.
Why is checks and balances divided in the federal government?
By dividing the United States government into three separate branches, it will take away the opportunity to have total power from any one of the groups. The separation of powers also created a checks and balance system which will not allow one of the branches of government to have more power over another.
Why is our federal government split up into 3 separate branches?
To ensure a separation of powers, the U.S. Federal Government is made up of three branches: legislative, executive and judicial. To ensure the government is effective and citizens' rights are protected, each branch has its own powers and responsibilities, including working with the other branches.
Why check and balance is important in the government?
Each branch has a certain job and the other branches have special powers to watch over it. These are called checks and balances, and they make the branches equal so that one doesn't become too powerful.
What's the separation of checks and balances?
Separation of powers is a doctrine of constitutional law under which the three branches of government (executive, legislative, and judicial) are kept separate. This is also known as the system of checks and balances, because each branch is given certain powers so as to check and balance the other branches.
How is the power to govern divided between the federal and state governments?
Federalism limits government by creating two sovereign powers—the national government and state governments—thereby restraining the influence of both. Separation of powers imposes internal limits by dividing government against itself, giving different branches separate functions and forcing them to share power.
What does the federal division of power imply?
A federal division of power or vertical division of power is when responsibilities are divided between a higher and lower level of government. Bigger nations find this system desirable to ensure efficient functioning of governments.
How does the check and balance system work?
Checks and balances operate throughout the U.S. government, as each branch exercises certain powers that can be checked by the powers given to the other two branches.
Why did the Framers create checks and balances?
In addition to this separation of powers, the framers built a system of checks and balances designed to guard against tyranny by ensuring that no branch would grab too much power. “If men were angels, no government would be necessary,” James Madison wrote in the Federalist Papers, of the necessity for checks and balances.
What were the three branches of government in Ancient Rome?
In his analysis of the government of Ancient Rome, the Greek statesman and historian Polybius identified it as a “mixed” regime with three branches: monarchy (the consul, or chief magistrate), aristocracy (the Senate) and democracy (the people). These concepts greatly influenced later ideas about separation of powers being crucial to a well-functioning government.
What branch of government can impeach the Supreme Court?
By passing amendments to the Constitution, Congress can effectively check the decisions of the Supreme Court. Congress (considered the branch of government closest to the people) can impeach both members of the executive and judicial branches.
Which three branches of government were divided into?
Constitution divided the powers and responsibilities of the new federal government among three branches: the legislative branch, the executive branch and the judicial branch.
Which branch of government was divided into three branches?
Constitution divided the powers and responsibilities of the new federal government among three branches: the legislative branch, the executive branch and the judicial branch. ...
Which branch of government can declare a law unconstitutional?
The Supreme Court and other federal courts (judicial branch) can declare laws or presidential actions unconstitutional, in a process known as judicial review.
How do the different branches of government work together?
Here are some examples of how the different branches work together: The legislative branch makes laws, but the President in the executive branch can veto those laws with a Presidential Veto. The legislative branch makes laws, but the judicial branch can declare those laws unconstitutional.
Which branch of government has responsibility for the enforcement of federal laws?
The executive bran ch, through the Federal agencies, has responsibility for day-to-day enforcement and administration of Federal laws. These Federal departments and agencies have missions and responsibilities that vary widely, from environmental protection to protecting the Nation’s borders.
Which branch of government has the power to approve presidential nominations?
The legislative branch has the power to approve Presidential nominations, control the budget, and can impeach the President and remove him or her from office.
Who interprets laws?
The judicial branch interprets laws, but the President nominates Supreme Court justices, court of appeals judges, and district court judges who make the evaluations.
Which branch of government can impeach judges?
The judicial branch interprets laws, but the Senate in the legislative branch confirms the President’s nominations for judicial positions, and Congress can impeach any of those judges and remove them from office. See our "Branches of Government" infographic to find the checks and balances you see illustrated.
Why did the founders put checks and balances in the Constitution?
Because the founders knew of the dangers of a democracy, they placed checks and balances in the Constitution to prevent majority tyranny. The USA was not intended to be a democracy because of the majority tyranny we see today. People today are taught we are a democracy and so they believe what the mob wants the mob gets.
When Congress passes a bill, does it become a law?
When Congress passes a bill, it doesn’t become a law unless the president signs it too. The president can prevent a bill from becoming a law.
Why does our vote no longer count?
Our vote no longer count because we are RULED by an unelected administrative state.
How many votes do you need to override a presidential veto?
They can override presidential veto with a vote of 2/3 in both houses.
What is the role of just governments?
The role of “just” governments (plural) are to secure our unalienable rights. If a law wasn’t seen by all entities, the exec and both chambers of congress, to be necessary and related to securing rights, it wouldn’t pass. The vast majority of what government does is in violation of the Supreme Law of the Land. See Amendment X [ 1] ,
When the Supreme Court moves from the left, progressive activism, to the rights, Constitutional governance, The could not allow?
When makeup of Supreme Court justices moved from the left, progressive activism, to the rights, Constitutional governance, The could not allow this to stand. So they will add as many justices as needs to regain power. The same for presidents. When a non-progressive is a threat to their dominant rule, they go on full attack.
Who can veto bills?
The President can veto bills and joint resolutions from Congress.
Legislative Powers
Article I of the US Constitution vests all law-making powers in a Congress made up of the House of Representatives and the Senate. Representation in the House of Representatives is based on the represented states’ population, while each state is entitled to elect two senators in the Senate, with all states equally represented.
Executive Powers
Article II vests executive powers in the Office of the President of the United States. An electoral college selects the President to serve a four-year term with one re-election.
Judicial Powers
Article III vests judicial powers in the US courts. The Constitution is interpreted by the courts, from the lower federal courts to the state courts, to the Supreme Court, the final court of appeal.
Relations Between States and Their Citizens
Article IV defines the relations between states and the privileges of the citizens of each state, recognizing the authority and relative independence of each state and asserting that these should be subsumed to uphold the individual liberty of citizens among states in interdependence with each other.
Constitutional Amendments Reflecting Checks and Balances
After these four articles in the main text of the US Constitution, a number of amendments in the 27 Amendments ratified so far also touch on the Separation of Powers doctrine’s application in the checks and balances system of a tripartite federal government.
Separation of Powers in Action
Here are examples now of how this Separation of Powers doctrine is enacted in the check and balance system of governance among the three branches of government —
A Constantly Evolving Tension
Even if the Separation of Powers doctrine is foundational to how the American government works, in practice, no democratic system exists with absolute separation of powers between the three branches, nor an absolute absence of separation of powers.
What was the purpose of the checks and balances system?
Once these branches were established, Congress realized they’d need to make sure no branch could simply overtake the others. This is where the system of checks and balances came in.
What is checks and balances?
Checks and Balances Definition. The definition of checks and balances is simply a system for distributing governmental powers. Each branch of the government has specific procedures only they can follow that help protect against fraud, errors, and illegal actions.
How often do checks and balances change?
Take a look at current events and you’ll probably see examples of checks and balances today in government proceedings. The president of the United States changes every four years, or eight years if a president is re-elected, and some government positions change more frequently. This keeps the system of checks and balances relevant as beliefs, attitudes, and opinions change. Continue exploring governmental powers by learning about the 25th Amendment.
What is the Constitution full of?
The U.S. Constitution is full of checks and balances of the three branches of government. The best example of checks and balances is that the president can veto any bill passed by Congress, but a two-thirds vote in Congress can override the veto.
What are the three branches of government?
The power of the new government was split into three branches, creating a clear separation of powers. The three branches of government are: 1 The executive branch (President, Vice President and cabinet) carries out laws. 2 The legislative branch (Congress: Senate and House of Representatives) makes laws. 3 The judicial branch (Supreme Court and other federal courts) interprets laws.
How to find out how the government structure was set up?
You can find out how the government structure was set up and what each branch is responsible for by looking at the Articles of the Constitution. The first three Articles tell you more details about each branch of the government: Article I outlines the powers of Congress, or the legislative branch. Article II outlines the executive branch and ...
Which branch of government has the power to impeach?
The House of Representatives has sole power of impeachment, but the Senate has all power to try any impeachment. Any bills that intend to raise revenue must originate in the House of Representatives, but the Senate also has to approve the bill. Congress has the power to set and collect any taxes or duties. The president is commander-in-chief of the ...
What is the purpose of checks and balances?
Ultimately, their checks and balances system establishes the nation’s security, providing a proper balance of power.
Which branch of government interprets laws and their constitutionality?
The judiciary interprets laws and their constitutionality, applying their decisions to individual cases. The Supreme Court is the highest judicial authority in the country. As such, some of their case rulings set a nationwide precedent.
What are the three sections of government?
Those sections of government include the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The Founders established them to create a system of checks and balances. Each unit exercises its powers and responsibilities, limiting overreach or abuse by the other two.
Which branch of government has the power to veto bills?
The legislative branch has the power of the purse. It controls the budget for itself and the other two parts of government. Likewise, the executive branch nominates members of the judiciary and has the authority to veto bills created by the legislature. The judicial branch reviews the constitutional authority of legislative and executive actions, effectively overturning them in instances of abuse or not aligning with the Constitution.
Who nominates ambassadors and judges?
The president also nominates ambassadors and judges and appoints cabinet members and other officers of the federal government.
Which branch of government is responsible for creating laws and declaring war?
Article I of the Constitution establishes the legislative branch. Comprising the House of Representatives and the Senate, its primary responsibilities include creating laws and declaring war.
Separation of Powers
The U.S. System of Checks and Balances
- Building on the ideas of Polybius, Montesquieu, William Blackstone, John Locke and other philosophers and political scientists over the centuries, the framers of the U.S. Constitution divided the powers and responsibilities of the new federal government among three branches: the legislative branch, the executive branch and the judicial branch. In addition to this separation of …
Checks and Balances Examples
- Checks and balances operate throughout the U.S. government, as each branch exercises certain powers that can be checked by the powers given to the other two branches. 1. The president (head of the executive branch) serves as commander in chief of the military forces, but Congress (legislative branch) appropriates funds for the military and votes to...
Checks and Balances in Action
- The system of checks and balances has been tested numerous times throughout the centuries since the Constitutionwas ratified. In particular, the power of the executive branch has expanded greatly since the 19th Century, disrupting the initial balance intended by the framers. Presidential vetoes—and congressional overrides of those vetoes—tend to fuel controversy, as do congressi…
Roosevelt and The Supreme Court
- The checks and balances system withstood one of its greatest challenges in 1937, thanks to an audacious attempt by Franklin D. Rooseveltto pack the Supreme Court with liberal justices. After winning reelection to his second term in office by a huge margin in 1936, FDR nonetheless faced the possibility that judicial review would undo many of his major policy achievements. From 193…
The War Powers Act and Presidential Veto
- The United States Congress passed the War Powers Act on November 7, 1973, overriding an earlier veto by President Richard M. Nixon, who called it an “unconstitutional and dangerous” check on his duties as commander-in-chief of the military. The act was created in the wake of the Korean War and during the Vietnam War and stipulates that the president has to consult Congre…
State of Emergency
- The first state of emergency was declared by President Harry Truman on December 16, 1950 during the Korean War. Congress did not pass The National Emergencies Act until 1976, formally granting congress checks on the power of the president to declare National Emergencies. Created in the wake of the Watergate scandal, the National Emergencies Act included several limits on p…
Sources
- Checks and Balances, The Oxford Guide to the United States Government. Baron de Montesquieu, Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. FDR’s Losing Battle to Pack the Supreme Court, NPR.org. State of Emergency, New York Times, Pacific Standard, CNN.